| Rotator cuff tear | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Rotator cuff injury, rotator cuff disease |
 | |
| Some of the muscles of the rotator cuff, with a tear in the supraspinatus muscle | |
| Specialty | Orthopedics |
| Symptoms | Shoulder pain, weakness |
| Types | Partial, complete |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, examination, medical imaging |
| Differential diagnosis | Subacromial bursitis, rotator cuff tendinitis, impingement syndrome |
| Treatment | Pain medication, specific exercises, surgery |
| Frequency | Common |
Rotator cuff tendinopathy is a process of senescence. The pathophysiology is mucoid degeneration. Most people develop rotator cuff tendinopathy within their lifetime.
As part of rotator cuff tendinopathy, the tendon can thin and develop a defect. This defect is often referred to as a rotator cuff tear. Acute, traumatic rupture of the rotator cuff tendons can also occur, but is less common. Traumatic rupture of the rotator cuff usually involves the tendons of more than one muscle.
Rotator cuff tendinopathy is, by far, the most common reason people seek care for shoulder pain. Pain related to rotator cuff tendinopathy is typically on the front side of the shoulder, down to the elbow, and worse reaching up or back. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and examination. Medical imaging is used mostly to plan surgery and is not needed for diagnosis.
Treatment may include pain medication such as NSAIDs and specific exercises. It is recommended that people who are unable to raise their arm above 90 degrees after two weeks should be further assessed. Surgery may be offered for acute ruptures and large attritional defects with good quality muscle. The benefits of surgery for smaller defects are unclear as of 2019.
Signs and symptoms

Rotator cuff tendinopathy is often asymptomatic even when there is thinning or a full thickness defect. Rotator cuff defects are common on post mortem and MRI studies in those without any history of shoulder pain or symptoms. Rotator cuff tendinopathy is associated with pain over the front and side (anterolateral) of the shoulder pain that radiates towards the elbow. The pain may occur with shoulder movement above the horizontal position, shoulder flexion and abduction. Pain is often described as weakness. Actual muscle weakness does not correlate with symptoms of weakness. Symptom severity does not correlate with rotator cuff defect size and associated muscle quality.
Risk factors

Epidemiological studies strongly support a relationship between age and cuff tear prevalence, with the most common cause being age-related degeneration and, less frequently, sports injuries or trauma.
Those most prone to failed rotator cuff syndrome are people 65 years of age or older; and those with large, sustained tears. Smokers, people with diabetes, individuals with muscle atrophy or fatty infiltration, and those who do not follow postoperative-care recommendations also are at greater risk. In a 2008 study the frequency of such tears increased from 13% in the youngest group (aged 50–59 y) to 20% (aged 60–69 y), 31% (aged 70–79 y), and 51% in the oldest group (aged 80–89 y).
Some risk factors, such as increased age and height, cannot be changed. Increased body mass index is also associated with tearing. Recurrent lifting and overhead motions are at risk for rotator cuff injury as well. This includes jobs that involve repetitive overhead work, such as carpenters, painters, custodians, and servers. People who play sports that involve overhead motions, such as swimming, water polo, volleyball, baseball, and tennis, and American football quarterbacks are at a greater risk of experiencing a rotator cuff tear. Striking-based combat sports, such as boxing, also account for severe rotator cuff injuries in competitors, typically when their punches miss the target, or overusing the shoulder by throwing an excessively large number of punches. Certain track-and-field activities, such as shot put and javelin throw are also of considerable risk, especially when athletes perform outdoors under cold weather conditions or neglect warming-up procedures; proper warm-up of the throwing and/or swinging arm can help reduce the stress on the musculature of the shoulder girdle. Corticosteroid injections around the tendons increase the risk of tendon tear and delay tendon healing.
Mechanisms of injury

The shoulder is a complex mechanism involving bones, ligaments, joints, muscles, and tendons.
The two main causes are acute injury or chronic and cumulative degeneration of the shoulder joint. Mechanisms can be extrinsic, intrinsic or a combination of both.
The cuff is responsible for stabilizing the glenohumeral joint to allow abduction and rotation of the humerus. When trauma occurs, these functions can be compromised. Because individuals are dependent on the shoulder for many activities, overuse can lead to tears, with the vast majority being in the supraspinatus tendon.
The role of the supraspinatus is to resist downward motion, both while the shoulder is relaxed and carrying weight. Supraspinatus tears usually occurs at its insertion on the humeral head at the greater tubercle. Though the supraspinatus is the most commonly injured tendon in the rotator cuff, the other three can also be injured at the same time.
Acute tears
The amount of stress needed to acutely tear a rotator cuff tendon will depend on the underlying condition of the tendon. If healthy, the stress needed will be high, such as with a fall on the outstretched arm. This stress may occur coincidentally with other injuries such as a dislocation of the shoulder or separation of the acromioclavicular joint. In the case of a tendon with pre-existing degeneration, the force may be more modest, such as with a sudden lift, particularly with the arm above the horizontal position. The type of loading involved with injury is usually eccentric, such as when two people are carrying a load and one lets go, forcing the other to maintain force while the muscle elongates.
Chronic tears
Chronic tears are indicative of extended use in conjunction with other factors such as poor biomechanics or muscular imbalance. Ultimately, most are the result of wear that occurs slowly over time as a natural part of aging. They are more common in the dominant arm, but a tear in one shoulder signals an increased risk of a tear in the opposing shoulder.
Several factors contribute to degenerative, or chronic, rotator cuff tears of which repetitive stress is the most significant. This stress consists of repeating the same shoulder motions frequently, such as overhead throwing, rowing, and weightlifting. Many jobs that require frequent shoulder movement such as lifting and overhead movements also contribute. In older populations impairment of blood supply can also be an issue. With age, circulation to the rotator cuff tendons decreases, impairing natural ability to repair, increasing risk for tear. Another potential contributing cause is impingement syndrome, the most common non-sports related injury and which occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles become irritated and inflamed while passing through the subacromial space beneath the acromion. This relatively small space becomes even smaller when the arm is raised in a forward or upward position. Repetitive impingement can inflame the tendons and bursa, resulting in the syndrome.
Extrinsic factors

Well-documented anatomic factors include the morphologic characteristics of the acromion, a bony projection from the scapula that curves over the shoulder joint. Hooked, curved, and laterally sloping acromia are strongly associated with cuff tears and may cause damage through direct traction on the tendon. Conversely, flat acromia may have an insignificant involvement in cuff disease and consequently may be best treated conservatively. The development of these different acromial shapes is likely both genetic and acquired. In the latter case, there can be a progression from flat to curved or hooked with increasing age. Repetitive mechanical activities such as sports and exercise may contribute to flattening and hooking of the acromion. Cricket bowling, swimming, tennis, baseball, and kayaking are often implicated. Progression to a hooked acromion could be an adaptation to an already damaged, poorly balanced rotator cuff with resultant stress on the coracoacromial arch. Other anatomical factors include an os acromiale and acromial spurs. Environmental factors include age, shoulder overuse, smoking, and medical conditions that affect circulation or impair the inflammatory and healing response, such as diabetes mellitus.
Intrinsic factors
Intrinsic factors refer to injury mechanisms that occur within the rotator cuff itself. The principal is a degenerative-microtrauma model, which supposes that age-related tendon damage compounded by chronic microtrauma results in partial tendon tears that then develop into full rotator cuff tears. As a result of repetitive microtrauma in the setting of a degenerative rotator cuff tendon, inflammatory mediators alter the local environment and oxidative stress induces tenocyte apoptosis, causing further rotator cuff tendon degeneration. A neural theory also exists that suggests neural overstimulation leads to the recruitment of inflammatory cells and may also contribute to tendon degeneration.
Surgical considerations
Depending upon the diagnosis, several treatment alternatives are available. They include revision repair, non-anatomic repair, tendon transfer, and arthroplasty. When possible, surgeons make tension-free repairs in which they use grafted tissues rather than stitching to reconnect tendon segments. This can result in a complete repair. Other options are a partial repair, and reconstruction involving a bridge of biologic or synthetic substances. Partial repairs are typically performed on retracted cuff tears.
Tendon transfers are prescribed for young, active cuff-tear individuals who experience weakness and decreased range of motion, but little pain. The technique is not considered appropriate for older people or those with pre-operative stiffness or nerve injuries. People diagnosed with glenohumeral arthritis and rotator cuff anthropathy have the alternative of total shoulder arthroplasty, if the cuff is largely intact or repairable. If the cuff is incompetent, a reverse shoulder arthroplasty is available and, although not as robust a prosthesis, does not require an intact cuff to maintain a stable joint.
Diagnosis

Diagnosis is based upon physical assessment and history, including description of previous activities and acute or chronic symptoms. A systematic physical examination of the shoulder comprises inspection, palpation, range of motion, provocative tests to reproduce the symptoms, neurological examination, and strength testing. The shoulder should also be examined for tenderness and deformity. Since pain arising from the neck is frequently 'referred' to the shoulder, the examination should include an assessment of the cervical spine looking for evidence suggestive of a pinched nerve, osteoarthritis, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Neer promoted the concept of three stages of rotator cuff disease. Stage I, according to Neer, occurred in those younger than 25 years and involved edema and hemorrhage of the tendon and bursa. Stage II involved tendinitis and fibrosis of the rotator cuff in 25- to 40-year-olds. Stage III involved tearing of the rotator cuff (partial or full thickness) and occurred in those older than 40 years. For surgical purposes, tears are also described by location, size or area, and depth. Further subclasses include the acromiohumeral distance, acromial shape, fatty infiltration or degeneration of muscles, muscle atrophy, tendon retraction, vascular proliferation, chondroid metaplasia, and calcification. Again, in surgical planning, age-related degeneration of thinning and disorientation of the collagen fibers, myxoid degeneration, and hyaline degeneration are considered.
Diagnostic modalities, dependent on circumstances, include X-ray, MRI, MR arthrography, double-contrast arthrography, and ultrasound. Although MR arthrography is currently considered the gold standard, ultrasound may be most cost-effective. Usually, a tear will be undetected by X-ray, although bone spurs, which can impinge upon the rotator cuff tendons, may be visible. Such spurs suggest chronic severe rotator cuff disease. Double-contrast arthrography involves injecting contrast dye into the shoulder joint to detect leakage out of the injured rotator cuff, and its value is influenced by the experience of the operator. The most common diagnostic tool is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which can sometimes indicate the size of the tear, as well as its location within the tendon. Furthermore, MRI enables the detection or exclusion of complete rotator cuff tears with reasonable accuracy and is also suitable for diagnosing other pathologies of the shoulder joint.
The logical use of diagnostic tests is an important component of effective clinical practice.
Clinical judgement, rather than over-reliance on MRI or any other modality, is strongly advised in determining the cause of shoulder pain, or planning its treatment, since rotator cuff tears are also found in some without pain or symptoms. The role of X-ray, MRI, and ultrasound is adjunctive to clinical assessment and serves to confirm a diagnosis provisionally made by a thorough history and physical examination. Over-reliance on imaging may lead to overtreatment or distract from the true dysfunction causing symptoms.
Symptoms
Symptoms may occur immediately after trauma (acute) or develop over time (chronic).
Acute injury is less frequent than chronic disease, but may follow bouts of forcefully raising the arm against resistance, as occurs in weightlifting, for example. In addition, falling forcefully on the shoulder can cause acute symptoms. These traumatic tears predominantly affect the supraspinatus tendon or the rotator interval and symptoms include severe pain that radiates through the arm, and limited range of motion, specifically during abduction of the shoulder. Chronic tears occur among individuals who constantly participate in overhead activities, such as pitching or swimming, but can also develop from shoulder tendinitis or rotator cuff disease. Symptoms arising from chronic tears include sporadic worsening of pain, debilitation, and atrophy of the muscles; noticeable pain during rest; crackling sensations (crepitus) when moving the shoulder; and inability to move or lift the arm sufficiently, especially during abduction and flexion motions.
Pain in the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder is not specific to the shoulder, and may arise from, and be referred from, the neck, heart, or gut.
Symptoms will often include pain or ache over the front and outer aspect of the shoulder, pain aggravated by leaning on the elbow and pushing upward on the shoulder (such as leaning on the armrest of a reclining chair), intolerance of overhead activity, pain at night when lying directly on the affected shoulder, and pain when reaching forward (e.g., unable to lift a gallon of milk from the refrigerator). Weakness may be reported, but is often masked by pain and is usually found only through examination. With longer-standing pain, the shoulder is favored and gradually loss of motion and weakness may develop, which, due to pain and guarding, are often unrecognized and only brought to attention during the physical exam.
Primary shoulder problems may cause pain over the deltoid muscle intensified by abduction against resistance – the impingement sign. This signifies pain arising from the rotator cuff, but cannot distinguish among inflammation, strain, or tear. Individuals may report that they are unable to reach upward to brush their hair or to lift a can of food from an overhead shelf.
Signs
No single physical examination test distinguishes reliably between bursitis, partial-thickness, and full-thickness tears. The most useful single test for infraspinatous tendon tears is the drop sign (the examiner lifts the arm straight out from the body with the palm up, the person then needs to hold it there for 10 seconds) and the external rotation lag sign (with the arm by the side and the elbow bent to 90 degrees the person tries to rotate outwards against resistance).
A combination of tests seems to provide the most accurate diagnosis. For impingement, these tests include the Hawkins-Kennedy impingement sign, in which an examiner medially rotates the injured individual's flexed arm, forcing the supraspinatus tendon against the coracoacromial ligament and so producing pain if the test is positive, a positive painful arc sign, and weakness in external rotation with the arm at the side. Another common impingement test is the neer test. The neer test is performed by the examiner maximally forward flexing the patient's arm with the scapula in a depressed position. Localized pain on the anterior shoulder suggests subacromial impingement, whereas posterior shoulder pain suggests internal impingement. For the diagnosis of full-thickness rotator cuff tear, the best combination appears to include once more the painful arc and weakness in external rotation, and in addition, the drop arm sign. This test is also known as Codman's test. The arm is raised to the side to 90° by the examiner. The injured individual then attempts to lower the arm back to neutral with palm down. If the arm drops suddenly or pain is experienced, the test is considered positive.
MRI


Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound are comparable in efficacy and helpful in diagnosis, although both have a false positive rate of 15–20%. MRI can reliably detect most full-thickness tears, although very small pinpoint tears may be missed. In such situations, an MRI combined with an injection of contrast material, an MR-arthrogram, may help to confirm the diagnosis. It should be realized that a normal MRI cannot fully rule out a small tear (a false negative) while partial-thickness tears are not as reliably detected. While MRI is sensitive in identifying tendon degeneration (tendinopathy), it may not reliably distinguish between a degenerative tendon and a partially torn tendon. Again, magnetic resonance arthrography can improve the differentiation. An overall sensitivity of 91% (9% false negative rate) has been reported, indicating that magnetic resonance arthrography is reliable in the detection of partial-thickness rotator cuff tears. However, its routine use is not advised, since it involves entering the joint with a needle, with the potential risk of infection. Consequently, the test is reserved for cases in which the diagnosis remains unclear.
Ultrasound
Musculoskeletal ultrasound has been advocated by experienced practitioners, avoiding the radiation of X-ray and the expense of MRI while demonstrating comparable accuracy to MRI for identifying and measuring the size of full-thickness and partial-thickness rotator cuff tears. This modality can also reveal the presence of other conditions that may mimic rotator cuff tear at clinical examination, including tendinosis, calcific tendinitis, subacromial subdeltoid bursitis, greater tuberosity fracture, and adhesive capsulitis. However, MRI provides more information about adjacent structures in the shoulder, such as the capsule, glenoid labrum muscles, and bone, and these factors should be considered in each case when selecting the appropriate study.
Xray


X-ray projectional radiography cannot directly reveal tears of the rotator cuff, a 'soft tissue', and consequently, normal X-rays cannot exclude a damaged cuff. However, indirect evidence of pathology may be seen in instances where one or more of the tendons has undergone degenerative calcification (calcific tendinitis). The humeral head may migrate upward (high-riding humeral head) secondary to tears of the infraspinatus, or combined tears of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus. The migration can be measured by the distance between:
- A line crossing the center of a line between the superior and inferior rims of the glenoid articular surface (blue in image).
- The center of a "best-fit" circle positioned over the humeral articular surface (green in image)
Normally, the former is positioned inferiorly to the latter, and a reversal therefore indicates a rotator cuff tear. Prolonged contact between a high-riding humeral head and the acromion above it may lead to X-ray findings of wear on the humeral head and acromion; secondary degenerative arthritis of the glenohumeral joint (the ball and socket joint of the shoulder), called cuff arthropathy, may follow. Incidental X-ray findings of bone spurs at the adjacent acromioclavicular joint may show a bone spur growing from the outer edge of the clavicle downward toward the rotator cuff. Spurs may also be seen on the underside of the acromion, once thought to cause direct fraying of the rotator cuff from contact friction, a concept currently regarded as controversial.
In-office testing
As part of clinical decision-making, a simple, minimally invasive, in-office procedure, the rotator cuff impingement test, may be performed. A small amount of a local anesthetic and an injectable corticosteroid are injected into the subacromial space to block pain and provide anti-inflammatory relief. If pain disappears and shoulder function remains good, no further testing is pursued. The test helps to confirm that the pain arises primarily from the shoulder, rather than being referred from the neck, heart, or gut.
If pain is relieved, the test is considered positive for rotator-cuff impingement, of which tendinitis and bursitis are major causes. However, partial rotator-cuff tears may also demonstrate good pain relief, so a positive response cannot rule out a partial rotator-cuff tear. However, with demonstration of good, pain-free function, the treatment will not change, so the test is useful in helping to avoid overtesting or performing unnecessary surgery.
Classification
Tears of the rotator cuff tendon are described as partial or full thickness, and full thickness with complete detachment of the tendons from bone.
- Partial-thickness tears often appear as fraying of an intact tendon.
- Full-thickness tears are "through-and-through". These tears can be small pinpoint or larger buttonhole, or involve the majority of the tendon where it still remains substantially attached to the humeral head and thus maintains function.
- Full-thickness tears may also involve complete detachment of the tendon(s) from the humeral head and may result in significantly impaired shoulder motion and function.
Shoulder pain is variable and may not be proportional to the size of the tear.
Tears are also sometimes classified based on the trauma that caused the injury:
- Acute, as a result of a sudden, powerful movement which might include falling onto an outstretched hand at speed, making a sudden thrust with a paddle in kayaking, or following a powerful pitch/throw
- Subacute, arising in similar situations but occurring in one of the five layers of the shoulder anatomy
- Chronic, developing over time, and usually occurring at or near the tendon (as a result of the tendon rubbing against the overlying bone), and usually associated with an impingement syndrome.
Prevention
Long-term overuse/abuse of the shoulder joint is generally thought to limit range of motion and productivity due to daily wear and tear of the muscles, and many public web sites offer preventive advice. (See external links) The recommendations usually include:
- regular shoulder exercises to maintain strength and flexibility
- using proper form when lifting or moving heavy weights
- resting the shoulder when experiencing pain
- application of cold packs and heat pads to a painful, inflamed shoulder
- strengthening program to include the back and shoulder girdle muscles as well as the chest, shoulder and upper arm
- adequate rest periods in occupations that require repetitive lifting and reaching
Size
According to a study which measured tendon length against the size of the injured rotator cuff, researchers learned that as rotator cuff tendons decrease in length, the average rotator cuff tear severity is proportionally decreased, as well. This shows that larger individuals are more likely to develop a severe rotator cuff tear if they do not "tighten the shoulder muscles around the joint".
Position
Another study observed 12 different positions of movements and their relative correlation with injuries occurred during those movements. The evidence shows that putting the arm in a neutral position relieves tension on all ligaments and tendons.
Stretching
One article observed the influence of stretching techniques on preventive methods of shoulder injuries. Increased velocity of exercise increases injury, but beginning a fast-movement exercise with a slow stretch may cause muscle/tendon attachment to become more resistant to tearing.
Muscle groups
When exercising, exercising the shoulder as a whole and not one or two muscle groups is also found to be imperative. When the shoulder muscle is exercised in all directions, such as external rotation, flexion, and extension, or vertical abduction, it is less likely to develop a tear of the tendon.
Treatment
A rotator cuff tear can be treated operatively or non-operatively. No benefit is seen from early rather than delayed surgery, and many with partial tears and some with complete tears will respond to nonoperative management. Consequently, an individual may begin with nonsurgical management. However, early surgical treatment may be considered in significant (>1 cm – 1.5 cm) acute tears, in young individuals with full-thickness tears who have a significant risk for the development of irreparable rotator cuff damage, or the patient is very active and/or uses their arms for overhead work or sports.
Rotator-cuff surgery appears to result in similar benefits as nonoperative management. As a conservative approach has less complications and is less expensive it is recommended as initial treatment.
Non-operative treatment
Those with pain but reasonably maintained function are suitable for nonoperative management. This includes medications that provide pain relief such as anti-inflammatory agents, topical pain relievers such as cold packs, and if warranted, subacromial corticosteroid or local anesthetic injection. Topical glyceryl trinitrate appears effective at relieving acute symptoms however, headaches were reported as a side effect. A sling may be offered for short-term comfort, with the understanding that undesirable shoulder stiffness can develop with prolonged immobilization. Early physical therapy may afford pain relief with modalities (e.g. iontophoresis) and help to maintain motion. Ultrasound treatment is not efficacious. As pain decreases, strength deficiencies and biomechanical errors can be corrected.
Shock wave therapy has seen widespread use since the 1990s to treat various musculoskeletal disorders including rotator cuff disease, but evidence of its efficacy remains dubious. In a review of 2020, the benefits and harms of shock wave therapy for rotator cuff disease, with or without calcificationcurrently, were investigated. They found low to moderate certainty evidence, that there were very few clinically important benefits of shock wave therapy, and uncertainty regarding its safety.
A conservative physical therapy program begins with preliminary rest and restriction from engaging in activities which gave rise to symptoms. Normally, inflammation can usually be controlled within one to two weeks, using a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and subacromial steroid injections to decrease inflammation, to the point that pain has been significantly decreased to make stretching tolerable. After this short period, rapid stiffening and an increase in pain can result if sufficient stretching has not been implemented.
A gentle, passive range-of-motion program should be started to help prevent stiffness and maintain range of motion during this resting period. Stiffness negatively affects the tendon-bone healing process, a critical part of recovery. Stiffness during rehabilitation is related to worse clinical outcomes, so it is important for the patient to understand the importance of a proactive regimen. Strain induced tendon remodeling, which is part of an accelerated rehabilitation protocol, has been shown to speed up the time to return to daily activities. Exercises, for the anterior, inferior, and posterior shoulder, should be part of this program. Codman exercises (giant, pudding-stirring), to "permit the patient to abduct the arm by gravity, the supraspinatus remains relaxed, and no fulcrum is required" are widely used. The use of NSAIDs, hot and cold packs, and physical therapy modalities, such as ultrasound, phonophoresis, or iontophoresis, can be instituted during this stretching period, if effective. Corticosteroid injections are recommended two to three months apart with a maximum of three injections. Multiple injections (four or more) have been shown to compromise the results of rotator cuff surgery which result in weakening of the tendon. Kinesio taping was compared to sham taping and other conservative treatment for the approach of the rotator cuff disease and has uncertain effects in terms of self‐reported pain, function, pain on motion and active range of motion.
Rockwood coined the term orthotherapy to describe the program which is aimed at creating an exercise regimen that initially gently improves motion, then gradually improves strength in the shoulder girdle. This program involves a home therapy kit which includes elastic bands of six different colors and strengths, a pulley set, and a three-piece, one-meter-long stick. The program is individually customized. Participants are asked to use their exercise program whether at home, work, or traveling.
Surgery
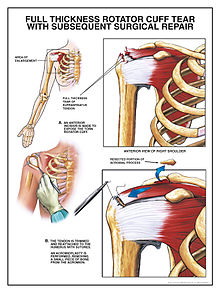
Benefits of surgery are unclear as of 2019. Several instances when surgery may be recommended include:
- 20 to 30-year-old active person with an acute tear and severe functional deficit from a specific event
- 30 to 50-year-old person with an acute rotator cuff tear secondary to a specific event
- a highly competitive athlete who is primarily involved in overhead or throwing sports
These individuals more often benefit from operative treatment because they are willing to tolerate the risks of surgery to return to their preoperative level of function, and have higher likelihood of a successful outcome. Those who do not respond to, or are unsatisfied with, conservative treatment can seek a surgical opinion.
The three general surgical approaches are arthroscopic, mini open, and open-surgical repair. In the past, small tears were treated arthroscopically, while larger tears would usually require an open procedure. Advances in arthroscopy now allow arthroscopic repair of even the largest tears, and arthroscopic techniques are now required to mobilize many retracted tears. The results match open surgical techniques, while permitting a more thorough evaluation of the shoulder at time of surgery, increasing the diagnostic value of the procedure, as other conditions may simultaneously cause shoulder pain. Arthroscopic surgery also allows for shorter recovery time although differences in postoperative pain or pain medication use are not seen between arthroscopic- and open-surgery. A 2019 review found that the evidence does not support decompression surgery in those with more than 3 months of shoulder pain without a history of trauma.
Even for full-thickness rotator cuff tears, conservative care (i.e., nonsurgical treatment) outcomes are usually reasonably good.
If a significant bone spur is present, any of the approaches may include an acromioplasty, a subacromial decompression, as part of the procedure. Subacromial decompression, removal of a small portion of the acromion that overlies the rotator cuff, aims to relieve pressure on the rotator cuff in certain conditions and promote healing and recovery. Although subacromial decompression may be beneficial in the management of partial and full-thickness tear repair, it does not repair the tear itself and arthroscopic decompression has more recently been combined with "mini-open" repair of the rotator cuff, allowing for the repair of the cuff without disruption of the deltoid origin. The results of decompression alone tend to degrade with time, but the combination of repair and decompression appears to be more enduring. Subacromial decompression may not improve pain, function, or quality of life.
Repair of a complete, full-thickness tear involves tissue suture. The method currently in favor is to place an anchor in the bone at the natural attachment site, with resuture of torn tendon to the anchor. If tissue quality is poor, mesh (collagen, Artelon, or other degradable material) may be used to reinforce the repair. Repair can be performed through an open incision, again requiring detachment of a portion of the deltoid, while a mini-open technique approaches the tear through a deltoid-splitting approach. The latter may cause less injury to muscle and produce better results. Contemporary techniques now use an all arthroscopic approach. Recovery can take as long as three–six months, with a sling being worn for the first one–six weeks. In the case of partial thickness tears, if surgery is undertaken, tear completion (converting the partial tear to a full tear) and then repair, is associated with better early outcomes than transtendinous repairs (where the intact fibres are preserved) and no difference in failure rates.
Biceps tenotomy and tenodesis are often performed concomitantly with rotator cuff repair or as separate procedures, and can also cause shoulder pain. Tenodesis, which may be performed as an arthroscopic or open procedure, generally restores pain free motion it the biceps tendon, or attached portion of the labrum, but can cause pain. Tenotomy is a shorter surgery requiring less rehabilitation, that is more often performed in older patients, though after surgery there can be a cosmetic 'popeye sign' visible in thin arms.
In a small minority of cases where extensive arthritis has developed, an option is shoulder joint replacement (arthroplasty). Specifically, this is a reverse shoulder replacement, a more constrained form of shoulder arthroplasty that allows the shoulder to function well even in the presence of large full thickness rotator cuff tears.
Shoulder Replacement
The latest systematic reviews suggests (with low quality evidence) that total shoulder arthroplasty does not provide important benefits over hemiarthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis and rotator cuff tears. It highlighted the current lack of high-quality evidence and need for randomized controlled trials.
Biologics
The main goal in biological augmentation is to enhance healing. There are a number of potential options. These include injecting an individual's own stem cells, growth factors or platelet rich plasma (PRP) into the repair site, and installing scaffolds as biological or synthetic supports to maintain tissue contour. A 2014 Cochrane review evaluated PRP and found insufficient evidence to make recommendations. Mesenchymal stem cells have no convincing evidence for their use overall, with quality human trials lacking. The greater tuberosity can also be microfractured to create a small blood clot just lateral to the repair site.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after surgery consists of three stages. First, the arm is immobilized so that the muscle can heal. Second, when appropriate, a therapist assists with passive exercises to regain range of motion. Third, the arm is gradually exercised actively, with a goal of regaining and enhancing strength. The empty can and full can exercises are amongst the most effective at isolating and strengthening the supraspinatus.
Following arthroscopic rotator-cuff repair surgery, individuals need rehabilitation and physical therapy. Exercise decreases shoulder pain, strengthens the joint, and improves range of motion. Therapists, in conjunction with the surgeon, design exercise regimens specific to the individual and their injury.
Traditionally, after injury the shoulder is immobilized for six weeks before rehabilitation. However, the appropriate timing and intensity of therapy are subject to debate. Most surgeons advocate using the sling for at least six weeks, though others advocate early, aggressive rehabilitation. The latter group favors the use of passive motion, which allows an individual to move the shoulder without physical effort. Alternatively, some authorities argue that therapy should be started later and carried out more cautiously. Theoretically, that gives tissues time to heal; though there is conflicting data regarding the benefits of early immobilization. A study of rats suggested that it improved the strength of surgical repairs, while research on rabbits produced contrary evidence. Individuals with a history of rotator cuff injury, particularly those recovering from tears, are prone to re-injury. Rehabbing too soon or too strenuously might increase the risk of retear or failure to heal. However, no research has proven a link between early therapy and the incidence of re-tears. In some studies, those who received earlier and more aggressive therapy reported reduced shoulder pain, less stiffness and better range of motion. Other research has shown that accelerated rehab results in better shoulder function.
There is consensus amongst orthopedic surgeons and physical therapists regarding rotator cuff repair rehabilitation protocols. The timing and duration of treatments and exercises are based on biologic and biomedical factors involving the rotator cuff. For approximately two to three weeks following surgery, an individual experiences shoulder pain and swelling; no major therapeutic measures are instituted in this window other than oral pain medicine and ice. Those at risk of failure should usually be more conservative with rehabilitations.
That is followed by the "proliferative" and "maturation and remodeling" phases of healing, which ensues for the following six to ten weeks. The effect of active or passive motion during any of the phases is unclear, due to conflicting information and a shortage of clinical evidence. Gentle physical therapy guided motion is instituted at this phase, only to prevent stiffness of the shoulder; the rotator cuff remains fragile. At three months after surgery, physical therapy intervention changes substantially to focus on scapular mobilization and stretching of the glenohumeral joint. Once full passive motion is regained (at usually about four to four and a half months after surgery) strengthening exercises are the focus. The strengthening focuses on the rotator cuff and the upper back/scapular stabilizers. Typically at about six months after surgery, most have made a majority of their expected gains.
The objective in repairing a rotator cuff is to enable an individual to regain full function. Surgeons and therapists analyze outcomes in several ways. Based on examinations, they compile scores on tests; some examples are those created by the University of California at Los Angeles and the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons. Other outcome measures include the Constant score; the Simple Shoulder Test; and the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand score. The tests assess range of motion and the degree of shoulder function.
Due to the conflicting information about the relative benefits of rehab conducted early or later, an individualized approach is necessary. The timing and nature of therapeutic activities are adjusted according to age and tissue integrity of the repair. Management is more complex in those who have had multiple tears.
Prognosis
While people with rotator cuff tears may not have any noticeable symptoms, studies have shown that, those with age related tears, over time 40% will have enlargement of the tear over a five-year period. Of those whose tears enlarge, 20% have no symptoms while 80% eventually develop symptoms.
Most usually regain function and experience less pain following surgery. For some, however, the joint continues to hurt. Weakness and a limited range of motion also may persist. Those who report such symptoms frequently are diagnosed with failed rotator cuff syndrome. There is no irrefutable evidence that rotator cuff surgery benefits more than non-surgical management and a percentage of individuals never regain full range of motion after surgery.
Arthroscopic procedures produce "satisfactory results" more than 90 percent of the time. However, 6-8 percent of patients have "incompetent" rotator cuffs because their repaired tendons either fail to heal or develop additional tears. In some cases, persistent rotator cuff type pain after surgery can be due to disease elsewhere. For example, cervical spine disease and can involve neck pain radiating into the shoulder. Suprascapular neuropathy, shoulder impingement, superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tears and arthritis can all mimic rotator cuff disease and cause persistent pain that does not respond to rotator cuff surgery.
One possible long-term consequence result of a rotator cuff tear is called proximal humeral head migration, this is where the "ball" of the shoulder joint rests higher in the shoulder joint "socket" disrupting normal shoulder mechanics. Only tear size is an independent predictor of humeral migration. Tears extending into the infraspinatus tendon are associated with greater humeral migration than is seen with isolated supraspinatus tears.
Epidemiology

Rotator cuff tears are among the most common conditions affecting the shoulder.
A rotator cuff tear can be caused by the weakening of the rotator cuff tendons. This weakening can be caused by age or how often the rotator cuff is used. Adults over the age of 60 are more susceptible to a rotator cuff tear, with the overall frequency of tears increasing with age. By the age of 50 10% of people with normal shoulders have a rotator cuff tear.
In an autopsy study of rotator cuff tears, the incidence of partial tears was 28%, and of complete rupture 30%. Frequently, tears occurred on both sides and occurred more often with females and with increasing age. Other cadaver studies have noted intratendinous tears to be more frequent (7.2%) than bursal-sided (2.4%) or articular-sided tears (3.6%). However, clinically, articular-sided tears are found to be 2 to 3 times more common than bursal-sided tears and among a population of young athletes, articular-sided tears constituted 91% of all partial-thickness tears. Rotator cuff tears may be more common in men between the ages of 50–60, though between 70 and 80 there is minimal difference across genders.
In terms of the size of tears, a study compared the ages of patient to the size of tears. It was emphasized the older you are, the more massive of a tear you will have. It was found that mean age increased with larger tear sizes (small tears 59 years, medium tears 62 years, large tears 64 years, and massive tears 66 years).
References
- ^ "Rotator Cuff Injury/Subacromial Bursitis". Merck Manuals Professional Edition. Retrieved 5 November 2018.
- ^ Athwal GS, Armstrong AD (March 2017). Fischer SJ, Wiater JM (eds.). "Rotator Cuff Tears". OrthoInfo – AAOS. Retrieved 5 November 2018.
- Ferri FF (2016). BOPOD – Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2017: 5 Books in 1. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1118e2. ISBN 9780323448383.
- Bruni, D. F.; Pierson, S. R.; Sarwar, F.; Ring, D.; Ramtin, S. (2023). "Are the Pathologic Features of Enthesopathy, Tendinopathy, and Labral and Articular Disc Disease Related to Mucoid Degeneration? A Systematic Review". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 481 (4): 641–650. doi:10.1097/CORR.0000000000002499. PMC 10013668. PMID 36563131.
- Teunis, T.; Lubberts, B.; Reilly, B. T.; Ring, D. (2014). "A systematic review and pooled analysis of the prevalence of rotator cuff disease with increasing age". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 23 (12): 1913–1921. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2014.08.001. PMID 25441568.
- Aagaard, K. E.; Abu-Zidan, F.; Lunsjo, K. (2015). "High incidence of acute full-thickness rotator cuff tears". Acta Orthopaedica. 86 (5): 558–562. doi:10.3109/17453674.2015.1022433. PMC 4564777. PMID 25708526.
- Crijns, T. J.; Ring, D.; Valencia, V. (2019). "Factors Associated with the Cost of Care for the Most Common Atraumatic Painful Upper Extremity Conditions". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 44 (11): 989.e1–989.e18. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2019.01.001. PMID 30782436. S2CID 73509093.
- McFarland, Edward; Maffulli, Nicola; Del Buono, Angelo (2013). "Impingement is not impingement: the case for calling it "Rotator Cuff Disease"". Muscles, Ligaments and Tendons Journal. 3 (3): 196–200. doi:10.32098/mltj.03.2013.11. PMC 3838328. PMID 24367779.
- Craig R, Holt T, Rees JL (December 2017). "Acute rotator cuff tears". BMJ. 359: j5366. doi:10.1136/bmj.j5366. PMID 29229593. S2CID 3514476.
- ^ Karjalainen TV, Jain NB, Heikkinen J, Johnston RV, Page CM, Buchbinder R (December 2019). "Surgery for rotator cuff tears". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD013502. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013502. PMC 6900168. PMID 31813166.
- Teunis, T.; Lubberts, B.; Reilly, B.; Ring, D. (2014). "A systematic review and pooled analysis of the prevalence of rotator cuff disease with increasing age". The Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 23 (12): P1913-1921. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2014.08.001. PMID 25441568.
- Harris JD, Pedroza A, Jones GL (February 2012). "Predictors of pain and function in patients with symptomatic, atraumatic full-thickness rotator cuff tears: a time-zero analysis of a prospective patient cohort enrolled in a structured physical therapy program". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 40 (2): 359–66. doi:10.1177/0363546511426003. PMC 3632074. PMID 22095706.
- Factor D, Dale B (April 2014). "Current concepts of rotator cuff tendinopathy". International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy. 9 (2): 274–88. PMC 4004132. PMID 24790788.
- Dunn, W. R.; Kuhn, J. E.; Sanders, R.; An, Q.; Baumgarten, K. M.; Bishop, J. Y.; Brophy, R. H.; Carey, J. L.; Holloway, G. B.; Jones, G. L.; Ma, C. B.; Marx, R. G.; McCarty, E. C.; Poddar, S. K.; Smith, M. V.; Spencer, E. E.; Vidal, A. F.; Wolf, B. R.; Wright, R. W. (2014). "Symptoms of pain do not correlate with rotator cuff tear severity: A cross-sectional study of 393 patients with a symptomatic atraumatic full-thickness rotator cuff tear". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 96 (10): 793–800. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.01304. PMC 4018774. PMID 24875019.
- ^ Williams GR, Rockwood CA, Bigliani LU, Iannotti JP, Stanwood W (December 2004). "Rotator cuff tears: why do we repair them?". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 86 (12): 2764–76. doi:10.2106/00004623-200412000-00027. PMID 15590865.
- Teunis T, Lubberts B, Reilly BT, Ring D (December 2014). "A systematic review and pooled analysis of the prevalence of rotator cuff disease with increasing age". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 23 (12): 1913–1921. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2014.08.001. PMID 25441568.
- Mohamadi A, Chan JJ, Claessen FM, Ring D, Chen NC (January 2017). "Corticosteroid Injections Give Small and Transient Pain Relief in Rotator Cuff Tendinosis: A Meta-analysis". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 475 (1): 232–243. doi:10.1007/s11999-016-5002-1. PMC 5174041. PMID 27469590.
- Armstrong AD, Wiater JM, Athwal GS. Fischer SJ (ed.). "Your Orthopaedic Connection: Rotator Cuff Tears and Treatment Options".
- ^ Nho SJ, Yadav H, Shindle MK, Macgillivray JD (May 2008). "Rotator cuff degeneration: etiology and pathogenesis". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 36 (5): 987–93. doi:10.1177/0363546508317344. PMID 18413681. S2CID 379019.
- Silverstein B, Welp E, Nelson N, Kalat J (December 1998). "Claims incidence of work-related disorders of the upper extremities: Washington state, 1987 through 1995". American Journal of Public Health. 88 (12): 1827–33. doi:10.2105/ajph.88.12.1827. PMC 1509055. PMID 9842381.
- Karantanas AH (11 December 2015). "Imaging of Water Sports Injuries". Imaging in Sports-Specific Musculoskeletal Injuries. 2015: 414. ISBN 9783319143071.
- "Manual of Sports Medicine", p. 548.
- Joseph J. Estwanik, "Injuries to the Extremities, Trunk, and Head" in the Boxing and Medicine, Robert C. Cantu (ed.,) 1995, p. 83.
- Kijowski R, Tuite MJ (11 December 2015). "Imaging of Track and Field Injuries". Imaging in Sports-Specific Musculoskeletal Injuries. 2015: 635. ISBN 9783319143071.
- Ronald P. Pfeiffer, Brent C. Mangus, "Concepts of Athletic Training", 2008, p. 161.
- Dean BJ, Lostis E, Oakley T, Rombach I, Morrey ME, Carr AJ (February 2014). "The risks and benefits of glucocorticoid treatment for tendinopathy: a systematic review of the effects of local glucocorticoid on tendon". Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 43 (4): 570–6. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.08.006. PMID 24074644.
- ^ Via AG, De Cupis M, Spoliti M, Oliva F (April 2013). "Clinical and biological aspects of rotator cuff tears". Muscles, Ligaments and Tendons Journal. 3 (2): 70–9. doi:10.11138/mltj/2013.3.2.070. PMC 3711705. PMID 23888289.
- ^ Saladin, Kenneth S. "Anatomy & Physiology." McGraw Hill, n.d. Web. 4 October 2016.
- ^ Athwal GS, Armstrong AD (March 2017). Fischer SJ, Wiater JM (eds.). "Rotator Cuff Tears". American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
There is no evidence of better results from surgery performed near the time of injury versus later on. For this reason, many doctors first recommend nonsurgical management of rotator cuff tears.
- Smith B, Lee C, Solomon D, Whitson M, Chang S (2 May 2004). "Mechanisms-Rotator Cuff". Brown University, Division of Biology and Medicine. Archived from the original on 9 December 2015. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- Marreez YM, Forman MD, Brown SR (May 2013). "Physical examination of the shoulder joint-Part I: Supraspinatus rotator cuff muscle clinical testing". Osteopathic Family Physician. 5 (3): 128–134. doi:10.1016/j.osfp.2013.01.005.
- Neer CS, Craig EV, Fukuda H (December 1983). "Cuff-tear arthropathy". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 65 (9): 1232–44. doi:10.2106/00004623-198365090-00003. PMID 6654936. S2CID 10289958.
- ^ Wolf BR, Dunn WR, Wright RW (June 2007). "Indications for repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 35 (6): 1007–16. doi:10.1177/0363546506295079. PMID 17337723. S2CID 21031012.
- Arend CF. Ultrasound of the Shoulder. Master Medical Books, 2013. Free chapter on ultrasound evaluation of rotator cuff disorders available at ShoulderUS.com
- Cassoobhoy A (11 August 2020). "Rotator Cuff Tears and Injuries". Webmd.com. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- ^ Shiel Jr WC (1 March 2021). Cunha JP (ed.). "Rotator Cuff Disease Symptoms, Causes, Treatment – What are symptoms of rotator cuff disease?". MedicineNet. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- ^ Gückel C, Nidecker A (November 1997). "Diagnosis of tears in rotator-cuff-injuries". European Journal of Radiology. 25 (3): 168–76. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(97)01171-6. PMID 9430826.
- Sox HC (1988). Medical decision making. Boston: Butterworths. ISBN 978-0-409-90091-0.
- Bernstein J (September 1997). "Decision analysis". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 79 (9): 1404–14. doi:10.2106/00004623-199709000-00018. PMID 9314406.
- ^ Wedro B (4 August 2020). Stöppler MS (ed.). "Rotator Cuff Injury: Click for Surgery Info and Healing Time". Emedicinehealth.com. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- McFarland EG, Selhi HS, Keyurapan E (February 2006). "Clinical evaluation of impingement: what to do and what works". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 88 (2): 432–41. doi:10.2106/00004623-200602000-00026. PMID 16475277.
- ^ Park HB, Yokota A, Gill HS, El Rassi G, McFarland EG (July 2005). "Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for the different degrees of subacromial impingement syndrome". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 87 (7): 1446–55. doi:10.2106/JBJS.D.02335. PMID 15995110. S2CID 4823685.
- ^ Sgroi M, Loitsch T, Reichel H, Kappe T (May 2019). "Diagnostic Value of Clinical Tests for Infraspinatus Tendon Tears". Arthroscopy. 35 (5): 1339–1347. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2018.12.003. PMID 30770251. S2CID 73478051.
- Jain, N. B.; Wilcox, R.; Katz, J. N.; Higgins, L. D. (2013). "Clinical Examination of the Rotator Cuff". PM & R. 5 (1): 45–56. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2012.08.019. PMC 3826176. PMID 23332909.
- Creech, J. A.; Silver, S. (2023). "Shoulder Impingement Syndrome". StatPearls. StatPearls. PMID 32119405.
- Jacobson JA (September 2009). "Musculoskeletal ultrasound: focused impact on MRI". AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 193 (3): 619–27. doi:10.2214/AJR.09.2841. PMID 19696273. S2CID 23394700.
- Lenza M, Buchbinder R, Takwoingi Y, Johnston RV, Hanchard NC, Faloppa F (September 2013). "Magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance arthrography and ultrasonography for assessing rotator cuff tears in people with shoulder pain for whom surgery is being considered". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014 (9): CD009020. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009020.pub2. PMC 6464715. PMID 24065456.
- ^ Stetson WB, Phillips T, Deutsch A (2005). "The use of magnetic resonance arthrography to detect partial-thickness rotator cuff tears". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 87 (suppl 2): 81–8. doi:10.2106/JBJS.E.00509. PMID 16326727.
- Teefey SA, Rubin DA, Middleton WD, Hildebolt CF, Leibold RA, Yamaguchi K (April 2004). "Detection and quantification of rotator cuff tears. Comparison of ultrasonographic, magnetic resonance imaging, and arthroscopic findings in seventy-one consecutive cases". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 86 (4): 708–16. doi:10.2106/00004623-200404000-00007. PMID 15069134.
- ^ Moosikasuwan JB, Miller TT, Burke BJ (2005). "Rotator cuff tears: clinical, radiographic, and US findings". Radiographics. 25 (6): 1591–607. doi:10.1148/rg.256045203. PMID 16284137. S2CID 23976563.
- ^ Keener JD, Wei AS, Kim HM, Steger-May K, Yamaguchi K (June 2009). "Proximal humeral migration in shoulders with symptomatic and asymptomatic rotator cuff tears". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 91 (6): 1405–13. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00854. PMC 2686133. PMID 19487518.
- Kim KC, Shin HD, Kim BK, Cha SM, Park JY (June 2012). "Changes in tendon length with increasing rotator cuff tear size". Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 20 (6): 1022–6. doi:10.1007/s00167-011-1664-0. PMID 21927954. S2CID 23618302.
- Howe C, Huber P, Wolf FM, Matsen F (February 2009). "Differential suture loading in an experimental rotator cuff repair". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 37 (2): 324–9. doi:10.1177/0363546508324308. PMID 18843038. S2CID 25742084.
- Zumstein MA, Frey E, von Rechenberg B, Frigg R, Gerber C, Meyer DC (May 2012). "Device for lengthening of a musculotendinous unit by direct continuous traction in the sheep". BMC Veterinary Research. 8: 50. doi:10.1186/1746-6148-8-50. PMC 3462135. PMID 22551079.
- Andarawis-Puri N, Ricchetti ET, Soslowsky LJ (September 2009). "Interaction between the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons: effect of anterior supraspinatus tendon full-thickness tears on infraspinatus tendon strain". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 37 (9): 1831–9. doi:10.1177/0363546509334222. PMC 2746054. PMID 19483078.
- Tashjian RZ (October 2012). "Epidemiology, natural history, and indications for treatment of rotator cuff tears". Clinics in Sports Medicine. 31 (4): 589–604. doi:10.1016/j.csm.2012.07.001. PMID 23040548.
- "Rotator Cuff Tears - OrthoInfo - AAOS".
- ^ Ryösä A, Laimi K, Äärimaa V, Lehtimäki K, Kukkonen J, Saltychev M (July 2017). "Surgery or conservative treatment for rotator cuff tear: a meta-analysis". Disability and Rehabilitation. 39 (14): 1357–1363. doi:10.1080/09638288.2016.1198431. PMID 27385156. S2CID 4361346.
- ^ Seida JC, LeBlanc C, Schouten JR, Mousavi SS, Hartling L, Vandermeer B, et al. (August 2010). "Systematic review: nonoperative and operative treatments for rotator cuff tears". Annals of Internal Medicine. 153 (4): 246–55. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-153-4-201008170-00263. PMID 20621893.
- Seida JC, Schouten JR, Mousavi SS, Tjosvold L, Vandermeer B, Milne A, Bond K, Hartling L, LeBlanc C, Sheps DM (July 2010). "Comparative Effectiveness of Nonoperative and Operative Treatments for Rotator Cuff Tears". Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. Vol. 22. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US). PMID 21028756. 10-EHC050-EF.
- ^ Mantone JK, Burkhead WZ, Noonan J (April 2000). "Nonoperative treatment of rotator cuff tears". The Orthopedic Clinics of North America. 31 (2): 295–311. doi:10.1016/s0030-5898(05)70149-8. PMID 10736398.
- Cumpston M, Johnston RV, Wengier L, Buchbinder R (July 2009). "Topical glyceryl trinitrate for rotator cuff disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD006355. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006355.pub2. PMID 19588386.
- Surace SJ, Deitch J, Johnston RV, Buchbinder R (March 2020). "Shock wave therapy for rotator cuff disease with or without calcification". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3 (3): CD008962. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd008962.pub2. PMC 7059880. PMID 32128761.
- Longo, Umile Giuseppe; Risi Ambrogioni, Laura; Berton, Alessandra; Candela, Vincenzo; Carnevale, Arianna; Schena, Emiliano; Gugliemelli, Eugenio; Denaro, Vincenzo (May 2020). "Physical therapy and precision rehabilitation in shoulder rotator cuff disease". International Orthopaedics. 44 (5): 893–903. doi:10.1007/s00264-020-04511-2. ISSN 1432-5195. PMID 32157371. S2CID 212642842.
- Gianola S, Iannicelli V, Fascio E, Andreano A, Li LC, Valsecchi MG, et al. (August 2021). "Kinesio taping for rotator cuff disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (8): CD012720. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd012720.pub2. PMC 8406708. PMID 34365646.
- Wirth MA, Basamania C, Rockwood CA (January 1997). "Nonoperative management of full-thickness tears of the rotator cuff". The Orthopedic Clinics of North America. 28 (1): 59–67. doi:10.1016/s0030-5898(05)70264-9. PMID 9024431.
- Williams G, Kraeutler MJ, Zmistowski B, Fenlin JM (September 2014). "No difference in postoperative pain after arthroscopic versus open rotator cuff repair". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 472 (9): 2759–65. doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3715-6. PMC 4117892. PMID 24912870.
- Vandvik PO, Lähdeoja T, Ardern C, Buchbinder R, Moro J, Brox JI, et al. (February 2019). "Subacromial decompression surgery for adults with shoulder pain: a clinical practice guideline". BMJ. 364: l294. doi:10.1136/bmj.l294. hdl:10138/313758. PMID 30728120. S2CID 73425732.
- Baydar M, Akalin E, El O, Gulbahar S, Bircan C, Akgul O, et al. (April 2009). "The efficacy of conservative treatment in patients with full-thickness rotator cuff tears". Rheumatology International. 29 (6): 623–8. doi:10.1007/s00296-008-0733-2. PMID 18850322. S2CID 7087636.
- "Rotator cuff injury Definition – Diseases and Conditions". Mayo Clinic. 19 February 2014. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- Norberg FB, Field LD, Savoie FH (January 2000). "Repair of the rotator cuff. Mini-open and arthroscopic repairs". Clinics in Sports Medicine. 19 (1): 77–99. doi:10.1016/s0278-5919(05)70297-0. PMID 10652666.
- ^ Lyons PM, Orwin JF (April 1998). "Rotator cuff tendinopathy and subacromial impingement syndrome". Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 30 (4 Suppl): S12-7. doi:10.1097/00005768-199804001-00003. PMID 9565951.
- Karjalainen TV, Jain NB, Page CM, Lähdeoja TA, Johnston RV, Salamh P, et al. (January 2019). "Subacromial decompression surgery for rotator cuff disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD005619. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd005619.pub3. PMC 6357907. PMID 30707445.
- "Rotator cuff repair". MedlinePlus. Retrieved 29 September 2009.
- Jordan RW, Bentick K, Saithna A (October 2018). "Transtendinous repair of partial articular sided supraspinatus tears is associated with higher rates of stiffness and significantly inferior early functional scores than tear completion and repair: A systematic review". Orthopaedics & Traumatology, Surgery & Research. 104 (6): 829–837. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2018.06.007. PMID 30036723.
- Al Mana L, Rajaratnam K (November 2020). "Cochrane in CORR®: Shoulder Replacement Surgery For Osteoarthritis And Rotator Cuff Tear Arthropathy". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 478 (11): 2431–2433. doi:10.1097/CORR.0000000000001523. PMC 7571914. PMID 33055541.
- Hogan MV, Bagayoko N, James R, Starnes T, Katz A, Chhabra AB (March 2011). "Tissue engineering solutions for tendon repair". The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 19 (3): 134–42. doi:10.5435/00124635-201103000-00002. PMID 21368094. S2CID 23149344.
- Schär MO, Rodeo SA, Zumstein MA (October 2014). "Biologics in rotator cuff surgery". Shoulder & Elbow. 6 (4): 239–44. doi:10.1177/1758573214536536. PMC 4935033. PMID 27582941.
- Saltzman BM, Jain A, Campbell KA, Mascarenhas R, Romeo AA, Verma NN, Cole BJ (May 2016). "Does the Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma at the Time of Surgery Improve Clinical Outcomes in Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair When Compared With Control Cohorts? A Systematic Review of Meta-analyses". Arthroscopy. 32 (5): 906–18. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2015.10.007. PMID 26725454.
- Cai YZ, Zhang C, Lin XJ (December 2015). "Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in arthroscopic repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears: a meta-analysis". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 24 (12): 1852–9. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2015.07.035. PMID 26456434.
- Moraes VY, Lenza M, Tamaoki MJ, Faloppa F, Belloti JC (April 2014). "Platelet-rich therapies for musculoskeletal soft tissue injuries". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014 (4): CD010071. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010071.pub3. PMC 6464921. PMID 24782334.
- Pas HI, Moen MH, Haisma HJ, Winters M (July 2017). "No evidence for the use of stem cell therapy for tendon disorders: a systematic review". British Journal of Sports Medicine. 51 (13): 996–1002. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2016-096794. PMID 28077355.
- McCormack RA, Shreve M, Strauss EJ (2014). "Biologic augmentation in rotator cuff repair--should we do it, who should get it, and has it worked?". Bulletin of the Hospital for Joint Disease. 72 (1): 89–96. PMID 25150331.
- "Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options". orthoinfo.aaos.org. 2012. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- Takeda Y, Kashiwaguchi S, Endo K, Matsuura T, Sasa T (2002). "The most effective exercise for strengthening the supraspinatus muscle: evaluation by magnetic resonance imaging". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 30 (3): 374–81. doi:10.1177/03635465020300031201. PMID 12016078. S2CID 28673200.
- ^ Strauss EJ, McCormack RA, Onyekwelu I, Rokito AS (May 2012). "Management of failed arthroscopic rotator cuff repair". The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 20 (5): 301–9. doi:10.5435/jaaos-20-05-301. PMID 22553102. S2CID 2650097.
- Tempelhof S, Rupp S, Seil R (1999). "Age-related prevalence of rotator cuff tears in asymptomatic shoulders". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 8 (4): 296–9. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(99)90148-9. PMID 10471998.
- Chung SW, Huong CB, Kim SH, Oh JH (February 2013). "Shoulder stiffness after rotator cuff repair: risk factors and influence on outcome". Arthroscopy. 29 (2): 290–300. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2012.08.023. PMID 23290184.
- "Superior and Anterior-Superior Migration of the Shoulder". 21 March 2023.
- Siow, M. Y.; Mitchell, B. C.; Hachadorian, M.; Wang, W.; Bastrom, T.; Kent, W. T.; Huang, B. K.; Edmonds, E. W. (2021). "Association Between Rotator Cuff Tears and Superior Migration of the Humeral Head: An MRI-Based Anatomic Study". Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine. 9 (6). doi:10.1177/23259671211009846. PMC 8202287. PMID 34179206.
- Keener, J. D.; Wei, A. S.; Kim, H. M.; Steger-May, K.; Yamaguchi, K. (2009). "Proximal Humeral Migration in Shoulders with Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Rotator Cuff Tears". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 91 (6): 1405–1413. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00854. PMC 2686133. PMID 19487518.
- ^ Yamamoto A, Takagishi K, Osawa T, Yanagawa T, Nakajima D, Shitara H, Kobayashi T (January 2010). "Prevalence and risk factors of a rotator cuff tear in the general population". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 19 (1): 116–20. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2009.04.006. PMID 19540777.
- Holland P. "Rotator Cuff Pain".
- Jerosch J, Müller T, Castro WH (1991). "The incidence of rotator cuff rupture. An anatomic study". Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. 57 (2): 124–9. PMID 1872155.
- ^ Matava MJ, Purcell DB, Rudzki JR (September 2005). "Partial-thickness rotator cuff tears". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 33 (9): 1405–17. doi:10.1177/0363546505280213. PMID 16127127. S2CID 29959313.
- Minagawa H, Yamamoto N, Abe H, Fukuda M, Seki N, Kikuchi K, et al. (2013). "Prevalence of symptomatic and asymptomatic rotator cuff tears in the general population: From mass-screening in one village". Journal of Orthopaedics. 10 (1): 8–12. doi:10.1016/j.jor.2013.01.008. PMC 3768248. PMID 24403741.
- Rashid, Mustafa S.; Cooper, Cushla; Cook, Jonathan; Cooper, David; Dakin, Stephanie G.; Snelling, Sarah; Carr, Andrew J. (December 2017). "Increasing age and tear size reduce rotator cuff repair healing rate at 1 year". Acta Orthopaedica. 88 (6): 606–611. doi:10.1080/17453674.2017.1370844. ISSN 1745-3682. PMC 5694804. PMID 28880113.
- This article contains text from the public domain document "Questions and Answers about Shoulder Problems" (PDF). National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), National Institutes of Health Public Health Service. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. March 2006. NIH Publication No. 01-4865. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 May 2007.
External links
- Rotator Cuff Tears. Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopedics. A description of rotator cuff tears from Wheeless'
- Physiotherpy program for rortator cuff tears
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Soft tissue disorders | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capsular joint |
| ||||||||||
| Noncapsular joint |
| ||||||||||
| Nonjoint |
| ||||||||||
| Dislocations/subluxations, sprains and strains | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joints and ligaments |
| ||||||||||||
| Muscles and tendons |
| ||||||||||||
Categories: