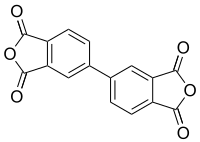
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name -1,1′,3,3′-tetrone | |
| Other names 3,3',4,4′-Biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride; 4,4′-Biphthalic dianhydride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | BPDA |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.585 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C16H6O6 |
| Molar mass | 294.218 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
BPDA or biphenyl-tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride is a monomer used in the production of some polyimides.
Applications
- Tape automated bonding (TAB), chip on film (COF), lead lock tape, high density flexible printed circuit (FPC), stiffener for FPC, office automation equipment, flexible solar cells, speaker diaphragms (for mobile phones, plasma televisions and car audio, etc.), heavy electric machinery, office automation equipment, thermal control film for satellites, printed circuit boards, metallic substrates, sheet heating elements, heat resistance wires.
Characteristics
- Physical, mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties under high-temperature conditions.
- High tensile strength and modulus, and also features outstanding long-term heat resistance.
Analytics
The chemical shifts in H and C NMR spectroscopy are given in the literature. The melting point is 299 - 301 °C.
See also
References
- ^ "An Efficient Synthetic Method for 3,3',4,4'-Biphenyltetracarboxylic Anhydride". Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society. 30 (9): 2161–2164. doi:10.5012/bkcs.2009.30.9.2161.