 The 52nd Ariane 4 carrying the TOPEX/Poseidon satellite. The 52nd Ariane 4 carrying the TOPEX/Poseidon satellite. | |
| Function | Expendable launch vehicle |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Aérospatiale |
| Country of origin | Europe |
| Size | |
| Height | 58.72 m (192.7 ft) |
| Diameter | 3.8 m (12 ft) |
| Mass | 240,000–470,000 kg (530,000–1,040,000 lb) |
| Stages | 3 |
| Capacity | |
| Payload to LEO | |
| Mass | 5,000–7,600 kg (11,000–16,800 lb) |
| Payload to GTO | |
| Mass | 2,000–4,300 kg (4,400–9,500 lb) |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Retired |
| Launch sites | Kourou, ELA-2 |
| Total launches | 116 (40: 7, 42P: 15, 42L: 13) (44P: 15, 44LP: 26, 44L: 40) |
| Success(es) | 113 (40: 7, 42P: 14, 42L: 13) (44P: 15, 44LP: 25, 44L: 39) |
| Failure(s) | 3 (42P: 1, 44L: 1, 44LP: 1) |
| First flight |
|
| Last flight |
|
| Boosters (Ariane 42L, 44LP or 44L) – PAL | |
| No. boosters | 0, 2 or 4 |
| Powered by | Viking 6 |
| Maximum thrust | 752.003 kN (169,057 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 278 seconds |
| Burn time | 142 seconds |
| Propellant | N2O4 / UDMH |
| Boosters (Ariane 42P, 44LP or 44P) – PAP | |
| No. boosters | 0, 2 or 4 |
| Maximum thrust | 650 kN (150,000 lbf) |
| Burn time | 33 seconds |
| Propellant | CTPB 1613 |
| First stage – L220 | |
| Powered by | 4 Viking 5C |
| Maximum thrust | 3,034.1 kN (682,100 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 278 seconds |
| Burn time | 205 seconds |
| Propellant | N2O4 / UDMH |
| Second stage – L33 | |
| Powered by | 1 Viking 4B |
| Maximum thrust | 720.965 kN (162,079 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 296 seconds |
| Burn time | 132 seconds |
| Propellant | N2O4 / UDMH |
| Third stage – H10 | |
| Powered by | 1 HM7-B |
| Maximum thrust | 62.703 kN (14,096 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 446 seconds |
| Burn time | 759 seconds |
| Propellant | LH2 / LOX |
| [edit on Wikidata] | |
The Ariane 4 was a European expendable launch vehicle, developed by the Centre national d'études spatiales (CNES), the French space agency, for the European Space Agency (ESA). The manufacturing of the launch vehicle was led by Aérospatiale and it was marketed by Arianespace. Since its first flight on 15 June 1988 until the final flight on 15 February 2003, it attained 113 successful launches out of 116 total launches.
In 1982, the Ariane 4 program was approved by ESA. Drawing heavily upon the preceding Ariane 3, it was designed to provide a launcher capable of delivering heavier payloads and at a lower cost per kilogram than the earlier members of the Ariane family. The Ariane 4 was principally an evolution of the existing technologies used, as opposed to being revolutionary in its design ethos; this approach quickly gained the backing of most ESA members, who funded and participated in its development and operation. Capable of being equipped with a wide variety of strap-on boosters, the Ariane 4 gained a reputation for being an extremely versatile launcher.
Once in service, the launcher soon became recognized for being ideal for launching communications and Earth observation satellites, as well as those used for scientific research. During its working life, the Ariane 4 managed to capture 50% of the market in launching commercial satellites, soundly demonstrating Europe's ability to compete in the commercial launch sector. In February 2003, the final Ariane 4 was launched; Arianespace had decided to retire the type in favour of the newer and larger Ariane 5, which effectively replaced it in service.
Development
Origins
In 1973, eleven nations decided to pursue joint collaboration in the field of space exploration and formed a new pan-national organisation to undertake this mission, the European Space Agency (ESA). Six years later, in December 1979, the arrival of a capable European expendable launch system was marked when the first Ariane 1 launcher was successfully launched from the Centre Spatial Guyanais (CSG) at Kourou, French Guiana. The Ariane 1 soon became considered to be a capable and competitive launcher in comparison to rival platforms offered by the Soviet Union and the United States of America, and it was quickly followed by improved derivatives in the form of the Ariane 2 and Ariane 3. By early 1986, the Ariane 1, along with the Ariane 2 and Ariane 3, had become the dominant launcher on the world market.
In January 1982, the ESA issued its authorisation for the development and construction of the Ariane 4; the development programme had the stated objective of increasing the usable payload by 90%. The Ariane 4 would be a considerably larger and more flexible launcher that the earlier members of its family, being intended to compete with the upper end of launchers worldwide. In comparison, while the Ariane 1 had a typical weight of 207 tonnes (456,000 lb) and could launch payloads of up to 1.7 tonnes (3,700 lb) into orbit; the larger Ariane 4 had a typical weight of 470 tonnes (1,040,000 lb) and could orbit payloads of up to 4.2 tonnes (9,300 lb). Work on the Ariane 4 was substantially eased via drawing heavily on both the technology and experiences gained from producing and operating the earlier members of the Ariane rocket. The total development cost for the Ariane 4 was valued at 476 million European Currency Units (ECU) in 1986.
Posed with the requirement to produce a rocket with substantially greater thrust, the design team considered various approaches to achieve this. One concept studied had involved the addition of a fifth engine to an enlarged first stage of the Ariane 3, but was found to involve a very high level of redesign work to achieve this; instead, the first stage was elongated to hold 210 tonnes (460,000 lb) of propellant instead of the 145 tonnes (320,000 lb) present on the Ariane 3. While the second and third stages remained identical to the Ariane 3, a range of strap-on boosters were developed to be applied to the type, designed to gradually increase the rocket's payload capacity. Overall, the Ariane 4 was 15% smaller than the Ariane 3.
In effect, the Ariane 4 was an improved and developed derivative of the earlier Ariane 3, primarily differing through the application of various solid-fuelled and liquid-fuelled boosters, the latter being the only all-new design feature of the Ariane 4; at this point, the practice of using liquid boosters was uncommon, having only previously been used in the Chinese space program. Another innovation of the Ariane 4 was the dual-launch SPELDA (Structure Porteuse Externe de Lancement Double Ariane) fairing. This had the function of allowing a pair of satellites, one placed on top of the other; several different SPELDA nose fairings could be installed, including normal and extended models. The SPELDA was considerably lighter than its predecessor; the guidance system also used much more accurate ring laser gyroscopes. According to aviation author Brian Harvey, the advances present in the design of the Ariane 4 represented a conservative and evolutionary, rather than revolutionary, philosophy.
Teaming and construction
As the Ariane 4 programme took shape, it gained the support of Belgium, Denmark, Spain, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Sweden, and Switzerland. The main contractors were Aérospatiale (responsible for the first and second stages), Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB) (produced the liquid-fuelled boosters), Société Européenne de Propulsion (SEP) (engine manufacturer), Matra (equipment bay assembly), Air Liquide (production of third stage tanks and insulation), BPD Snia (maker of solid-fuelled boosters), and British Aerospace/Contraves Space AG (manufacturers of the fairing). For their work on the Ariane 4, the Launch Team were subsequently awarded the Space Achievement Award by the Space Foundation in 2004.
In conjunction with the development of the Ariane 4 itself, a new purpose-built launch preparation area and launch pad for the rocket, collectively designated as ELA-2, was constructed at the Centre Spatial Guyanais to service the Ariane 4 and provide a launch rate of 8 launches per year (this feat was near-unprecedented for a single large rocket, other than within the Soviet Union). Unlike the earlier ELA-1 which had been used for the previous members of the Ariane family and other rockets, preparation activity for the rocket would be performed in a purpose-built 80-metre (260 ft) tall hall rather than on the pad itself; the completed rocket was then transported using a specially-designed railway to slowly traverse from the hall to the launch pad, taking one hour. This railway provided the additional benefit of enabling faulty rockets to be withdrawn from the pad and be substituted for relatively quickly.
On 15 June 1988, the first successful launch of the Ariane 4 was conducted. For this first test flight, it was decided to fire the second most powerful version of the rocket, designated 44LP, equipped with four main engines, two solid boosters and two liquid boosters; it was also furnished with the multi-satellite SPELDA fairing. 50 seconds after take-off, the solid boosters would be expended and be detached in order to reduce the rocket's weight. 143 seconds after take-off, the liquid boosters also detached, further lightening the vehicle. The maiden flight was considered a success, putting multiple satellites into orbit.
Further development
For the V50 launch onwards, an improved third stage, known as the H10+, was adopted for the Ariane 4. The H10+ third stage featured a new tank, which was 26 kg (57 lb) lighter, 32 cm (13 in) longer, and contained 340 kg (750 lb) more fuel, which raised the rocket's overall payload capacity by 110 kg (240 lb) and increased its burn time by 20 seconds.
Even prior to the first flight of the Ariane 4, development of a successor, designated as the Ariane 5, had already commenced. In January 1985, the Ariane 5 had been officially adopted as an ESA programme. It lacked the high levels of commonality that the Ariane 4 had with its predecessors, and had been designed not only for launching heavier payloads of up to 5.2 tonnes (11,000 lb) and at a 20% cost reduction over the Ariane 4, but for a higher margin of safety due to the fact that the Ariane 5 was designed to conduct crewed space launches as well, being intended to transport astronauts using the proposed Hermes space vehicle. Development of the Ariane 5 was not without controversy as some ESA members considered the more mature Ariane 4 to be more suited for meeting established needs for such launchers; it was for this reason that Britain chose not to participate in the Ariane 5 programme. For some years, Ariane 4 and Ariane 5 launchers were operated interchangeably; however, it was eventually decided to terminate all Ariane 4 operations in favour of concentrating on the newer Ariane 5.
Design
The Ariane 4 was the ultimate development from the preceding members of the Ariane rocket family. Compared with the Ariane 2 and Ariane 3, the Ariane 4 featured a stretched first (by 61%) and third stages, a strengthened structure, new propulsion bay layouts, new avionics, and the SPELDA (Structure Porteuse Externe de Lancement Double Ariane) dual-payload carrier. The basic 40 version did not employ any strap-on motors, while the Ariane 42L, 44L, 42P, 44P, and 44LP variants all used various combinations of solid and liquid boosters. Originally designed to place 2,000 to 4,200 kg (4,400 to 9,300 lb) payloads in geostationary orbit, the six Ariane 4 variants, aided by strap-on boosters, enabled the launch of payloads in excess of 4,900 kg (10,800 lb) on several occasions. The Ariane 4 launcher reduced the launch costs per kilo by 55% in comparison to the original Ariane 1.
The rocket was used in a number of variants - it could be fitted with two or four additional solid (PAP for Propulseurs d'Appoint à Poudre) or liquid fueled booster rockets (PAL for Propulseurs d'Appoint à Liquide). The launcher included a satellite payload carrier system called SPELDA (Structure porteuse externe de lancement double Ariane, French for External Carrying Structure for Ariane Double Launches) for launching more than one satellite at a time. The rocket captured nearly 60% of the world's commercial launch services market, serving both European and international clients. Atop the third stage was a vehicle equipment stage which housed a computer that performed various functions, including sequencing, guidance, control, tracking, telemetry and an explosive-based self-destruct.
The Ariane 4 AR 40 was the basic version, with three stages: 58.4 m (192 ft) high, a diameter of 3.8 m (12 ft), a liftoff mass of 245,000 kg (540,000 lb) and a maximum payload of 2,100 kg (4,600 lb) to GTO or 5,000 kg (11,000 lb) to low Earth orbit (LEO). Main power was provided by four Viking 2B motors, each producing 667 kN (150,000 lbf) of thrust. The second stage was powered by a single Viking 4B motor, and the third stage was equipped with an HM7-B liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen motor. The Ariane 4 AR 44L, which was outfitted with the maximum additional boost of four liquid fuel rocket strap-ons, was a four-stage rocket, weighing 470,000 kg (1,040,000 lb) and capable of transferring a payload of 4,730 kg (10,430 lb) to GTO, or alternatively 7,600 kg (16,800 lb) to LEO.
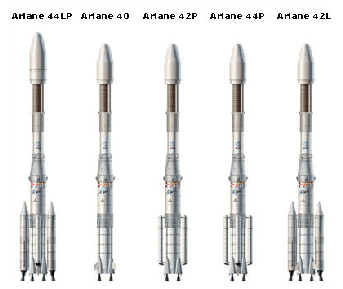
| Model | PAL | PAP | Payload to GTO (kg) | Launches | Successes | Failure date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR 40 | 0 | 0 | 2100 | 7 | 7 | |
| AR 42P | 0 | 2 | 2930 | 15 | 14 | 1 December 1994 |
| AR 42L | 2 | 0 | 3480 | 13 | 13 | |
| AR 44P | 0 | 4 | 3460 | 15 | 15 | |
| AR 44LP | 2 | 2 | 4220 | 26 | 25 | 24 January 1994 |
| AR 44L | 4 | 0 | 4720 | 40 | 39 | 22 February 1990 |
Operational history
Main article: List of Ariane launchesIn June 1988, the inaugural flight of the Ariane 4 occurred, which was a success. Since then, Ariane 4 has flown 116 times, 113 of which were successful, yielding a success rate of 97.4%.
On 22 February 1990, the first failure occurred during the eighth Ariane 4 launch, flight V36. The rocket exploded 9 km above Kourou. The failure occurred because a worker assembling a Viking rocket motor had left a handkerchief in one of the motor's coolant tubes. He had done so as a reminder to himself to inform his superior, as per procedure, of an unplanned polishing he had made to fit the tube. But he fell ill before he could do so and was replaced by other workers who did not notice the handkerchief. In flight, the handkerchief blocked the coolant tube, the motor overheated and failed, and the Ariane self-destructed after veering off its trajectory. Its payload, two communications satellites worth 500 million US dollars (Superbird-B and BS-2X) landed in pieces in the swamps near Kourou. The ensuing investigation recommended 44 modifications, including numbering and checking all pieces of cloth used in the rocket's assembly. The following 26 launches were all completed successfully.
The system became the basis for European satellite launches with a record of 113 successful and three launch failures. Ariane 4 provided a payload increase from 1,700 kg (3,700 lb) for Ariane 3 to a maximum of 4,800 kg (10,600 lb) to geostationary transfer orbit (GTO). The record for Ariane 4 to GTO was 4,946 kg (10,904 lb).
On 15 February 2003, the final launch of Ariane 4 rocket occurred, placing Intelsat 907 into geosynchronous orbit. Arianespace had decided to phase out the Ariane 4 launcher in favour of the newer heavy-lift Ariane 5 rocket, which had already been in service for some years. In 2011, the medium-lift Soyuz ST complemented the offering of launch vehicles from the Centre Spatial Guyanais. Spacecraft launched by the Soyuz reused the payload platform and dispenser which had been originally designed for the Ariane.
Comparable rockets
- Delta II (retired)
- GSLV Mk II
- GSLV Mk III
- Long March 3B
- Soyuz-U (retired)
See also
- Comparison of orbital launchers families
- Tsyklon-4 (Ukrainian carrier rocket with fairing derived from Ariane 4)
References
- Wade, Mark (ed.). "Ariane 4". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 28 December 2016. Retrieved 22 June 2021.
- "Ariane 4". European Space Agency. 14 May 2004. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
- ^ Harvey, Brian (2003). Europe's Space Programme: To Ariane and Beyond. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 1-8523-3722-2.
- ^ Wade, Mark (ed.). "Ariane". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 7 February 2024. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
- "Awards". Space Foundation. Archived from the original on 19 May 2024. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
- "Ariane 4, un défi pour l'Europe spatiale" [Ariane 4 - A challenge for Europe's space industry] (in French). CNES. 9 June 2015. Archived from the original on 23 September 2023. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
- ^ Castanos, Francis (7 December 2020). "The Space Review: The cloth of doom: The weird, doomed ride of Ariane Flight 36". www.thespacereview.com. Archived from the original on 4 December 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- "Ariane 4". Airbus Defence and Space. Archived from the original on 27 September 2016. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
- "Arianespace Flight 159: Mission Accomplished! 23rd launch for Intelsat" (Press release). Arianespace. 15 February 2003. Archived from the original on 6 July 2023. Retrieved 28 May 2024.
- "Soyuz User's Manual" (PDF). Arianespace. March 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 December 2013. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
External links
- ESA Ariane 4 launchers
- FAS Ariane 4 Archived 14 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- A cutaway drawing of the Ariane 4
| Ariane (rocket family) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rockets |
|  | ||||||
| Launch sites | ||||||||
| Engines | ||||||||
| Launches | ||||||||
| Flights | ||||||||
| Organizations |
| |||||||
| Related |
| |||||||
| European orbital launch systems | |
|---|---|
| Active | |
| In development | |
| Retired | |
| Cancelled | |