| Articular tubercle | |
|---|---|
 Left temporal bone seen from outside (articular tubercle is top label at left side) Left temporal bone seen from outside (articular tubercle is top label at left side) | |
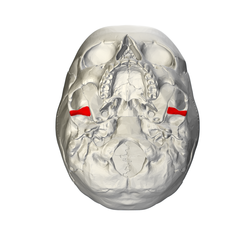 Base of skull seen from below Base of skull seen from below | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tuberculum articulare ossis temporalis |
| TA98 | A02.1.06.073 |
| TA2 | 714 |
| FMA | 55416 |
| Anatomical terms of bone[edit on Wikidata] | |
The articular tubercle (eminentia articularis) is a bony eminence on the temporal bone in the skull. It is a rounded eminence of the anterior root of the posterior end of the outer surface of the squama temporalis. This tubercle forms the front boundary of the mandibular fossa, and in the fresh state is covered with cartilage.
The mandibular condyle normally moves over the articular tubercle during physiologic maximal opening of the jaw. The articular tubercle is the site of attachment of the lateral ligament of the temporomandibular joint.
References
- Silveira, Olívia dos Santos; Silva, Fernanda Cristina Santos; Almeida, Carlos Eduardo Neves de; Tuji, Fabrício Mesquita; Seraidarian, Paulo Isaias; Manzi, Flávio Ricardo (2014). "Utilização da tomografia computadorizada para o diagnóstico da articulação temporomandibular". Revista CEFAC. 16 (6): 2053–2059. doi:10.1590/1982-0216201418013. ISSN 1982-0216.
- articular tubercle: Earth's Lab- Retrieved 2018-08-30
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 139 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 139 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Image at wayne.edu
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.
| Neurocranium of the skull | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occipital |
| ||||||||||
| Parietal | |||||||||||
| Frontal |
| ||||||||||
| Temporal |
| ||||||||||
| Sphenoid |
| ||||||||||
| Ethmoid |
| ||||||||||
This human musculoskeletal system article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |