 Color printing typically uses ink of four colors: cyan, magenta, yellow, and black.
Color printing typically uses ink of four colors: cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. When subtractive CMY inks are combined at full strength, pairwise combinations are red, green, and blue. Combining all three gives an imperfect black color.
When subtractive CMY inks are combined at full strength, pairwise combinations are red, green, and blue. Combining all three gives an imperfect black color.

 What appears as cerulean ( ) in the top image is actually a blend of cyan, magenta, yellow and black, as magnification under a microscope demonstrates.
What appears as cerulean ( ) in the top image is actually a blend of cyan, magenta, yellow and black, as magnification under a microscope demonstrates.
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation CMYK refers to the four ink plates used: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (most often black).
The CMYK model works by partially or entirely masking colors on a lighter, usually white, background. The ink reduces the light that would otherwise be reflected. Such a model is called subtractive because inks subtract some colors from white light; in the CMY model, white light minus red leaves cyan, white light minus green leaves magenta, and white light minus blue leaves yellow.
In additive color models, such as RGB, white is the additive combination of all primary colored lights, and black is the absence of light. In the CMYK model, it is the opposite: white is the natural color of the paper or other background, and black results from a full combination of colored inks. To save cost on ink, and to produce deeper black tones, unsaturated and dark colors are produced by using black ink instead of or in addition to combinations of cyan, magenta, and yellow.
The CMYK printing process was invented in the 1890s, when newspapers began to publish color comic strips.
Halftoning

With CMYK printing, halftoning (also called screening) allows for less than full saturation of the primary colors; tiny dots of each primary color are printed in a pattern small enough that humans perceive a solid color. Magenta printed with a 20% halftone, for example, produces a pink color, because the eye perceives the tiny magenta dots on the large white paper as lighter and less saturated than the color of pure magenta ink. Halftoning allows for a continuous variability of each color, which enables continuous color mixing of the primaries. Without halftoning, each primary would be binary, i.e. on/off, which only allows for the reproduction of eight colors: white, the three primaries (cyan, magenta, yellow), the three secondaries (red, green, blue), and black.
Comparison to CMY


 The image above, (left) separated for printing with process cyan, magenta, and yellow (CMY) inks, and (right) separated for CMY and black (K)
The image above, (left) separated for printing with process cyan, magenta, and yellow (CMY) inks, and (right) separated for CMY and black (K)

The CMYK color model is based on the CMY color model, which omits the black ink. Four-color printing uses black ink in addition to subtractive primaries for several reasons:
- In traditional preparation of color separations, a red keyline on the black line art marked the outline of solid or tint color areas. In some cases a black keyline was used when it served as both a color indicator and an outline to be printed in black because usually the black plate contained the keyline. The K in CMYK represents the keyline, or black, plate, also sometimes called the key plate.
- Text is typically printed in black and includes fine detail (such as serifs). To avoid even slight blurring when reproducing text (or other finely detailed outlines) using three inks would require impractically accurate registration.
- A combination of 100% cyan, magenta, and yellow inks soaks the paper with ink, making it slower to dry, causing bleeding, or (especially on low-quality paper such as newsprint) weakening the paper so much that it tears.
- Although a combination of 100% cyan, magenta, and yellow inks would, in theory, completely absorb the entire visible spectrum of light and produce a perfect black, practical inks fall short of their ideal characteristics, and the result is a dark, muddy color that is not quite black. Black ink absorbs more light and yields much better blacks.
- Black ink is less expensive than the combination of colored inks that makes black.
A black made with just CMY inks is sometimes called a composite black.
When a very dark area is wanted, a colored or gray CMY "bedding" is applied first, then a full black layer is applied on top, making a rich, deep black; this is called rich black.
The amount of black to use to replace amounts of the other inks is variable, and the choice depends on the technology, paper and ink in use. Processes called under color removal, under color addition, and gray component replacement are used to decide on the final mix; different CMYK recipes will be used depending on the printing task.
Other printer color models
CMYK, as well as all other process color printing, is contrasted with spot color printing, in which specific colored inks are used to generate the colors seen. Some printing presses are capable of printing with both four-color process inks and additional spot color inks at the same time. High-quality printed materials, such as marketing brochures and books, often include photographs requiring process-color printing, other graphic effects requiring spot colors (such as metallic inks), and finishes such as varnish, which enhances the glossy appearance of the printed piece.
CMYK are the process printers which often have a relatively small color gamut. Processes such as Pantone's proprietary six-color (CMYKOG) Hexachrome considerably expand the gamut. Light, saturated colors often cannot be created with CMYK, and light colors in general may make visible the halftone pattern. Using a CcMmYK process, with the addition of light cyan and magenta inks to CMYK, can solve these problems, and such a process is used by many inkjet printers, including desktop models.
Comparison with RGB displays
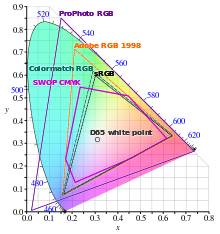
Comparisons between RGB displays and CMYK prints can be difficult, since the color reproduction technologies and properties are very different. A computer monitor mixes shades of red, green, and blue light to create color images. A CMYK printer instead uses light-absorbing cyan, magenta, and yellow inks, whose colors are mixed using dithering, halftoning, or some other optical technique.
Similar to electronic displays, the inks used in printing produce color gamuts that are only a subsets of the visible spectrum, and the two color modes have their own specific ranges, each being capable of producing colors the other is not. As a result of this, an image rendered on an electronic display and rendered in print can vary in appearance. When designing images to be printed, designers work in RGB color spaces (electronic displays) capable of rendering colors a CMYK process cannot, and it is often difficult to accurately visualize a printed result that must fit into a different color space that both lacks some colors an electronic display can produce and includes colors it cannot.
Spectrum of printed paper
To reproduce color, the CMYK color model codes for absorbing light rather than emitting it (as is assumed by RGB). The K component ideally absorbs all wavelengths and is therefore achromatic. The cyan, magenta, and yellow components are used for color reproduction and they may be viewed as the inverse of RGB: Cyan absorbs red, magenta absorbs green, and yellow absorbs blue (−R,−G,−B).
Conversion


Since RGB and CMYK spaces are both device-dependent spaces, there is no simple or general conversion formula that converts between them. Conversions are generally done through color management systems, using color profiles that describe the spaces being converted. An ICC profile defines the bidirectional conversion between a neutral "profile connection" color space (CIE XYZ or Lab) and a selected colorspace, in this case both RGB and CMYK. The precision of the conversion depends on the profile itself, the exact methodology, and because the gamuts do not generally match, the rendering intent and constraints such as ink limit.
ICC profiles, internally built out of lookup tables and other transformation functions, are capable of handling many effects of ink blending. One example is the dot gain, which show up as non-linear components in the color-to-density mapping. More complex interactions such as Neugebauer blending can be modelled in higher-dimension lookup tables.
The problem of computing a colorimetric estimate of the color that results from printing various combinations of ink has been addressed by many scientists. A general method that has emerged for the case of halftone printing is to treat each tiny overlap of color dots as one of 8 (combinations of CMY) or of 16 (combinations of CMYK) colors, which in this context are known as Neugebauer primaries. The resultant color would be an area-weighted colorimetric combination of these primary colors, except that the Yule–Nielsen effect of scattered light between and within the areas complicates the physics and the analysis; empirical formulas for such analysis have been developed, in terms of detailed dye combination absorption spectra and empirical parameters.
Standardization of printing practices allow for some profiles to be predefined. One of them is the US Specifications for Web Offset Publications, which has its ICC color profile built into some software including Microsoft Office (as Agfa RSWOP.icm).
See also
- CMY color model
- CcMmYK color model
- Cycolor
- RGB color model
- Gray component replacement
- Jacob Christoph Le Blon
- SWOP CMYK standard
- Color management
- Technicolor, the three-strip version of which is based on the CMYK model
References
- Kang, Henry R. (1999). Digital Color Halftoning. SPIE Press. p. 1. ISBN 0-8194-3318-7.
- Roger Pring (2000). WWW.Color. Watson–Guptill. p. 178. ISBN 0-8230-5857-3.
- Menegus, Bryan (May 20, 2016). "The Difference Between RGB and CMYK, Explained". Gizmodo. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- Sigel, Jay A. (2015). Forensic Chemistry: Fundamentals and Applications. John Wiley & Sons. p. 331. ISBN 978-1-118-89772-0.
- R. S. Hodges (2003). The Guild Handbook of Scientific Illustration. John Wiley and Sons. p. 242. ISBN 0-471-36011-2.
- Kipphan, Helmut, ed. (2001). Handbook of Print Media: Technologies and Production Methods. Springer. p. 87. ISBN 3-540-67326-1.
- Davies, Helen (August 3, 2020). "Top 8 Large Format Printing Tips To Achieve High-End Projects". Front Signs. Archived from the original on September 29, 2020. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- Zeng, Huanzhao (2003). Eschbach, Reiner; Marcu, Gabriel G (eds.). "3-D Color Separation Maximizing the Printer Gamut". Proceedings of SPIE. Color Imaging VIII: Processing, Hardcopy, and Applications. 5008: 260. Bibcode:2003SPIE.5008..260Z. doi:10.1117/12.472012. S2CID 20555157.
- Carla Rose (2003). Sams Teach Yourself Adobe Photoshop Elements 2 in 24 Hours. Sams Publishing. p. 108. ISBN 0-672-32430-X.
- "Overview of color in Illustrator". Adobe Inc. Archived from the original on February 7, 2023. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- Damien van Holten, Printinternational, "RGB Vs CMYK"
- "Subtractive Color Mixing". L. R. Ingersoll Physics Museum. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^ Gaurav Sharma (2003). Digital Color Imaging Handbook. CRC Press. p. 68. ISBN 0-8493-0900-X.
- "KB933845 How to obtain and install the Microsoft Standard CMYK Profile (RSWOP.icm) in Windows Vista". Beta Archive > Microsoft KB Archive. March 15, 2007. Retrieved 1 September 2023.
The RSWOP.icm cyan-magenta-yellow-black (CMYK) color profile targets the "Specifications for Web Offset Publications" (SWOP) printing standard. This color profile is installed when you install Microsoft Office. However, by default, this color profile is not installed in Windows Vista. Therefore, you may experience unexpected results when you use certain programs that manage color.
External links
- XCmyk – A Windows software with source code for converting CMYK to RGB.
- RGB to CMYK converter – Tool for RGB to CMYK color converter online.
- Color Space Fundamentals – animated illustration of RGB vs. CMYK
- ICC profile registry, which lists some standard CMYK profiles, their paper types, and color separation limits
| Color space | |
|---|---|
| CAM | |
| CIE | |
| RGB | |
| Y′UV | |
| Other | |
| Color systems and standards | |
| For the vision capacities of organisms or machines, see | |