| |||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 50.57% (first round) 51.04% (second round) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
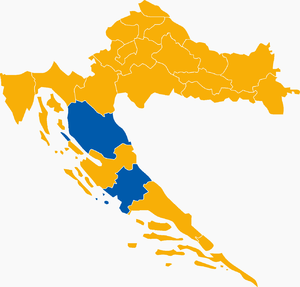 Second round results by county Second round results by countyStjepan Mesić Jadranka Kosor | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Presidential elections were held in Croatia in January 2005, the fourth such elections since independence in 1991. They were the first presidential elections held after the constitutional reforms of November 2000, which replaced a semi-presidential system with an incomplete parliamentary system, greatly reducing the powers of the president in favor of the Prime Minister and the cabinet. Incumbent president Stjepan Mesić, who had been elected in 2000 as the candidate of the Croatian People's Party, was eligible to seek reelection to a second term and ran as an independent as the constitution prohibited the president from holding party membership while in office.
The elections resulted in the landslide re-election of Mesić for a second five-year term. They were also the first in which a woman, Croatian Democratic Union candidate Jadranka Kosor, took part in the runoff. The percentage of the vote received by Mesić in the second round – 66% – is the highest of any president to date. Mesić had received an absolute majority of the votes cast within Croatia itself in the first round, but the votes of Croatian citizens living abroad forced a run-off by reducing Mesić's overall percentage to just under the necessary 50% + 1 vote threshold needed to win in the first round. Voter turnout was 51% in both rounds.
Mesić was sworn in for a second term on 18 February 2005 by the Chief justice of the Constitutional Court.
Background
The Croatian State Elections Committee published a list of potential candidates on 15 December 2004. President Stjepan Mesić stood for re-election, and the governing HDZ nominated cabinet minister Jadranka Kosor. A total of thirteen candidates were accepted, each after having submitted 10,000 citizen signatures, an endorsement required by law.
Results
| Candidate | Party | First round | Second round | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | |||
| Stjepan Mesić | Croatian People's Party and others | 1,089,398 | 49.37 | 1,454,451 | 65.93 | |
| Jadranka Kosor | Croatian Democratic Union | 452,218 | 20.49 | 751,692 | 34.07 | |
| Boris Mikšić | Independent | 396,093 | 17.95 | |||
| Đurđa Adlešič | Croatian Social Liberal Party | 59,795 | 2.71 | |||
| Slaven Letica | Croatian Party of Rights | 57,748 | 2.62 | |||
| Ljubo Ćesić | Independent | 41,216 | 1.87 | |||
| Ivić Pašalić | Croatian Bloc–Movement for a Modern Croatia | 40,637 | 1.84 | |||
| Anto Kovačević | Croatian Christian Democratic Union | 19,145 | 0.87 | |||
| Miroslav Blažević | Independent | 17,847 | 0.81 | |||
| Miroslav Rajh | Croatian Youth Party | 14,766 | 0.67 | |||
| Doris Košta | Independent | 8,271 | 0.37 | |||
| Mladen Kešer | Independent | 7,056 | 0.32 | |||
| Tomislav Petrak | Croatian Popular Party | 2,614 | 0.12 | |||
| Total | 2,206,804 | 100.00 | 2,206,143 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 2,206,804 | 99.09 | 2,206,143 | 98.41 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 20,269 | 0.91 | 35,617 | 1.59 | ||
| Total votes | 2,227,073 | 100.00 | 2,241,760 | 100.00 | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 4,403,933 | 50.57 | 4,392,220 | 51.04 | ||
| Source: State Election Committee | ||||||
Analysis
Most polls before the first round predicted that incumbent president Stjepan Mesić would be reelected without a runoff, securing 50% + 1 vote. However, Jadranka Kosor benefited from the votes coming from the citizens living abroad, which narrowed the president's victory by only a couple of points, but enough to secure a second round. The greatest surprise of the election was the independent candidate Boris Mikšić, a Croatian businessman and entrepreneur living in the United States. His campaign was heavily based on the message of a 'Croatian dream', similar to the American dream he said he achieved during his career in the US. On the night of the election, the first exit polls indicated president Mesić might secure a second term without the need of a runoff, while Kosor and Mikšić were shown battling for second place. As the first results started coming in it was evident that Mesić was not going to secure 50% + 1 vote and that a runoff is inevitable. As votes from the citizens living abroad were tallied, Kosor overtook Mikšić, placing second and qualifying for the second round. The campaign began immediately the next day and during the two-week-long campaign, three presidential debates were held, one on each of Croatia's three major television networks. Despite most observers and post debate polls indicating Kosor won the debates, Mesić maintained his lead in the polls. As Election Day neared, the Kosor campaign exceeded all previous campaign spending records, trying to motivate the conservative base. On Election Day, as polls around the country closed at 7 pm, all television networks announced Mesić won a landslide victory based on the exit polls, which official results later confirmed. Kosor conceded and congratulated Mesić on his victory. After the elections, Boris Mikšić claimed the elections were fraud and that Mesić and Prime Minister Ivo Sanader made a deal of "bringing" Kosor in the second round. He claimed to have received 15,000 election ballots with serial numbers that were not evidented.
References
- "Jutarnji list i Mediana: Bandić treći, a još se nije ni kandidirao". Jutarnji list (in Croatian). 19 September 2009. Archived from the original on 1 October 2018. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- "Prema zadnjim projekcijama izbornih rezultata Mesić uvjerljivo vodi". Index.hr (in Croatian). 2 January 2005. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- "Kosor u prvom krugu potrošila najmanje 8,7 milijuna kuna". Index.hr (in Croatian). 8 January 2005. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- "B. Mikšić: Mesić i Sanader dogovorili su 2005. Da u 2. Krug ide J. Kosor". Večernji list (in Croatian). 16 December 2009.
External links
| Parliamentary elections | |
|---|---|
| Presidential elections | |
| European elections | |
| Chamber of Counties elections | |
| Local elections | |
| Minorities elections | |
| Referendums | |
| |


