


A candle is an ignitable wick embedded in wax, or another flammable solid substance such as tallow, that provides light, and in some cases, a fragrance. A candle can also provide heat or a method of keeping time. Candles have been used for over two millennia around the world, and were a significant form of indoor lighting until the invention of other types of light sources. Although electric light has largely made candle use nonessential for illumination, candles are still commonly used for functional, symbolic and aesthetic purposes and in specific cultural and religious settings.
Early candles may be made of beeswax, but these candles were expensive and their use was limited to the elite and the churches. Tallow was a cheaper but a less aesthetically pleasing alternative. A variety of different materials have been developed in the modern era for making candles, including paraffin wax, which together with efficient production techniques, made candles affordable for the masses. Various devices can be used to hold candles, such as candlesticks, or candelabras, chandeliers, lanterns and sconces. A person who makes candles is traditionally known as a chandler.
The combustion of the candle proceeds in self-sustaining manner. As the wick of candle is lit, the heat melts and ignites a small amount of solid fuel (the wax), which vaporizes and combines with oxygen in the air to form a flame. The flame then melts the top of the mass of solid fuel, which moves upward through the wick via capillary action to be continually burnt, thereby maintaining a constant flame. The candle shortens as the solid fuel is consumed, so does the wick. Wicks of pre-19th century candles required regular trimming with scissors or "snuffers" to promote steady burning and prevent smoking. In modern candles, the wick is constructed so that it curves over as it burns, and the end of the wick gets trimmed by itself through incineration by fire.
Etymology
The word candle comes from Middle English candel, from Old English and from Anglo-Norman candele, both from Latin candēla, from candēre 'to shine'.
History
Main article: History of candle making
Prior to the invention of candles, ancient people used open fire, torches, splinters of resinous wood, and lamps to provide artificial illumination at night. Primitive oil lamps in which a lit wick rested in a pool of oil or fat were used from the Paleolithic period, and pottery and stone lamps from the Neolithic period have been found. Because candle making requires a reliable supply of animal or vegetable fats, it is certain that candles could not have developed before the early Bronze Age; however, it is unclear when and where candles were first used. Objects that could be candlesticks have been found in Babylonian and middle Minoan cultures, as well in the tomb of Tutankhamun. The "candles" used in these early periods would not have resembled the current forms; more likely they were made of plant materials dipped in animal fat.
Early evidence of candle use may be found in Italy, where depiction of a candlestick exists in an Etruscan tomb at Orvieto, and the earliest excavated Etruscan candlestick dates from the 7th century BC. Candles may have evolved from taper with wick of oakum and other plant fibre soaked in fat, pitch or oil and burned in lamps or pots. Candles of antiquity were made from various forms of natural fat, tallow, and wax, and Romans made true dipped candles from tallow and beeswax. Beeswax candles were expensive and their use was limited to the wealthy, instead oil lamps were the more commonly used lighting devices in Roman times. Ancient Greece used torches and oil lamps, and likely adopted candle use in a later period from Rome. Early record in China suggests that candle was used in the Qin dynasty before 200 BC. These early Chinese candles may have been made from whale fat.

In Christianity, candles gained significance in their decorative, symbolic and ceremonial uses in churches. Wax candles, or candela cerea recorded at the end of the 3rd century, were documented as Easter candles in Spain and Italy in the fourth century, the Christian festival Candlemas was named after it, and Pope Sergius I instituted the procession of lighted candles. Papal bulls decreed that tallow be excluded for use in altar candles, and a high beeswax content is necessary for candles of the high altar.
In medieval Europe, candles were initially used primarily in Christian churches. Its use spread later to the households of the wealthy as a luxury item. In northern Europe, rushlight made of greased rushes were commonly used especially in England, but tallow candles were used during the Middle Ages, with a mention of tallow candles in English appearing in 1154. Beeswax was widely used in church ceremonies, and compared to animal-based tallow, it burns cleanly without smoky flame, and does not release an unpleasant smell like tallow. Beeswax candles were expensive, and relatively few people could afford to burn them in their homes in medieval Europe.

The candles were produced using a number of methods: dipping the wick in molten fat or wax, rolling the candle by hand around a wick, or pouring fat or wax onto a wick to build up the candle. In the 14th century Sieur de Brez introduced the technique of using a mould, but real improvement for the efficient production of candles with mould was only achieved in the 19th century. Wax and tallow candles were made in monasteries in the medieval period, and in rural households, tallow candles may be made at home. By the 13th century, candle making had become a guild craft in England and France, with a French guild documented as early as 1061. The candle makers (chandlers) went from house to house making candles from the kitchen fats saved for that purpose, or made and sold their own candles from small candle shops.
By the 16th century, beeswax candles were appearing as luxury household items among the wealthy. Candles were widely used in the 17th and 18th centuries, and a party in Dresden was said to have been lit by 14,000 candles in 1779.
In the Middle East, during the Abbasid and Fatimid Caliphates, beeswax was the dominant material used for candle making. Beeswax was often imported from long distances; for example, candle makers from Egypt used beeswax from Tunis. As in Europe, these candles were expensive and limited to the elite, and most commoners used oil lamps instead. According to legend, the practice of using lamps and candles in mosque started with Tamim al-Dari who lit a lamp he brought from Syria in the Prophet's Mosque in Medina. The Umayyad caliph Al-Walid II was known to have used candles in the court in Damascus, while the Abbasid caliph al-Mutawakkil was said to have spent 1.2 million silver dirhams annually on candles for his royal palaces.
In early modern Syria, candles were in high demand by all socioeconomic classes because they were customarily lit during marriage ceremonies. There were candle makers' guilds in the Safavid capital of Isfahan during the 1500s and 1600s. However, candle makers had a relatively low social position in Safavid Iran, comparable to barbers, bathhouse workers, fortune tellers, bricklayers, and porters.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, spermaceti, a waxy substance produced by the sperm whale, was used to produce a superior candle that burned longer, brighter and gave off no offensive smell. Later in the 18th century, colza oil and rapeseed oil came into use as much cheaper substitutes.
Modern era

A number of improvements were made to candle in the 19th century. In older candles, the wick of a burning candle was not in direct contact with air, so it charred instead of being burnt. The charred wick inhibited further burning and produced black smoke, so the wick needed to be constantly trimmed or "snuffed". In 1825, a French man M. Cambacérès introduced the plaited wick soaked with mineral salts, which when burnt, curled towards the outer edge of the flame and become incinerated by it, thereby trimming itself. These are referred to as "self-trimming" or "self-consuming" wicks. In 1823, Michel Eugène Chevreul and Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac separate out stearin in animal fats, and obtained a patent in 1825 to produce candles that are harder and can burn brighter.
The manufacture of candles became an industrialized mass market in the mid 19th century. In 1834, Joseph Morgan, a pewterer from Manchester, England, patented a machine that revolutionised candle making. It allowed for continuous production of molded candles by using a cylinder with a moveable piston to eject candles as they solidified. This more efficient mechanized production produced about 1,500 candles per hour. This allowed candles to be an affordable commodity for the masses.
In the mid-1850s, James Young succeeded in distilling paraffin wax from coal and oil shales at Bathgate in West Lothian and developed a commercially viable method of production. Paraffin could be used to make inexpensive candles of high quality. It was a bluish-white wax, which burned cleanly and left no unpleasant odor, unlike tallow candles. By the end of the 19th century, candles were made from paraffin wax and stearic acid.
By the late 19th century, Price's Candles, based in London, was the largest candle manufacturer in the world. Founded by William Wilson in 1830, the company pioneered the implementation of the technique of steam distillation, and was thus able to manufacture candles from a wide range of raw materials, including skin fat, bone fat, fish oil and industrial greases.
Despite advances in candle making, the candle industry declined rapidly upon the introduction of superior methods of lighting, including kerosene and lamps and the 1879 invention of the incandescent light bulb. From this point on, candles came to be marketed as more of a decorative item.
Use
See also: Ceremonial use of lights
Before the invention of electric lighting, candles and oil lamps were commonly used for illumination. In areas without electricity, they are still used routinely. Until the 20th century, candles were more common in northern Europe. In southern Europe and the Mediterranean, oil lamps predominated.

In the developed world today, candles are used mainly for their aesthetic value and scent, particularly to set a soft, warm, or romantic ambiance, for emergency lighting during electrical power failures. Candles, however, are still commonly used in religious and ceremonial contexts. Examples include votive candles, Paschal candles and yahrzeit candles. In the days leading to Christmas, some people burn a candle a set amount to represent each day, as marked on the candle. The type of candle used in this way is called the Advent candle, although this term is also used to refer to a candle that are used in an Advent wreath.
Symbolic use of candles has extended from the religious to the secular, for example, a candlelight vigil may be held in remembrance for a person, for a cause or an event, or as a form of political action or protest. In a social setting, candles are commonly used on birthday cakes.
In the 21st century, there has been a huge spike in sales of scented candles in recent years. The COVID-19 pandemic and the ensuing lockdowns led to a dramatic increase in the sales of scented candles, diffusers and room sprays.
Other uses

With the fairly consistent and measurable burning of a candle, a common use of candles was to tell the time. The candle designed for this purpose might have time measurements, usually in hours, marked along the wax. The Song dynasty in China (960–1279) used candle clocks.
By the 18th century, candle clocks were being made with weights set into the sides of the candle. As the candle melted, the weights fell off and made a noise as they fell into a bowl.
Components
Wax

For most of recorded history candles were made from tallow (rendered from beef or mutton-fat) or beeswax. From the mid-1800s, they were also made from spermaceti, a waxy substance derived from the Sperm whale, which in turn spurred demand for the substance. Candles were also made from stearin (initially manufactured from animal fats but now produced almost exclusively from palm waxes). Today, most candles are made from paraffin wax, a byproduct of petroleum refining.

Candles can also be made from microcrystalline wax, beeswax (a byproduct of honey collection), gel (a mixture of polymer and mineral oil), or some plant waxes (generally palm, carnauba, bayberry, or soybean wax).
The size of the flame and corresponding rate of burning is controlled largely by the candle wick. The kind of wax also affects the burn rate, with beeswax and coconut wax burning longer than paraffin or soy wax.
Production methods utilize extrusion moulding. More traditional production methods entail melting the solid fuel by the controlled application of heat. The liquid is then poured into a mould, or a wick is repeatedly immersed in the liquid to create a dipped tapered candle. Often fragrance oils, essential oils or aniline-based dye is added.
Wick
Main article: Candle wick
A candle wick works by capillary action, drawing ("wicking") the melted wax or fuel up to the flame. When the liquid fuel reaches the flame, it vaporizes and combusts. The candle wick influences how the candle burns. Important characteristics of the wick include diameter, stiffness, fire resistance, and tethering.
A candle wick is a piece of string or cord that holds the flame of a candle. Commercial wicks are made from braided cotton. The wick's capillarity determines the rate at which the melted hydrocarbon is conveyed to the flame. If the capillarity is too great, the molten wax streams down the side of the candle. Wicks are often infused with a variety of chemicals to modify their burning characteristics. For example, it is usually desirable that the wick not glow after the flame is extinguished. Typical agents are ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate.
Characteristics
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (January 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Light

Based on measurements of a taper-type, paraffin wax candle, a modern candle typically burns at a steady rate of about 0.1 g/min, releasing heat at roughly 80 W. The light produced is about 13 lumens, for a luminous efficacy of about 0.16 lumens per watt (luminous efficacy of a source) – almost a hundred times lower than an incandescent light bulb. If a 1 candela source emitted uniformly in all directions, the total radiant flux would be only about 18.40 mW.
The luminous intensity of a typical candle is approximately one candela. The SI unit, candela, was in fact based on an older unit called the candlepower, which represented the luminous intensity emitted by a candle made to particular specifications (a "standard candle"). The modern unit is defined in a more precise and repeatable way, but was chosen such that a candle's luminous intensity is still about one candela.
Temperature
See also: CombustionThe hottest part of a candle flame is just above the very dull blue part to one side of the flame, at the base. At this point, the flame is about 1,400 °C (2,550 °F). However, this part of the flame is very small and releases little heat energy. The blue color is due to chemiluminescence, while the visible yellow color is due to radiative emission from hot soot particles. The soot is formed through a series of complex chemical reactions, leading from the fuel molecule through molecular growth, until multi-carbon ring compounds are formed. The thermal structure of a flame is complex, hundreds of degrees over very short distances leading to extremely steep temperature gradients. On average, the flame temperature is about 1,000 °C (1,800 °F). The color temperature is approximately 1,000 K.
Combustion
For a candle to burn, a heat source (commonly a naked flame from a match or lighter) is used to light the candle's wick, which melts and vaporizes a small amount of fuel (the wax). Once vaporized, the fuel combines with oxygen in the atmosphere to ignite and form a constant flame. This flame provides sufficient heat to keep the candle burning via a self-sustaining chain of events: the heat of the flame melts the top of the mass of solid fuel; the liquefied fuel then moves upward through the wick via capillary action; the liquefied fuel finally vaporizes to burn within the candle's flame.
As the fuel (wax) is melted and burned, the candle becomes shorter. The end of the plaited wick bends and get consumed in the flame. The incineration of the wick limits the length of the exposed portion of the wick, thus maintaining a constant burning temperature and rate of fuel consumption. Pre-19th century wicks required regular trimming with scissors (or a specialized wick trimmer), usually to about one-quarter inch (~0.7 cm), to promote steady burning and to prevent it from releasing black smoke. Special candle scissors called "snuffers" were produced for this purpose in the 20th century and were often combined with an extinguisher. In modern candles, the wick is made in such a way that it curves over as it burns, which ensures that the end of the wick gets incinerated by fire, thereby trimming itself.
Candle flame
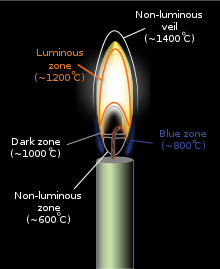
A candle flame is formed because wax vaporizes on burning. A candle flame is widely recognized as having between three and five regions or "zones":
- Zone I – this is the non-luminous, lowest, and coolest part of the candle flame. It is located around the base of the wick where there is insufficient oxygen for fuel to burn. Temperatures are around 600 °C (1,112 °F).
- Zone II – this is the blue zone, which surrounds the base of the flame. Here the supply of oxygen is plentiful, and the fuel burns clean and blue. It is heat from this zone which causes the wax to melt. Temperatures are around 800 °C (1,470 °F).
- Zone III – the dark zone is a region directly above the wick containing unburnt wax. Pyrolysis takes place here. Temperature is around 1,000 °C (1,830 °F).
- Zone IV – the middle or luminous zone is yellow/white and is located above the dark zone. It is the brightest zone, but not the hottest. It is an oxygen-depleted zone with insufficient oxygen to burn all of the wax vapor rising from below it, resulting in only partial combustion. The zone also contains unburnt carbon particles. Temperature is around 1,200 °C (2,190 °F).
- Zone V – The non-luminous outer zone or veil surrounds Zone IV. Here, the flame is at its hottest, at around 1,400 °C (2,550 °F), and complete combustion occurs. It is light blue in color, though most of it is invisible.
The main determinant of the height of a candle flame is the diameter of the wick. This is evidenced in tealights where the wick is very thin and the flame is very small. Candles whose main purpose is illumination use a much thicker wick.
History of study
One of Michael Faraday's significant works was The Chemical History of a Candle, where he gives an in-depth analysis of the evolutionary development, workings and science of candles.
Hazards
According to the National Fire Protection Association, candles are a leading source of residential fires in the United States with almost 10% of civilian injuries and 6% of fatalities from fire attributed to candles.
A candle flame that is longer than its laminar smoke point will emit soot. Proper wick trimming will reduce soot emissions from most candles.
The liquid wax is hot and can cause skin burns, but the amount and temperature are generally rather limited and the burns are seldom serious. The best way to avoid getting burned from splashed wax is to use a candle snuffer instead of blowing on the flame. A candle snuffer is usually a small metal cup on the end of a long handle. Placing the snuffer over the flame cuts off the oxygen supply. Snuffers were common in the home when candles were the main source of lighting before electric lights were available. Ornate snuffers, often combined with a taper for lighting, are still found in those churches which regularly use large candles.
Glass candle-holders are sometimes cracked by thermal shock from the candle flame, particularly when the candle burns down to the end. When burning candles in glass holders or jars, users should avoid lighting candles with chipped or cracked containers, and stop use once a half-inch or less of wax remains.
A former worry regarding the safety of candles was that a lead core was used in the wicks to keep them upright in container candles. Without a stiff core, the wicks of a container candle could sag and drown in the deep wax pool. Concerns rose that the lead in these wicks would vaporize during the burning process, releasing lead vapors – a known health and developmental hazard. Lead core wicks have not been common since the 1970s. Today, most metal-cored wicks use zinc or a zinc alloy, which has become the industry standard. Wicks made from specially treated paper and cotton are also available.
Candles emit volatile organic compounds into the environment, which releases carbon into the air. The combustion process of lighting a candle includes the release of light, heat, carbon dioxide and water vapor, to fuel the flame. Candle use can be unsafe if fragrances are inhaled at high doses Non-toxic candles have been created as an alternative to prevent these volatile organic compounds from being released into the environment. Candle companies such as "The Plant Project" have created candles that are more environmentally sustainable and better for lung health. These alternatives include non-toxic wax blends, safe fragrances and eco-friendly packaging. Safer candles include candles made from coconut, soy, vegetable, and beeswax.
Users who seek the aesthetics of a candle sometimes install an electric flameless candle to avoid the hazards.
Regulation
International markets have developed a range of standards and regulations to ensure compliance, while maintaining and improving safety, including:
- Europe: GPSD, EN 15493, EN 15494, EN 15426, EN 14059, REACH, RAL-GZ 041 Candles (Germany), French Decree 91-1175
- United States: ASTM F2058, ASTM F2179, ASTM F2417, ASTM F2601, ASTM F2326 (all are federal and applies in all 50 states), California Proposition 65 (California only), CONEG (New England and New York states only)
- China: QB/T 2119 Basic Candle, QB/T 2902 Art Candle, QB/T 2903 Jar Candle, GB/T 22256 Jelly Candle
Accessories
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (January 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Candle holders

Decorative candleholders, especially those shaped as a pedestal, are called candlesticks; if multiple candle tapers are held, the term candelabra is also used. The root form of chandelier is from the word for candle, but now often refers to an electric fixture. The word chandelier is used to describe a hanging fixture designed to hold multiple lights. Other forms of candle holders include the wall-mounted sconces, lanterns, and girandoles.

Many candle holders use a friction-tight socket to keep the candle upright. In this case, a candle that is slightly too wide will not fit in the holder, and a candle that is slightly too narrow will wobble. Candles that are too big can be trimmed to fit with a knife; candles that are too small can be fitted with aluminium foil. Traditionally, the candle and candle holders were made in the same place, so they were appropriately sized, but international trade has combined the modern candle with existing holders, which makes the ill-fitting candle more common. This friction-tight socket is only needed for the federals and the tapers.
For tea light candles, there is a variety of candle holders, including small glass holders and elaborate multi-candle stands. The same is true for votives. Wall sconces are available for tea light and votive candles. For pillar-type candles, the assortment of candle holders is broad. A fireproof plate, such as a glass plate or small mirror, can be a candle holder for a pillar-style candle. A pedestal of any kind, with the appropriate-sized fireproof top, is another option. A large glass bowl with a large flat bottom and tall mostly vertical curved sides is called a hurricane. The pillar-style candle is placed at the bottom center of the hurricane. A hurricane on a pedestal is sometimes sold as a unit.
A bobèche is a drip-catching ring, which may also be affixed to a candle holder, or used independently of one. Bobèches can range from ornate metal or glass to simple plastic, cardboard, or wax paper. Use of paper or plastic bobèches is common at events where candles are distributed to a crowd or audience, such as Christmas carolers or people at other concerts or festivals.

Candle snuffers
Main article: Candle snuffer
Candle snuffers are instruments used to extinguish burning candles by smothering the flame with a small metal cup that is suspended from a long handle, and thus depriving it of oxygen. An older meaning refers to a scissor-like tool used to trim the wick of a candle. With skill, this could be done without extinguishing the flame. The instrument now known as a candle snuffer was formerly called an "extinguisher" or "douter".
Candle followers
These are glass or metal tubes with an internal stricture partway along, which sit around the top of a lit candle. As the candle burns, the wax melts and the follower holds the melted wax in, whilst the stricture rests on the topmost solid portion of wax. Candle followers are often deliberately heavy or weighted to ensure they move down as the candle burns lower, maintaining a seal and preventing wax escape. The purpose of a candle follower is threefold:
- To contain the melted wax, making the candle more efficient, avoiding mess, and producing a more even burn.
- As a decoration, either due to the ornate nature of the device, or (in the case of a glass follower) through light dispersion or colouration.
- If necessary, to shield the flame from wind.
Candle followers are often found in churches on altar candles.
Gallery
-
 Object in the tomb of Tutankhamun
Object in the tomb of Tutankhamun
-
 Candlelight vigil
Candlelight vigil
-
 Candles used in Iran in a mourning ceremony
Candles used in Iran in a mourning ceremony
-
 Candles used in a Chinese temple
Candles used in a Chinese temple
-
 Multi-wick candles used in a Sicilian festival
Multi-wick candles used in a Sicilian festival
-
 Lighting candles for the Indian festival of Diwali
Lighting candles for the Indian festival of Diwali
-
 A candelabra with candles in a Swedish cathedral
A candelabra with candles in a Swedish cathedral
-
 Handmade candles
Handmade candles
-
A decorative candle in Mexico
-
 A small ornamental candle with a gold stand
A small ornamental candle with a gold stand
See also
- Candle-making
- Candle warmer
- Candelabra
- Eulachon
- Julleuchter
- Outdoor candle
- Rushlight
- Singing candle
- Trick candles
- Trudon
- Unity candle
- Yahrzeit candle
References
- "Chandler". The Free Dictionary By Farlex. Retrieved 2012-05-19.
- ^ European Candle Association FAQ Archived 2012-01-13 at the Wayback Machine.
- "Candle". The Free Dictionary By Farlex. Retrieved 2012-05-19.
- Forbes 1966, p. 127.
- Forbes 1966, p. 126.
- ^ Forbes 1966, p. 134.
- ^ Baur 1996, p. 7.
- "Let There be Light: A History of Candles". Hellenic Museum. 3 December 2021.
- ^ Forbes 1966, p. 140.
- Baur 1996, p. 18.
- "Candles, Roman, 500 BCE". Smith College Museum.
- "The Best Candle Pouring Pots for Learning an Ancient Craft". Art News. 6 December 2020. Retrieved 2023-02-02.
- Forbes 1966, p. 141.
- Baur 1996, p. 8–9.
- Baur 1996, pp. 7–8.
- "history of candle". national candle association.
- ^ Forbes 1966, p. 138–139.
- ^ Baur 1996, p. 8.
- "History of candles". National Candle Association. Archived from the original on May 17, 2012. Retrieved 2012-05-19.
- ^ Baur 1996, p. 9.
- ^ Beg 1997, p. 288.
- Shillito, M. Larry; David J. De Marle (1992). Value: Its Measurement, Design, and Management. Wiley-IEEE. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-471-52738-1.
- ^ LeFever 2007, p. 65.
- "A Brief History of Candles". Archived from the original on 2013-03-18. Retrieved 2015-07-06.
- "Joseph Morgan and Son". Graces Guide.
- Phillips, Gordon (1999). Seven Centuries of Light: The Tallow Chandlers Company. Book Production Consultants. p. 74. ISBN 978-1-85757-064-9.
- Golan, Tal (2004). Laws of Men and Laws of Nature: The History of Scientific Expert Testimony in England and America. Harvard University Press. pp. 89–91. ISBN 978-0674012868.
- Geoff Marshall (2013). London's Industrial Heritage. The History Press. ISBN 9780752492391.
- Ball, Michael; David Sunderland (2001). An Economic History of London, 1800-1914. Routledge. pp. 131–132. ISBN 978-0415246910.
- Sekimoto, Hiroshi; Ryu, Kouichi; Yoshimura, Yoshikane (2001-11-01). "CANDLE: The New Burnup Strategy". Nuclear Science and Engineering. 139 (3): 306–317. Bibcode:2001NSE...139..306S. doi:10.13182/NSE01-01. ISSN 0029-5639. S2CID 121714669.
- ^ Ferrier, Morwenna (19 December 2018). "The cult of 'smellness': what's behind the extraordinary rise in sales of scented candles?". The Guardian. Guardian News & Media Limited. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- Geddes, Gordon; Jane Griffiths (2002). Christianity. Heinemann. p. 89. ISBN 978-0-435-30693-9.
- "What Is a Candlelight Vigil: Meaning, Types & Symbolism". Endly. August 2, 2023.
- Wood, Zoe (10 November 2020). "UK sales of scented candles soar as Covid restrictions tighten". The Guardian. The Guardian News & Media Limited. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- Thomas, Ellen (10 April 2020). "Candles Burn Bright Amid Coronavirus Pandemic". WWD. Retrieved 24 May 2021.
- Whitrow, G. J. (1989). Time in History: Views of Time from Prehistory to the Present Day. Oxford University Press. pp. 90–91. ISBN 978-0-19-285211-3. Archived from the original on June 10, 2015.
- "Using stearic acid or stearin in candlemaking". happynews.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- "Stearic acid (stearin)". howtomakecandles.info. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ Franz Willhöft and Fredrick Horn "Candles" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2000, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_029
- Camp, William R.; Vollenweider, Jeffrey L.; Schutz, Wendy J. (12 October 1999). "Scented candle gel". United States Patent 5,964,905.
- "Candle Wax Guide: Comparing Soy, Paraffin, Coconut, and Beeswax". valiantcandle.com. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- Hamins, Anthony; Bundy, Matthew; Dillon, Scott E. (November 2005). "Characterization of Candle Flames" (PDF). Journal of Fire Protection Engineering. 15 (4): 277. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.548.3798. doi:10.1177/1042391505053163.
- "On Fire – Background Essay". PBS LearningMedia. PBS and WGBH Educational Foundation. Archived from the original on April 3, 2015. Retrieved April 8, 2015.
- Allen R. White (2013). "FTIR Study of Combustion Species In Several Regions of a Candle Flame". Ohio State University. hdl:1811/55436.
- National Council of Educational Research and Training. "Science: Textbook for Class VIII". Publication Department, 2010, p. 72.
- Sunderland, P.B.; Quintiere, J.G.; Tabaka, G.A.; Lian, D.; Chiu, C.-W. (6 October 2010). "Analysis and measurement of candle flame shapes" (PDF). Proceedings of the Combustion Institute. 33 (2): 2489–2496. doi:10.1016/j.proci.2010.06.095. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 2015-02-10.
- "Internet History Sourcebooks". Fordham.edu. Retrieved 2012-12-25.
- John Hall, NFPA 2009, "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original on 2011-07-27. Retrieved 2013-01-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). - K.M. Allan, J.R. Kaminski, J.C. Bertrand, J. Head, Peter B. Sunderland, Laminar Smoke Points of Wax Candles, Combustion Science and Technology 181 (2009) 800–811.
- "10 Eco-Friendly Sustainable Candles For A Clean Burn - The Eco Hub". theecohub.com. 2021-04-08. Retrieved 2022-11-07.
- "Candles: What do they emit when lit?". Office for Science and Society. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- ^ "You Need To Follow These Expert Tips To Make Sure You're Using Your Scented Candles Safely". Women's Health. 2022-09-27. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- ^ "10 Eco-Friendly Sustainable Candles For A Clean Burn - The Eco Hub". theecohub.com. 2021-04-08. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- ^ "The Ultimate Guide To Non-Toxic Candles". British Vogue. 2020-05-12. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- Joanna Banham, ed. (1997). Encyclopedia of Interior Design. Taylor & Francis. pp. 225–226. ISBN 9781136787584.
Bibliography
- Baur, Veronika (1996). Metal Candlesticks: History, Styles and Techniques. Schiffer Publishing. ISBN 9780764301568.
- Beg, M.A.J. (1997). "SHAMMĀ'". In Bosworth, C.E.; van Donzel, E.; Heinrichs, W.P.; Lecomte, G. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Vol. IX (SAN-SZE) (PDF). Leiden: Brill. p. 288. ISBN 90-04-10422-4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-03-25. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- Forbes, Robert James (1966). Studies in Ancient Technology. Brill. ISBN 978-9004006263.
- LeFever, Gregory (2007). "Early Candle Making" (PDF). Early American Life. pp. 62–71.
External links
 Media related to Candles at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Candles at Wikimedia Commons- National Candle Association of the U.S.
- The Chemical History of a Candle by Michael Faraday
- Association of European Candlemakers(AECM) Archived 2011-07-04 at the Wayback Machine
- European Candle Association (ECA)
- Latin American Candle Manufacturers Association (ALAFAVE)
- Guide To Candle Safety At Home - Osmology
| Lighting | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concepts | |||||||||||||
| Methods of generation |
| ||||||||||||
| Stationary | |||||||||||||
| Portable | |||||||||||||
| Automotive | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Related topics | |||||||||||||