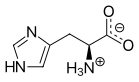
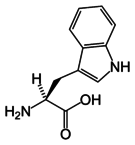

An aromatic amino acid is an amino acid that includes an aromatic ring.

Among the 20 standard amino acids, histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine, are classified as aromatic.
Properties and function
Optical properties
Aromatic amino acids, excepting histidine, absorb ultraviolet light above and beyond 250 nm and will fluoresce under these conditions. This characteristic is used in quantitative analysis, notably in determining the concentrations of these amino acids in solution. Most proteins absorb at 280 nm due to the presence of tyrosine and tryptophan. Of the aromatic amino acids, tryptophan has the highest extinction coefficient; its absorption maximum occurs at 280 nm. The absorption maximum of tyrosine occurs at 274 nm.
Role in protein structure and function
Aromatic amino acids stabilize folded structures of many proteins. Aromatic residues are found predominantly sequestered within the cores of globular proteins, although often comprise key portions of protein-protein or protein-ligand interaction interfaces on the protein surface.
Aromatic amino acids as precursors
Aromatic amino acids often serve as the precursors to important biochemicals.
- Histidine is the precursor to histamine.
- Tryptophan is the precursor to 5-hydroxytryptophan and then serotonin, tryptamine, auxin, kynurenines, and melatonin.
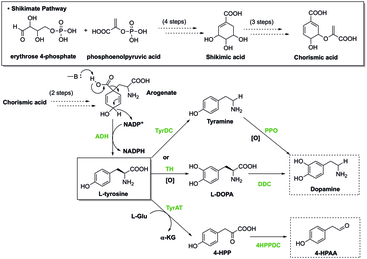
- Tyrosine is the precursor to L-DOPA, dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline), and the thyroid hormone thyroxine. It is also precursor to octopamine and melanin in numerous organisms.
- Phenylalanine is the precursor to tyrosine.
Biosynthesis
Shikimate pathway
In plants, the shikimate pathway first leads to the formation of chorismate, which is the precursor of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. These aromatic amino acids are the precursors of many secondary metabolites, all essential to a plant's biological functions, such as the hormones salicylate and auxin. This pathway contains enzymes that can be regulated by inhibitors, which can cease the production of chorismate, and ultimately the organism's biological functions. Herbicides and antibiotics work by inhibiting these enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids, thereby rendering them toxic to plants. Glyphosate, a type of herbicide, is used to control the accumulation of excess greens. In addition to destroying greens, Glyphosate can easily affect the maintenance of the gut microbiota in host organisms by specifically inhibiting the 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase which prevents the biosynthesis of essential aromatic amino acids. Inhibition of this enzyme results in disorders such as gastrointestinal diseases and metabolic diseases.
Nutritional requirements
Animals obtain aromatic amino acids from their diet, but nearly all plants and some micro-organisms must synthesize their aromatic amino acids through the metabolically costly shikimate pathway in order to make them. Histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, are essential amino acids for animals. Since they are not synthesized in the human body, they must be derived from the diet. Tyrosine is semi-essential; therefore, it can be synthesized by the animal, but only from phenylalanine. Phenylketonuria, a genetic disorder that occurs as a result of the inability to breakdown phenylalanine, is due to a lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. A dietary lack of tryptophan can cause stunted skeletal development. Excessive intake of aromatic amino acids far beyond levels obtained through normal protein consumption might lead to hypertension, something which could go un-noticed for a long time in healthy individuals. It could be caused by other factors as well such as the use of various herbs and foods like chocolate which inhibit monoamine oxidase enzymes to varying degrees, and also some medications. Aromatic trace amines like tyramine can displace norepinephrine from peripheral monoamine vesicles and in people taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) this occurs to the extent of being life threatening. Blue diaper syndrome is an autosomal recessive disease that is caused by poor tryptophan absorption in the body.
See also
- Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase
- Expanded genetic code
- Phenylketonuria
- Tyrosine hydroxylase
- Neurotransmitter
Notes
- There exist parasitic plants, these plants don't have to synthesize amino acids. Carnivorous plants can get amino acids from digestion, too.
References
- Möller M, Denicola A (2002-05-01). "Protein tryptophan accessibility studied by fluorescence quenching". Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education. 30 (3): 175–178. doi:10.1002/bmb.2002.494030030035. ISSN 1539-3429. S2CID 42862291.
- Schmid FX (April 2001). "Biological Macromolecules: UV‐visible Spectrophotometry" (PDF). Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. doi:10.1038/npg.els.0003142. ISBN 0470016175.
- "Peptide and Amino Acid Quantification Using UV Fluorescence in Synergy HT Multi-Mode Microplate Reader | April 18, 2003". www.biotek.com. Retrieved 2020-03-23.
- Xu, Qingping; Biancalana, Matthew; Grant, Joanna C.; Chiu, Hsiu-Ju; Jaroszewski, Lukasz; Knuth, Mark W.; Lesley, Scott A.; Godzik, Adam; Elsliger, Marc-André; Deacon, Ashley M.; Wilson, Ian A. (September 2019). "Structures of single-layer β-sheet proteins evolved from β-hairpin repeats". Protein Science. 28 (9): 1676–1689. doi:10.1002/pro.3683. ISSN 1469-896X. PMC 6699103. PMID 31306512.
- Biancalana, Matthew; Makabe, Koki; Yan, Shude; Koide, Shohei (May 2015). "Aromatic cluster mutations produce focal modulations of β-sheet structure". Protein Science. 24 (5): 841–849. doi:10.1002/pro.2657. ISSN 1469-896X. PMC 4420532. PMID 25645104.
- ^ Han Q, Phillips RS, Li J (2019-04-10). "Editorial: Aromatic Amino Acid Metabolism". Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. 6: 22. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2019.00022. PMC 6468166. PMID 31024928.
- Tzin V, Galili G (2010-05-17). "The Biosynthetic Pathways for Shikimate and Aromatic Amino Acids in Arabidopsis thaliana". The Arabidopsis Book. 8: e0132. doi:10.1199/tab.0132. PMC 3244902. PMID 22303258.
- Nielsen LN, Roager HM, Casas ME, Frandsen HL, Gosewinkel U, Bester K, et al. (February 2018). "Glyphosate has limited short-term effects on commensal bacterial community composition in the gut environment due to sufficient aromatic amino acid levels" (PDF). Environmental Pollution. 233: 364–376. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.016. PMID 29096310.
- Moehn S, Pencharz PB, Ball RO (December 2012). "Lessons learned regarding symptoms of tryptophan deficiency and excess from animal requirement studies". The Journal of Nutrition. 142 (12): 2231S – 2235S. doi:10.3945/jn.112.159061. PMID 23077198.
- Teymoori F, Asghari G, Mirmiran P, Azizi F (January 2018). "High dietary intake of aromatic amino acids increases risk of hypertension". Journal of the American Society of Hypertension. 12 (1): 25–33. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2017.11.004. PMID 29208471.
Further reading
- Maeda H, Dudareva N (2012). "The shikimate pathway and aromatic amino Acid biosynthesis in plants". Annual Review of Plant Biology. 63: 73–105. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105439. PMID 22554242.
- "Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency". Genetics Home Reference. U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2020.
External links
 Media related to Aromatic amino acids at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Aromatic amino acids at Wikimedia Commons- Aromatic+Amino+Acids at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)