| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Brush rabbit" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Brush rabbit | |
|---|---|

| |
| Brush rabbit (Finley National Wildlife Refuge) | |
| Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Lagomorpha |
| Family: | Leporidae |
| Genus: | Sylvilagus |
| Species: | S. bachmani |
| Binomial name | |
| Sylvilagus bachmani (Waterhouse, 1839) | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
| |
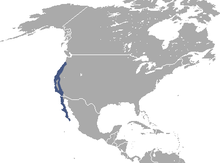
| Brush rabbit range | |
The brush rabbit (Sylvilagus bachmani), or western brush rabbit, or Californian brush rabbit, is a species of cottontail rabbit found in western coastal regions of North America, from the Columbia River in Oregon to the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula. Its range extends as far east as the eastern sides of the Sierra Nevada and Cascade mountain ranges.
Description and taxonomy

The brush rabbit is a small rabbit with short legs and a short tail. It is dark gray on the sides and back, and pale gray on the belly and the underside of the tail. The whiskers are mostly black, although some have white tips. Adult rabbits measure anywhere from 30.3 to 36.9 cm (11.9 to 14.5 in) in length, and range in weight from 511 to 917 g (1.127 to 2.022 lb).
Large numbers of geographically defined subspecies have been proposed, including in Oregon, ubericolor; in California, cinerascens, mariposae, riparius, tehamae and trowbridgii; and in Baja California, cerrosensis, exiguus, howelli, peninsularis and rosaphagus. Subspecies bachmani, macrorhinus and virgulti are less geographically restricted. Of the various proposed subspecies, only the following are currently recognized, the others are synonyms: S. b. ubericolor, S. b. cinerascens, S. b. bachmani, S. b. exiguus, S. b. howelli, S. b. cerrosensis.
It has been noted that numbers of the eastern cottontail were brought west to reproduce and provide a food source for the settlers. The interbreeding of the two species has occurred where the brush rabbit has in parts of Oregon developed the white cottontail although retaining its smaller size.
Habitat and ecology
Brush rabbits require dense bramble clumps or other thick, brushy habitat. These bramble clumps often have extensive networks of trails and runways. The species occasionally uses burrows made by other species, but does not dig its own. The home range is very small, less than 2,000 m (22,000 sq ft).
Brush rabbits most commonly live in chaparral vegetation, but are also found in oak and conifer habitats. In the San Francisco Bay Area, the brush rabbit was found to concentrate its activities at the edge of brush and exhibits much less use of grassy areas. It uses the interior brush of the wilderness, and this may be a better environment for it than the chaparral one. Studies done on the brush rabbit in Oregon also showed that it rarely left the brushy areas it inhabits. Brush may be used more in the drier seasons, while grasses are used in the wetter seasons in relation to growth of annual vegetation. Use of habitat also probably is related to the breeding season.
Distribution
The brush rabbit is confined to the Pacific Coast, from the Columbia River in the north to the tip of Baja, Mexico in the south. It does not occur east of the Sierra Nevada and Cascade Mountain ranges.
Behavior
Brush rabbits forage alone or in small groups. They can be seen sunning in the mid-morning, but are otherwise secretive and wary. They thump the ground with their back feet when startled.
The brush rabbit feeds mainly on grasses and forbs, especially green clover. It also eats berries and browses on shrubs.
A trapping study of the brush rabbit in the Berkeley Hills in Northern California indicated that males had larger home ranges than females at all times of the year, and especially in May when females were moving the least. The home ranges of the brush rabbit are estimated to average just under 4,000 square meters (1 acre) for males and just under 2,000 square meters (0.5 acres) for females. The shapes of these home ranges are usually circular, but depending on the vegetation, can differ in size and shape. Range use probably is not circular in shape or uniform, but rather consists of a series of runways that directly connects high-use areas within brush habitat. Intraspecific sociospatial behavior appears to be variable and may reflect local resource conditions. Several rabbits have been observed to feed in the same area simultaneously, but maintained interindividual distances of 0.3 to 7.3 meters (1 to 24 ft) before aggressive chases occurred. Females tended to not overlap, while males showed relatively extensive overlapping; this may indicate that females are territorial. Groups of brush rabbits may serve social purposes, such as predator detection, but this has not been proven.
Reproduction
The brush rabbit's breeding season varies from north to south. In Oregon, breeding begins in February and ends in August, while in California it begins in December and ends in May or June. Litter size also varies between regions. Studies have found the average litter size in Oregon to be 2.8, in northern and central California to be 3.5, and in west central California to be 4.0. The brush rabbit is one of the less fecund members of the genus, producing about 15 young in five to six litters per year. The gestation period of the brush rabbit is about 22 days, and kits are altricial. Male brush rabbits breed from around October to November through June to July. The brush rabbit's most reproductive activity occurs from January to April. In the areas of San Francisco, pregnant female brush rabbits can be found from the first week of December until the ends of June. Female brush rabbits have about four litters per year.
Predators and survival techniques
Its predators include cougar, coyote, fox, bobcat, weasel, and various raptors and snakes. Its survival strategies include remaining immobile when in brushy areas, and zig-zag running when found in open spaces. It also climbs onto low branches to escape from predators and other perceived threats.
Human interaction and conservation status
The brush rabbit is not hunted as are many other cottontail species, probably because of its small size. It is not a major cause of damage to crops or other human developments in its habitat.
While the overall population of brush rabbits is stable, one of its subspecies, the riparian brush rabbit (S. b. riparius), is listed as an endangered species by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Formerly numerous along the San Joaquin River and Stanislaus River, it is now reduced to a population of a few hundred in the Caswell Memorial State Park and is being reintroduced to the adjacent San Joaquin River National Wildlife Refuge in the San Joaquin Valley, California. This population has been negatively impacted by the destruction of the riparian habitat. Another subspecies, the San José brush rabbit, is considered critically endangered.
Myxomatosis
Brush rabbits are a natural carrier of the myxoma virus, a poxvirus in the genus Leporipoxvirus. This virus causes only a mild disease in brush rabbits, but causes a severe and usually fatal disease called myxomatosis in European (pet) rabbits. The disease is usually transmitted from one rabbit to another by biting insects.
Subspecies
Three geographic subspecies of the brush rabbit are acknowledged as follows.
Sylvilagus bachmani tehamae
This subspecies of Sylvilagus bachmani is geographically found from the Rogue River Valley, Jackson County, Oregon, through Northern California, along the inner coast ranges, to southern Lake County and along the Sierra Nevada to Placer County. It is also found in the Sacramento Valley.
The subspecies is medium in size, paler in color, has larger ears and shorter hind feet.
Sylvilagus bachmani macrorhinus
This subspecies of Sylvilagus bachmani is geographically found in west-central California—from San Francisco to the north end of Monterey Bay and inland from Solano County south to Santa Clara County.
It is smaller in size but has longer ears.
Sylvilagus bachmani riparius
This subspecies of Sylvilagus bachmani is geographically found on the west side of the San Joaquin River in northern Stanislaus and southern San Joaquin counties. This subspecies is pale and gray-sided.
Sylvilagus bachmani riparius is listed as an endangered species both by California and federally, primarily due to habitat destruction. In the San Joaquin Valley, over 93% of the habitat was destroyed for urban and agricultural use. A population of riparian brush rabbits has moved into restored habitat in the new Dos Rios State Park.
References
- ^ Hoffman, R.S.; Smith, A.T. (2005). "Order Lagomorpha". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 208. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- Kelly, P.A.; Lorenzo, C.; Alvarez-Castaneda, S.T. (2019). "Sylvilagus bachmani". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41302A45192710. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41302A45192710.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- Marshall, I. D.; Regnery, David C. (1960). "Myxomatosis in a Californian Brush Rabbit (Sylvilagus bachmani)". Nature. 188 (4744): 73–74. Bibcode:1960Natur.188...73M. doi:10.1038/188073b0. PMID 13767210. S2CID 4264949.
- ^ Kays, Roland (2009). Mammals of North America (2nd ed.). Princeton University Press. p. 40. ISBN 978-0691140926.
- ^ Chapman, Joseph (1990). Rabbits, hares, and pikas : status survey and conservation action plan. International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources. p. 99. ISBN 2-8317-0019-1.
- Mossman, Archie S. (1955). "Reproduction of the Brush Rabbit in California". The Journal of Wildlife Management. 19 (2): 177–184. doi:10.2307/3796850. ISSN 0022-541X. JSTOR 3796850.
- "Riparian brush rabbit (Sylvilagus bachmani riparius)". U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. Retrieved 12 August 2019.
- Sommer, Lauren (May 4, 2023). "The latest to be evacuated from California's floods? Bunnies". NPR News.
- "Sylvilagus bachmani riparius". NatureServe Explorer. Retrieved 12 August 2019.
- Meredith, Anna (2013). "Viral skin diseases of the rabbit". Veterinary Clinics of North America: Exotic Animal Practice. 16 (3): 705–714. doi:10.1016/j.cvex.2013.05.010. PMID 24018033.
- ^ Orr, R T; Orr, R. T. (1935). "Descriptions of three new races of brush rabbit from California". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 48: 27––30.
- Kelt, Douglas A.; Kelly, Patrick A.; Phillips, Scott E.; Williams, Daniel F. (2014-06-26). "Home range size and habitat selection of reintroduced Sylvilagus bachmani riparius". Journal of Mammalogy. 95 (3): 516–524. doi:10.1644/13-MAMM-A-187. ISSN 0022-2372. S2CID 73661738.
- Smith, H.R. (Spring 2024). "The Everything Park". Bay Nature. 24 (2): 28–33.
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Sylvilagus bachmani |
|
| Lepus bachmani | |