This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
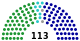
All 225 seats to the Legislative Yuan 113 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Elected member party by seat Elected member party by seat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2004 Taiwanese legislative election was held on 11 December 2004. All 225 seats of the Legislative Yuan were up for election: 168 elected by single non-transferable vote, 41 elected through party-list Proportional representation, eight elected from overseas Chinese constituencies on the basis of the proportion of nationwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected by popular vote among the aboriginal populations. Members served three-year terms beginning on 1 February 2005, and ending 31 January 2008. The next term served four years.
This was the first election following Pan-Blue coalition candidate Lien Chen's narrow defeat in the presidential election in March. With the results of the presidential election still contested, many saw the legislative election as a referendum on Chen Shui-bian's Government and on the Pan-Blue Coalition's electoral viability. With the failure of the Pan-Green Coalition to win a majority, President Chen Shui-bian found it difficult, as in the past, to enact his policies.
Campaign issues
In the 5th Legislative Yuan (2002–2005), the opposition pan-blue coalition held a narrow majority, resulting in much of government-sponsored bills being deadlocked or heavily amended. The pan-blue coalition strongly argued that having a majority pan-green legislature would lead to a "super-president" while the pan-green coalition stated that a majority pan-green legislature was necessary to prevent deadlock and chaos and to finally eliminate the vestiges of the KMT's previous authoritarian government on Taiwan.
A major issue of the election was whether to amend or replace the Constitution of the Republic of China. In his second inaugural address in May 2004, President Chen Shui-bian proposed to hold a referendum in 2006 on an entirely new constitution to be adopted in 2008. The Pan-Green Coalition argued that the current constitution, drafted by the Kuomintang in mainland China in 1947, is outdated and unfit for Taiwan as it was originally designed for all of China. Though President Chen promised not to change the sovereignty status of the Republic of China (which still officially claims all of mainland China and Mongolia), the symbols of the Republic of China, or to declare an independent Taiwan, this proposal drew intense criticism from the People's Republic of China, which saw a new Constitution as a means to further the separation of Taiwan from the mainland. In Taiwan there is a general consensus across party lines that the Constitution needs reworking, but disagreement on the degree and type of reform. The Pan-Blue Coalition opposes enacting a new constitution, seeing the act as unnecessary, but supports amending it. In the summer of 2004, the legislature overwhelmingly passed a series of proposed constitutional amendments to halve the size of the legislature and abolish the National Assembly, among other measures. These measures will have to be approved by the National Assembly (elected ad hoc from the results of the 2004 election).
In addition, other issues were Chen's accusations of a soft coup after his March 2004 victory, as well as legal efforts (which most consider unlikely to succeed) by the leaders of the pan-blue coalition to overturn the results of the March presidential election. In a related issue, there were concerns that the 3-19 shooting incident was staged; an investigatory committee established by the legislature (only by overriding a cabinet veto) was criticized by the pan-green coalition, which refused to appoint any of its members to the committee as mandated by law.
Another initiative that was discussed was a US$18 billion arms deal with the United States. President Chen regarded the arms deal as necessary for the defense of Taiwan against China, but the Pan-Blue Coalition has blocked the deal from passing the legislature, arguing the money should be spent on other measures.
President Chen also complained that the party emblem of the KMT is too similar to the national emblem of the Republic of China, and if the KMT does not change its emblem, a newly elected pan-green legislature will force it. (In response, the KMT noted that its emblem has existed before the ROC and challenged the government to change the national emblem instead.) Chen announced on December 5 that state-owned enterprises and foreign offices bearing the name "China", such as the Chinese Petroleum Corporation, would be renamed to bear the name "Taiwan". The U.S. government objected to this proposal, saying it would "unilaterally change Taiwan's status", but the DPP argued it is meant to avoid confusion and was not politically motivated. Chen reacted to the American concerns by blasting the United States. This appeared to cause a great deal of consternation among American officials with one analyst stating bluntly that President George W. Bush was "more than a little irritated" by Chen.
During the campaign, the KMT had been laying off workers and shedding millions of dollars' worth of assets it accumulated when it monopolized power. Analysts say the downsizing was prompted by fear that a DPP-controlled legislature might call for new investigations of the party's finances.
Campaign tactics
The legislative elections were the last in Taiwan using the single non-transferable vote, as a constitutional amendment was passed in 2005 to convert the election format in the next legislative elections. The new electoral system supported by KMT and DPP, created interesting strategies such as vote allocation, as parties did not want to nominate too many candidates for a district, out of fear that it would divide party votes among too many candidates. In addition, the voting method resulted in complex negotiations between parties with similar ideological beliefs. The need to allocate votes resulted in a system in which political parties took out newspaper ads telling supporters how to vote based on their birthday.
The leaders of the KMT, PFP, and New Party, which all share similar political views, expressed concern over overcrowding. In 2001 elections, the DPP won 40% of the seats even though they only polled 36% of the vote, due in large part to the inability of the KMT, PFP, and New Party to coordinate their electoral strategies. To maintain its majority of the Pan-Blue Coalition, Kuomintang Chairman Lien Chan and People First Party Chairman James Soong proposed in May 2004 to merge their parties. In the election, the New Party ran seven of its eight candidates (the minimum number required to form a legislative caucus) under the KMT banner to avoid splitting the vote though their campaigns were funded and organized by the New Party. However, one candidate—Wu Cheng-tien of Kinmen, whose strongly Chinese unification-supporting district was considered safe—ran and won as a New Party candidate to signify the party's continued existence.
Similarly, negotiations between TSU "Spiritual Leader" Lee Teng-hui and Chen Shui-bian occurred, presumably over calls for the TSU and DPP avoid splitting up their votes but not much occurred towards this result.
However, the dynamics of the election have permitted intra-coalition competition, either from candidates not wanting to be "sacrificed" to more popular candidates in another party or from party leaders seeking to increase their proportional representation. For example, the Lee Teng-hui criticized President Chen Shui-bian for equating the "Republic of China" with "Taiwan" saying "If we continue to use the "Republic of China" as the nation's title, China may view our nation (as a rebellion group)...Taiwan itself is a nation" while campaigning for a TSU candidate in danger of losing the race to five other DPP candidates.
Faced with defections by independence supporters to the TSU accusing the DPP as being too moderate (President Chen's senior adviser for international affairs, Lai Shin-yuan, resigned from the administration and won a seat as a TSU candidate), President Chen seemed to be moving his party's campaign towards stronger support for Taiwan independence, calling for the renaming of state-owned enterprises. This strategy seemed to have worked in preventing defections to the TSU—the TSU, predicted to increase its presence to as many as 20 seats instead lost its membership by one seat. However, this might have alienated the center of the electorate and contributed to Pan-Green's overall defeat.
Results

The pro Republic of China conservative Pan-Blue Coalition (consisting of the Kuomintang, People First Party, and New Party) retained its majority in the legislature, winning 114 seats, compared to 101 seats won by the Taiwan independence-leaning Pan-Green Coalition (consisting of the Democratic Progressive Party and Taiwan Solidarity Union). The remaining ten seats went to independents and other groups.
A significant result was that voter participation was only 59% and was markedly lower than in previous elections (80% in the previous presidential election). Many commentators were concerned about this as it seemed to reflect public disillusionment with the tone of politics on Taiwan. The election also appeared to call into question the accuracy of public opinion polls, most of which failed to project a pan-blue victory just as they failed to predict the election of Chen Shui-bian. The DPP itself predicted that the pan-green coalition would capture 113 seats, and the TSU predicted that it would win at least 25 seats. On the other hand, the KMT underestimated itself by predicting that the pan-blue coalition altogether would win 109 seats.
Among the notable candidates elected, independent candidate Li Ao won a legislative seat, whereas former DPP chairmen turned pan-blue supporter Shi Ming-teh and Hsu Hsing-liang failed to get elected in their seats. Also of interest is a non-party legislator from Yunlin County, Chang Li-shan, the sister of the former county magistrate who was captured by the police the day before the election on corruption charges.
In their post-election speeches, all of the party spokesman called for moderation as well as unity and cooperation between the parties. Significantly, the pan-blue coalition consistently referred to the country by its legal name of the Republic of China whereas pan-green referred to the country with the term Taiwan.
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic Progressive Party | 3,471,429 | 35.72 | 89 | +2 | |
| Kuomintang | 3,190,081 | 32.83 | 79 | +11 | |
| People First Party | 1,350,613 | 13.90 | 34 | –12 | |
| Taiwan Solidarity Union | 756,712 | 7.79 | 12 | –1 | |
| Non-Partisan Solidarity Union | 353,164 | 3.63 | 6 | New | |
| New Party | 12,137 | 0.12 | 1 | 0 | |
| Labor & Education Worker's Alliance | 3,176 | 0.03 | 0 | New | |
| Taiwan Independence Party | 1,935 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | |
| Wisdom Action Party | 820 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | |
| Independents | 577,292 | 5.94 | 4 | –5 | |
| Total | 9,717,359 | 100.00 | 225 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 9,717,359 | 99.19 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 78,940 | 0.81 | |||
| Total votes | 9,796,299 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 16,559,254 | 59.16 | |||
| Source: Election Study Center, CEC | |||||
Analysis
Although the party strengths were similar to the election of the 2001 ROC legislative election, but the results were widely seen as a major defeat for President Chen Shui-bian, who had campaigned hoping for an absolute majority for the pan green coalition. Reasons for the result included:
- tactical voting strategies – the pan-blue coalition greatly limited the number of candidates nominated while the pan-green coalition nominated a very large number of candidates. This had a major impact on the result due to the Taiwanese electoral system. In addition, the DPP nominated a large number of new unknown candidates, in part because the big names in the DPP were in the government, whereas the pan-blue coalition, being in opposition, found it easier to nominate people with a large amount of name recognition. The DPP's strategy was to "slit the throats" (割喉) of the pan-blue coalition by dominating the government with many candidates, following their success in the presidential election. After the election, there was a consensus that this strategy seriously backfired. While the number of seats that the DPP and TSU gained was similar to that of 2001, many experienced and famous DPP and TSU legislators lost their seats.
- intra-coalition cooperation – many observers noted that the parts of the pan-blue coalition were much more adept at cooperating than the parts of the pan-green coalition. In particular, the NP ran seven of its candidates under the KMT banner and only ran one under NP in sure-win Kinmin county (Quemoy). Also, the PFP was willing to give up seats in order to improve the results of the overall coalition whereas the TSU was not as willing to coordinate in this way with the DPP. James Soong, leader of the PFP, was quoted earlier as stating that he was willing to have the KMT win all of the seats in the pan-blue coalition if this was necessary to keep the pan-blue in power, whereas the TSU actively campaigned for a large number of seats and in some cases sharply criticized the DPP, and Lee Teng-hui urged the husband from each household to vote for DPP, and the wife to vote for TSU so both parties would have equal representation.
- pan-green emphasis on symbolic issues of Taiwan independence – Although the pan-green coalition began the campaign focusing on good governance and reform issues, as the campaign progressed the pan-green coalition focused more on the symbolic issues of Taiwan independence such as calling for referendum, removing the name "China" from state owned corporations and schools, moving the history of the ROC to a section on general Chinese history in textbooks, demanding that the KMT change its party emblem, which is similar to the national emblem. While these efforts were intended to placate the voters of the TSU, most analysts feel that they did nothing to attract more moderate voters.
Although the pan-green coalition improved both their seat totals and their vote percentage over the last election, the legislative elections were widely interpreted as a major defeat for the pan-green coalition, given their goal of gaining a majority of seats in the Legislative Yuan. In the aftermath of the election, Chen Shui-bian resigned as chairman of the Democratic Progressive Party and was replaced by Su Tseng-Chang.
Some of the consequences of the election were:
- the election established the Kuomintang as senior party within the pan-blue coalition and set the stage for the merger between all of the parties within the pan-blue coalition into a new Kuomintang. Seven of the KMT candidates were actually members of the New Party, and it is expected that a merger between the New Party and the KMT will occur very soon after the election. Somewhat more difficult is the planned merger between the KMT and PFP. These mergers are widely seen as essential due to the electoral changes that will occur in the next legislative elections. In addition, the elections appeared to end speculation that the KMT was about to collapse, calls for the resignation of Lien Chan, and calls for the KMT to drop some of the "China"-based symbols.
- the victory of the pan-blue coalition also strained the relationship between the KMT and PFP. Although cooperating with the KMT before the election, after the election PFP Soong Chu-yu complained about his parties poor showing and began moving toward cooperation with the DPP.
- the election completely marginalized candidates outside the pan-blue and pan-green coalitions. Even candidates such as Shi Ming-teh and Hsu Hsin-liang, who both served long prison terms during the democratization movement of Taiwan and were pivotal in the Kaohsiung Incident but have since distanced away from the DPP, were defeated. Out of a total of 154 candidates from both the Non-Partisan Solidarity Union and Non-Party, only 10 were elected.
- after the election, the PRC announced that it would pass an Anti-Secession Law. Most Western observers have stated that this was intended as a harsh measure to counteract an expected pan-Green coalition victory, but that when the election results were unexpectedly favorable to the PRC, that the planning for the law had been too far advanced to stop completely.
References
External links
- Taiwan 2004 Legislative Yuan Election (English)
- Election of the 6th Legislative Yuan (Chinese)
- Official announcement (Chinese)
| Presidential elections | |
|---|---|
| Legislative Yuan elections | |
| Local elections | |
| Referendums | |
| National Assembly elections | |