| Statistical mechanics |
|---|
 |
| Particle statistics |
Thermodynamic ensembles
|
| Models |
| Potentials |
| Scientists |

In statistical mechanics, Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics describes the distribution of classical material particles over various energy states in thermal equilibrium. It is applicable when the temperature is high enough or the particle density is low enough to render quantum effects negligible.
The expected number of particles with energy for Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics is
where:
- is the energy of the i-th energy level,
- is the average number of particles in the set of states with energy ,
- is the degeneracy of energy level i, that is, the number of states with energy which may nevertheless be distinguished from each other by some other means,
- μ is the chemical potential,
- k is the Boltzmann constant,
- T is absolute temperature,
- N is the total number of particles:
- Z is the partition function:
- e is Euler's number
Equivalently, the number of particles is sometimes expressed as
where the index i now specifies a particular state rather than the set of all states with energy , and .
History
Further information: Maxwell–Boltzmann distributionMaxwell–Boltzmann statistics grew out of the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution, most likely as a distillation of the underlying technique. The distribution was first derived by Maxwell in 1860 on heuristic grounds. Boltzmann later, in the 1870s, carried out significant investigations into the physical origins of this distribution. The distribution can be derived on the ground that it maximizes the entropy of the system.
Applicability
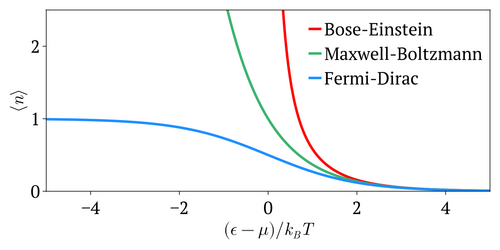
Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics is used to derive the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution of an ideal gas. However, it can also be used to extend that distribution to particles with a different energy–momentum relation, such as relativistic particles (resulting in Maxwell–Jüttner distribution), and to other than three-dimensional spaces.
Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics is often described as the statistics of "distinguishable" classical particles. In other words, the configuration of particle A in state 1 and particle B in state 2 is different from the case in which particle B is in state 1 and particle A is in state 2. This assumption leads to the proper (Boltzmann) statistics of particles in the energy states, but yields non-physical results for the entropy, as embodied in the Gibbs paradox.
At the same time, there are no real particles that have the characteristics required by Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics. Indeed, the Gibbs paradox is resolved if we treat all particles of a certain type (e.g., electrons, protons,photon etc.) as principally indistinguishable. Once this assumption is made, the particle statistics change. The change in entropy in the entropy of mixing example may be viewed as an example of a non-extensive entropy resulting from the distinguishability of the two types of particles being mixed.
Quantum particles are either bosons (following Bose–Einstein statistics) or fermions (subject to the Pauli exclusion principle, following instead Fermi–Dirac statistics). Both of these quantum statistics approach the Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics in the limit of high temperature and low particle density.
Derivations
Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics can be derived in various statistical mechanical thermodynamic ensembles:
- The grand canonical ensemble, exactly.
- The canonical ensemble, exactly.
- The microcanonical ensemble, but only in the thermodynamic limit.
In each case it is necessary to assume that the particles are non-interacting, and that multiple particles can occupy the same state and do so independently.
Derivation from microcanonical ensemble
| This section may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (December 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Suppose we have a container with a huge number of very small particles all with identical physical characteristics (such as mass, charge, etc.). Let's refer to this as the system. Assume that though the particles have identical properties, they are distinguishable. For example, we might identify each particle by continually observing their trajectories, or by placing a marking on each one, e.g., drawing a different number on each one as is done with lottery balls.
The particles are moving inside that container in all directions with great speed. Because the particles are speeding around, they possess some energy. The Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution is a mathematical function that describes about how many particles in the container have a certain energy. More precisely, the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution gives the non-normalized probability (this means that the probabilities do not add up to 1) that the state corresponding to a particular energy is occupied.
In general, there may be many particles with the same amount of energy . Let the number of particles with the same energy be , the number of particles possessing another energy be , and so forth for all the possible energies To describe this situation, we say that is the occupation number of the energy level If we know all the occupation numbers then we know the total energy of the system. However, because we can distinguish between which particles are occupying each energy level, the set of occupation numbers does not completely describe the state of the system. To completely describe the state of the system, or the microstate, we must specify exactly which particles are in each energy level. Thus when we count the number of possible states of the system, we must count each and every microstate, and not just the possible sets of occupation numbers.
To begin with, assume that there is only one state at each energy level (there is no degeneracy). What follows next is a bit of combinatorial thinking which has little to do in accurately describing the reservoir of particles. For instance, let's say there is a total of boxes labelled . With the concept of combination, we could calculate how many ways there are to arrange into the set of boxes, where the order of balls within each box isn’t tracked. First, we select balls from a total of balls to place into box , and continue to select for each box from the remaining balls, ensuring that every ball is placed in one of the boxes. The total number of ways that the balls can be arranged is
As every ball has been placed into a box, , and we simplify the expression as
This is just the multinomial coefficient, the number of ways of arranging N items into k boxes, the l-th box holding Nl items, ignoring the permutation of items in each box.
Now, consider the case where there is more than one way to put particles in the box (i.e. taking the degeneracy problem into consideration). If the -th box has a "degeneracy" of , that is, it has "sub-boxes" ( boxes with the same energy . These states/boxes with the same energy are called degenerate states.), such that any way of filling the -th box where the number in the sub-boxes is changed is a distinct way of filling the box, then the number of ways of filling the i-th box must be increased by the number of ways of distributing the objects in the "sub-boxes". The number of ways of placing distinguishable objects in "sub-boxes" is (the first object can go into any of the boxes, the second object can also go into any of the boxes, and so on). Thus the number of ways that a total of particles can be classified into energy levels according to their energies, while each level having distinct states such that the i-th level accommodates particles is:
This is the form for W first derived by Boltzmann. Boltzmann's fundamental equation relates the thermodynamic entropy S to the number of microstates W, where k is the Boltzmann constant. It was pointed out by Gibbs however, that the above expression for W does not yield an extensive entropy, and is therefore faulty. This problem is known as the Gibbs paradox. The problem is that the particles considered by the above equation are not indistinguishable. In other words, for two particles (A and B) in two energy sublevels the population represented by is considered distinct from the population while for indistinguishable particles, they are not. If we carry out the argument for indistinguishable particles, we are led to the Bose–Einstein expression for W:
The Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution follows from this Bose–Einstein distribution for temperatures well above absolute zero, implying that . The Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution also requires low density, implying that . Under these conditions, we may use Stirling's approximation for the factorial:
to write:
Using the fact that for we can again use Stirling's approximation to write:
This is essentially a division by N! of Boltzmann's original expression for W, and this correction is referred to as correct Boltzmann counting.
We wish to find the for which the function is maximized, while considering the constraint that there is a fixed number of particles and a fixed energy in the container. The maxima of and are achieved by the same values of and, since it is easier to accomplish mathematically, we will maximize the latter function instead. We constrain our solution using Lagrange multipliers forming the function:
Finally
In order to maximize the expression above we apply Fermat's theorem (stationary points), according to which local extrema, if exist, must be at critical points (partial derivatives vanish):
By solving the equations above () we arrive to an expression for :
Substituting this expression for into the equation for and assuming that yields:
or, rearranging:
Boltzmann realized that this is just an expression of the Euler-integrated fundamental equation of thermodynamics. Identifying E as the internal energy, the Euler-integrated fundamental equation states that :
where T is the temperature, P is pressure, V is volume, and μ is the chemical potential. Boltzmann's equation is the realization that the entropy is proportional to with the constant of proportionality being the Boltzmann constant. Using the ideal gas equation of state (PV = NkT), It follows immediately that and so that the populations may now be written:
Note that the above formula is sometimes written:
where is the absolute activity.
Alternatively, we may use the fact that
to obtain the population numbers as
where Z is the partition function defined by:
In an approximation where εi is considered to be a continuous variable, the Thomas–Fermi approximation yields a continuous degeneracy g proportional to so that:
which is just the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution for the energy.
Derivation from canonical ensemble
| This section may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (December 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In the above discussion, the Boltzmann distribution function was obtained via directly analysing the multiplicities of a system. Alternatively, one can make use of the canonical ensemble. In a canonical ensemble, a system is in thermal contact with a reservoir. While energy is free to flow between the system and the reservoir, the reservoir is thought to have infinitely large heat capacity as to maintain constant temperature, T, for the combined system.
In the present context, our system is assumed to have the energy levels with degeneracies . As before, we would like to calculate the probability that our system has energy .
If our system is in state , then there would be a corresponding number of microstates available to the reservoir. Call this number . By assumption, the combined system (of the system we are interested in and the reservoir) is isolated, so all microstates are equally probable. Therefore, for instance, if , we can conclude that our system is twice as likely to be in state than . In general, if is the probability that our system is in state ,
Since the entropy of the reservoir , the above becomes
Next we recall the thermodynamic identity (from the first law of thermodynamics):
In a canonical ensemble, there is no exchange of particles, so the term is zero. Similarly, This gives
where and denote the energies of the reservoir and the system at , respectively. For the second equality we have used the conservation of energy. Substituting into the first equation relating :
which implies, for any state s of the system
where Z is an appropriately chosen "constant" to make total probability 1. (Z is constant provided that the temperature T is invariant.)
where the index s runs through all microstates of the system. Z is sometimes called the Boltzmann sum over states (or "Zustandssumme" in the original German). If we index the summation via the energy eigenvalues instead of all possible states, degeneracy must be taken into account. The probability of our system having energy is simply the sum of the probabilities of all corresponding microstates:
where, with obvious modification,
this is the same result as before.
Comments on this derivation:
- Notice that in this formulation, the initial assumption "... suppose the system has total N particles..." is dispensed with. Indeed, the number of particles possessed by the system plays no role in arriving at the distribution. Rather, how many particles would occupy states with energy follows as an easy consequence.
- What has been presented above is essentially a derivation of the canonical partition function. As one can see by comparing the definitions, the Boltzmann sum over states is equal to the canonical partition function.
- Exactly the same approach can be used to derive Fermi–Dirac and Bose–Einstein statistics. However, there one would replace the canonical ensemble with the grand canonical ensemble, since there is exchange of particles between the system and the reservoir. Also, the system one considers in those cases is a single particle state, not a particle. (In the above discussion, we could have assumed our system to be a single atom.)
See also
Notes
- For example, two simple point particles may have the same energy, but different momentum vectors. They may be distinguished from each other on this basis, and the degeneracy will be the number of possible ways that they can be so distinguished.
References
- Tolman, R. C. (1938). The Principles of Statistical Mechanics. Dover Publications. ISBN 9780486638966.
Bibliography
- Carter, Ashley H., "Classical and Statistical Thermodynamics", Prentice–Hall, Inc., 2001, New Jersey.
- Raj Pathria, "Statistical Mechanics", Butterworth–Heinemann, 1996.
| Statistical mechanics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Theory | ||
| Statistical thermodynamics | ||
| Models | ||
| Mathematical approaches | ||
| Critical phenomena | ||
| Entropy | ||
| Applications | ||
 for Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics is
for Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics is

 is the average number of particles in the set of states with energy
is the average number of particles in the set of states with energy  is the
is the 


 .
.
 is shown versus energy
is shown versus energy  relative to the system chemical potential
relative to the system chemical potential  , where
, where  is the system temperature, and
is the system temperature, and  is the Boltzmann constant.
is the Boltzmann constant. . Let the number of particles with the same energy
. Let the number of particles with the same energy  be
be  , the number of particles possessing another energy
, the number of particles possessing another energy  be
be  , and so forth for all the possible energies
, and so forth for all the possible energies  To describe this situation, we say that
To describe this situation, we say that  is the occupation number of the energy level
is the occupation number of the energy level  If we know all the occupation numbers
If we know all the occupation numbers  then we know the total energy of the system. However, because we can distinguish between which particles are occupying each energy level, the set of occupation numbers
then we know the total energy of the system. However, because we can distinguish between which particles are occupying each energy level, the set of occupation numbers  does not completely describe the state of the system. To completely describe the state of the system, or the microstate, we must specify exactly which particles are in each energy level. Thus when we count the number of possible states of the system, we must count each and every microstate, and not just the possible sets of occupation numbers.
does not completely describe the state of the system. To completely describe the state of the system, or the microstate, we must specify exactly which particles are in each energy level. Thus when we count the number of possible states of the system, we must count each and every microstate, and not just the possible sets of occupation numbers.
 (there is no degeneracy). What follows next is a bit of combinatorial thinking which has little to do in accurately describing the reservoir of particles. For instance, let's say there is a total of
(there is no degeneracy). What follows next is a bit of combinatorial thinking which has little to do in accurately describing the reservoir of particles. For instance, let's say there is a total of  boxes labelled
boxes labelled  . With the concept of
. With the concept of  into the set of boxes, where the order of balls within each box isn’t tracked. First, we select
into the set of boxes, where the order of balls within each box isn’t tracked. First, we select  balls from a total of
balls from a total of  , and continue to select for each box from the remaining balls, ensuring that every ball is placed in one of the boxes. The total number of ways that the balls can be arranged is
, and continue to select for each box from the remaining balls, ensuring that every ball is placed in one of the boxes. The total number of ways that the balls can be arranged is

 , and we simplify the expression as
, and we simplify the expression as

 (the first object can go into any of the
(the first object can go into any of the  that a total of
that a total of 
 relates the thermodynamic
relates the thermodynamic 
 . The Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution also requires low density, implying that
. The Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution also requires low density, implying that  . Under these conditions, we may use
. Under these conditions, we may use 

 for
for 
 and a fixed energy
and a fixed energy  in the container. The maxima of
in the container. The maxima of  are achieved by the same values of
are achieved by the same values of 



 ) we arrive to an expression for
) we arrive to an expression for 
 and assuming that
and assuming that  yields:
yields:



 is the realization that the entropy is proportional to
is the realization that the entropy is proportional to  and
and  so that the populations may now be written:
so that the populations may now be written:


 is the absolute
is the absolute 


 so that:
so that:

 , then there would be a corresponding number of microstates available to the reservoir. Call this number
, then there would be a corresponding number of microstates available to the reservoir. Call this number  . By assumption, the combined system (of the system we are interested in and the reservoir) is isolated, so all microstates are equally probable. Therefore, for instance, if
. By assumption, the combined system (of the system we are interested in and the reservoir) is isolated, so all microstates are equally probable. Therefore, for instance, if  , we can conclude that our system is twice as likely to be in state
, we can conclude that our system is twice as likely to be in state  . In general, if
. In general, if  is the probability that our system is in state
is the probability that our system is in state  ,
,

 , the above becomes
, the above becomes


 term is zero. Similarly,
term is zero. Similarly,  This gives
This gives

 and
and  denote the energies of the reservoir and the system at
denote the energies of the reservoir and the system at  , respectively. For the second equality we have used the conservation of energy. Substituting into the first equation relating
, respectively. For the second equality we have used the conservation of energy. Substituting into the first equation relating  :
:




