| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,3-Dioxetane | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name 1,3-Dioxacyclobutane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C2H4O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 60.052 g·mol | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
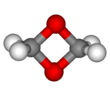
1,3-Dioxetane (1,3-dioxacyclobutane) is a heterocyclic organic compound with formula C2O2H4, whose backbone is a four-member ring of alternating oxygen and carbon atoms. It can be viewed as a dimer of formaldehyde (COH2).
Derivatives of 1,3-dioxetane are rarely encountered as intermediates in the literature. Usually, they are prepared via cycloadditions of two carbonyl compounds. Molecular orbital theory calculations suggest that they should be more stable than the 1,2-isomers, which are more intensively studied.
See also
References
- Cordier, C.; Leach, S.; Nelson, A. (2014). Science of Synthesis: Houben-Weyl Methods of Molecular Transformations Vol. 29: Acetals: Hal/X and O/O, S, Se, Te. Georg Thieme Verlag. p. 407. ISBN 9783131720412.
This article about a heterocyclic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |