| Bofors 25 mm M/32 | |
|---|---|
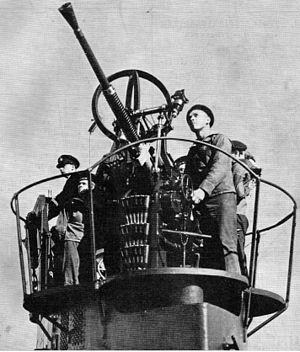 Bofors 25 mm automatic cannon M/32 on a Swedish submarine. Bofors 25 mm automatic cannon M/32 on a Swedish submarine. | |
| Type | Anti-aircraft gun |
| Place of origin | Sweden |
| Service history | |
| Used by | Sweden |
| Wars | World War II |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Bofors |
| Designed | 1932 |
| Manufacturer | Bofors |
| Produced | 1932–1945 |
| Variants | M/38 25×187 mm (early variants 25x205 mm) R |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | Single: 570 kg (1,260 lb) Twin: 1,100 kg (2,400 lb) |
| Barrel length | 1.6 m (5 ft 3 in) L/64 |
| Shell | Fixed QF 25×205 mm R |
| Shell weight | .25 kg (8.8 oz) |
| Caliber | 25 mm (0.98 in) |
| Action | Long-recoil |
| Recoil | Hydro-spring |
| Carriage | Single or twin fixed pedestal mounts |
| Elevation | −5° to 90° |
| Traverse | 360° |
| Rate of fire | 160 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 850 m/s (2,800 ft/s) |
| Effective firing range | 3.5 km (11,000 ft) AA ceiling |
| Maximum firing range | 5.6 km (18,000 ft) Horizontal range |
| Feed system | 6-round clips |
The Bofors 25 mm M/32 was a Swedish- designed and built light anti-aircraft gun that was used aboard ships of the Swedish Navy during the Second World War.
History
The development of Bofors first automatic weapons began in 1925 when the Navy requested the development of a 20 mm anti-aircraft gun. In 1928 the Navy requested a new 40 mm AA gun and a 25 mm AA gun which was produced in parallel and known as the M/32.
Design

The M/32 was designed with a barrel 64 calibers in length, fired a 25×205mmR cartridge, at 160–180 rpm and with a muzzle velocity of 850 m/s. Later a shorter version firing a 25×187mmR cartridge was produced in limited numbers. The M/32 looked similar to its larger 40 mm sibling and used the same long-recoil operating system and hydro-spring recoil mechanism. Its feed mechanism consisted of 6-round clips which were held in a vertical frame above the gun breech. Two clips were mounted side by side so that continuous fire could be maintained without the need to pause and change magazines. The clips were in two halves, which split and fell away as the cartridges entered the frames.
The gun was available in fixed single mount, fixed twin mount or on a mobile four-wheeled carriage with twin collapsible outriggers. In addition to fixed pedestal mounts, a retractable gun mount was designed for submarine use. Although available in land mounts it was primarily a naval weapon. At first the 40 mm gun was considered to be too heavy, so preference was given to single and twin mounts of the M/32 aboard ships of the Swedish navy.
Gallery
-
 A single M/32 mount aboard HSwMS Malmö
A single M/32 mount aboard HSwMS Malmö
-
 A single M/32 mount at Vaxholm Fortress, Sweden.
A single M/32 mount at Vaxholm Fortress, Sweden.
-
 A twin M/32 at Vaxholm Fortress, Sweden.
A twin M/32 at Vaxholm Fortress, Sweden.
-
 A twin M/32 at Vaxholm Fortress, Sweden.
A twin M/32 at Vaxholm Fortress, Sweden.
See also
- 25 mm Hotchkiss anti-aircraft gun
- 25 mm automatic air defense gun M1940 (72-K)
- Type 96 25 mm AT/AA Gun
Notes
- ^ "21-29 MM CALIBRE CARTRIDGES". www.quarryhs.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2019-04-07. Retrieved 2017-09-20.
- ^ "BOFORS AUTOMATIC CANNON". www.quarryhs.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2012-12-28. Retrieved 2017-09-20.
Bibliography
- Gander, T 1990, The 40mm Bofors Gun, 2nd edn, Patrick Stephens, Wellingborough, Eng.
External links
- http://www.quarryhs.co.uk/Bofors.htm Archived 2012-12-28 at the Wayback Machine
- http://www.quarryhs.co.uk/ammotable3.html Archived 2019-04-07 at the Wayback Machine
| Weapons and military equipment designed in Sweden 1914–1945 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firearms |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Artillery |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Armored fighting vehicles |
| ||||||||||||||||