Community in South America Ethnic group
| |
|---|---|
 A statue, representing a tribute from the Armenian Collective to the Uruguayan government, located in Montevideo. A statue, representing a tribute from the Armenian Collective to the Uruguayan government, located in Montevideo. | |
| Total population | |
| 15,000 – 20,000 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Montevideo | |
| Languages | |
| Uruguayan Spanish, Armenian | |
| Religion | |
| Armenian Apostolic, Armenian Catholic, Evangelical and Protestant | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Armenian, Armenian Argentines |
Armenian Uruguayans (Armenian: Հայերն Ուրուգվայում, romanized: Hayern Urugvayum; Spanish: Armenio-uruguayos) number around 15,000–20,000 of the population, making Uruguay to have one of the largest Armenian diaspora populations around the world. The Armenian community in Uruguay is one of the oldest communities in South America, with most of them residing in the capital Montevideo. The majority of Armenians in Uruguay are either third or fourth-generation descendants of the first wave of immigrants coming from the Ottoman Empire between the end of the 19th century and the Armenian genocide.
History

Armenians in Uruguay began to settle around the 19th century. Around 1900, Uruguay already saw about 15 Armenians arriving to Montevideo. That number drastically increased by 1912, with large numbers of Marash residents, Kessab residents, Ayntap residents, Zeytun residents, Caesareans and Yozgat residents arriving to the capital. The first Armenians settled in Uruguay were mostly engaged in tailoring, shoemaking and small trade. The Uruguayan-Armenian community began to form in the 1920s, when large groups of Armenian refugees who had been rescued from the genocide and settled from the Middle East into Uruguay.
In 1923, a 35-member initiative group founded the first Uruguayan-Armenian structure, the Colonial Union, with 5 people elected as representatives. In the same year, Armenians set up a house in the Montevideo district called El Cerro, which served as a church and school. During that period, the number of local Armenians was about 3,000. The Armenian General Benevolent Union (AGBU) established a chapter in Uruguay in 1939 and inaugurated a community center complex in 1953. Recognition of the Armenian genocide by various world parliaments was spearheaded by Uruguay's Parliament, when in 1965 it became the first country in the world to recognize the Genocide. The Parliament has subsequently consistently supported various resolutions in favor of the Armenians. In 1987, the Uruguayan government issued a special postage stamp on the occasion of the 100th anniversary of the founding of the Social Democrat Hunchakian Party.
Community
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (December 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Between 1974 and 1975, the Armenian General Benevolent Union, a non-profit Armenian organization that preserves and promotes the Armenian identity and heritage through educational, cultural and humanitarian programs, established an educational center in Uruguay which was completed in two phases. The first to be completed was the Nubarian Elementary School in honor of the founder of the AGBU, Boghos Nubar, and eventually the Alex Manoogian High School, named after the AGBU President at that time.
Most of the community is headed and formally represented by the Central Administrative Council of the Armenian Apostolic Church. There is one apostolic, one Catholic and two evangelical churches, two daily schools, local organizations of Armenian national parties such as the Armenian Revolutionary Federation, the Social Democrat Hunchakian Party, and the Armenian Democratic Liberal Party, with their unions and clubs, patriotic, charitable, cultural and youth unions. There are also numerous Armenian dance groups, choirs, orchestras and theater groups within the community along with three Armenian radio stations broadcast through Uruguay.
The Armenians are very active in the arts. Alvaro Hagopian is the conductor of the Montevideo Philharmonic Orchestra. Also operating is the "Gayane" Dance Group, which belongs to the Armenian National Center.
Montevideo has both an urban square and a nearby coast avenue named after the country of Armenia.
Religion



Most Armenians belong to the Armenian Apostolic Church. The main center is the Armenian Church of Montevideo, Uruguay (Spanish: Iglesia Armenia del Uruguay). This church has a memorial statue by sculptor Nerses Ounanian, dedicated to the victims of the Armenian genocide.
There is also a significant presence of Armenian Catholics and Armenian Evangelicals.
The main Armenian places of worship in Montevideo are:
- St. Nerses Shnorhali Church (Armenian Apostolic)
- Cathedral of Our Lady of Bzommar (Armenian Catholic)
- Armenian Evangelical Church (Armenian Evangelical)
Gastronomy
Armenian cuisine is very present in Montevideo. Several small restaurants and pizzerias serve lahmajun (locally known as "lehmeyún").
Notable people
Art and Music
- Coriún Aharonián, musicologist and composer
- Nerses Ounanian, sculptor and artist
Education and Government
- Dora Bagdassarián, dean of the Law School of the University of the Republic
- Liliam Kechichián, government minister
- Roberto Markarian Abrahamian, mathematician and rector of the University of the Republic
- Vartan Matiossian, scholar of Armenian studies
Media and entertainment
- Daniel Ketchedjian (aka Daniel K), magician
- Johana Riva Garabetian, model, Miss Uruguay 2014
- Avedis Badanian, journalist
- Asadur Vaneskahian, journalist
- Berch Rupenian, radio personality and DJ
- Nisham Sarkissian, journalist
Politics
- Liliam Kechichian, Tourism minister 2012-2020
- José Luis Satdjian, deputy Health minister 2020-2024
Sports
- Mikael Aprahamian, judoka
- Pablo Aprahamian, judoka
- José Bademian Orchanian, chess player
- Joaquín Boghossián, footballer
- Manuel Dienavorian Lacherian, chess player
- Mauro Guevgeozián, footballer
- Manuel Keosseián, football coach and retired footballer
- Sergio Markarián Abrahamián, football coach and retired footballer
- Gabriel Melconian, swimmer
- Martin Melconian, swimmer
- Diego Rossi Marachlian, footballer
- Carlos Ádrian Sarkissian, retired footballer
- Germán Tozdjián, weightlifter
- Christian Apraham Yeladián, footballer
Other Professions
- Hakob Kedenjian, archbishop of the Armenian Church in Uruguay
See also
Bibliography
- Caetano, Gerardo; Neves, Salvador; Rodríguez, Mauricio (2020). La causa armenia entre el Ararat y Uruguay. Historia de un reconocimiento. Montevideo: Fundación Zelmar Michelini. p. 326. ISBN 9789915931203.
References
- ^ AGBU – AGBU XVIII World Games Takes Montevideo by Storm, 1,000 People Participate Archived December 5, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ ArmenianDiaspora website Archived May 11, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- AGBU Uruguay ChapterArchived March 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- "Armenian Genocide – Recognition of the Armenian Genocide".
- Armenians in Uruguay
- "How to prepare lahmajun, a traditional dish from the Middle East". El Observador. October 21, 2022. Retrieved February 8, 2023.
- 1980 TV debate moderated by Asadur Vaneskahian
- Berch Rupenian, the Lord of Music
External links
- AGBU
- Web site for Armenians of Uruguay
- Tigran Ghanalanyan, Armenian Protestant communities in South America, http://noravank.am/eng/issues/detail.php?ELEMENT_ID=5722
- Armenian-Uruguayan cultural identity (in Spanish)
| Armenian diaspora | ||
|---|---|---|
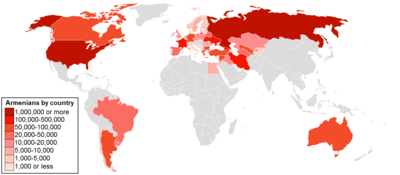 | ||
| Historic areas of Armenian settlement | ||
| Caucasus | ||
| Former Soviet Union | ||
| Americas | ||
| Europe | ||
| Middle East | ||
| Asia | ||
| Africa | ||
| Oceania | ||
| Uruguayan people | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indigenous | |||||||||
| Non-Indigenous |
| ||||||||
