Cathepsin K, abbreviated CTSK, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CTSK gene.
Function
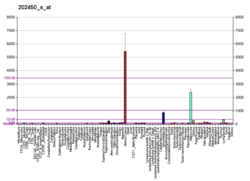
The protein encoded by this gene is a cysteine cathepsin, a lysosomal cysteine protease involved in bone remodeling and resorption. This protein, which is a member of the peptidase C1 protein family, is expressed predominantly in osteoclasts.
Cathepsin K is a protease, which is defined by its high specificity for kinins, that is involved in bone resorption. The enzyme's ability to catabolize elastin, collagen, and gelatin allows it to break down bone and cartilage. This catabolic activity is also partially responsible for the loss of lung elasticity and recoil in emphysema. Cathepsin K inhibitors show great potential in the treatment of osteoporosis. Cathepsin K is degraded by Cathepsin S, in a process referred to as Controlled Cathepsin Cannibalism.
Cathepsin K expression is stimulated by inflammatory cytokines that are released after tissue injury.
Clinical significance
Cathepsin K is expressed in a significant fraction of human breast cancers, where it could contribute to tumor invasiveness. Mutations in this gene are the cause of pycnodysostosis, an autosomal recessive disease characterized by osteosclerosis and short stature. Cathepsin K has also been found to be over-expressed in glioblastoma.
That the expression of cathepsin K is characteristic for some cancers and not others has been documented. Cathepsin K antibodies are marketed for research into expression of this enzyme by various cells.
Merck had a cathepsin K inhibitor, odanacatib, in Phase III clinical trials for osteoporosis. In September, 2016, Merck announced they were discontinuing development of odanacatib after their own assessment of adverse events and an independent assessment showed increased risk of stroke. Other cathepsin K inhibitors are in various stages of development. Medivir has a cathepsin K inhibitor, MIV-711 (L-006235), in Phase IIa clinical trial, as a disease modifying osteoarthritis drug, as of October 2017.
References
- ^ GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000143387 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028111 – Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: CTSK cathepsin K".
- Inaoka T, Bilbe G, Ishibashi O, Tezuka K, Kumegawa M, Kokubo T (January 1995). "Molecular cloning of human cDNA for cathepsin K: novel cysteine proteinase predominantly expressed in bone". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 206 (1): 89–96. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.1013. PMID 7818555.
- Duong LT, Wesolowski GA, Leung P, Oballa R, Pickarski M (23 September 2014). "Efficacy of a Cathepsin K Inhibitor in a Preclinical Model for Prevention and Treatment of Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis". Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 13 (12): 2898–909. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0253. PMID 25249554. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- "CTSK cathepsin K [ Homo sapiens (human) ]". NCBI Gene. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine. 4 September 2016. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- Verbovšek U, Motaln H, Rotter A, Atai NA, Gruden K, Van Noorden CJ, Lah TT (30 October 2014). "Expression Analysis of All Protease Genes Reveals Cathepsin K to Be Overexpressed in Glioblastoma". PLOS ONE. 9 (10): e111819. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9k1819V. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111819. PMC 4214761. PMID 25356585.
- Argani, Pedram; et al. (1 February 2013). "A Broad Survey of Cathepsin K Immunoreactivity in Human Neoplasms". American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 139 (2): 151–159. doi:10.1309/AJCPDTRTO2Z4UEXD. PMC 3957187. PMID 23355199.
- "Cathepsin K Antibodies". Novus Biologicals online catalog. Novus Biologicals, LLC. 2016. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- "Anti-Cathepsin K antibody (ab19027)". Abcam plc online catalog. Abcam plc. 2016. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- "Anti-Cathepsin K Antibody (A5871)". Antibodies.com online catalog. Antibodies.com Ltd. 2018. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- Brömme, Dieter; Lecaille, Fabien (24 April 2009). "Cathepsin K inhibitors for osteoporosis and potential off-target effects". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 18 (5): 585–600. doi:10.1517/13543780902832661. PMC 3110777. PMID 19388876.
- "Merck Provides Update on Odanacatib Development Program". Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. 2 September 2016. Retrieved 1 October 2016.
- Asagiri M, Hirai T, Kunigami T, Kamano S, Gober HJ, Okamoto K, Nishikawa K, Latz E, Golenbock DT, Aoki K, Ohya K, Imai Y, Morishita Y, Miyazono K, Kato S, Saftig P, Takayanagi H,. (2008). Cathepsin K-dependent toll-like receptor 9 signaling revealed in experimental arthritis. Science, 319(5863), 624-627.
- Hussein, H., Ishihara, A., Menendez, M., & Bertone, A. (2014). Pharmacokinetics and bone resorption evaluation of a novel Cathepsin K inhibitor (VEL-0230) in healthy adult horses. Journal of veterinary pharmacology and therapeutics.
- Ren, Zhong-Yuan; Machuca-Gayet, Irma; Domenget, Chantal; Buchet, Rene; Wu, Yuqing; Jurdic, Pierre; Mebarek, Saida (13 July 2015). "Azanitrile Cathepsin K Inhibitors: Effects on Cell Toxicity, Osteoblast-Induced Mineralization and Osteoclast-Mediated Bone Resorption". PLOS ONE. 10 (7): e0132513. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1032513R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132513. PMC 4500499. PMID 26168340.
- "MIV-711 for the treatment of ostheoarthritis". www.medivir.se. Archived from the original on 6 October 2017. Retrieved 6 October 2017.
- Burston JJ, Xu L, Mapp PI, Grabowska U, Tunblad K, Lindström E, Chapman V (April 2016). "The Cathepsin K Inhibitor L-006235 Demonstrates Both Disease Modification and Attenuation of Pain Behaviour in the in the [sic] Mia Model of Osteoarthritis" (PDF). www.medivir.se. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2017. Retrieved 6 October 2017.
- "Data monitoring committee gives "Go Ahead" in the MIV-711 osteoarthritis extension study" (PDF). mb.cision.com. 14 September 2017.
Further reading
- Motyckova G, Fisher DE (2003). "Pycnodysostosis: role and regulation of cathepsin K in osteoclast function and human disease". Current Molecular Medicine. 2 (5): 407–21. doi:10.2174/1566524023362401. PMID 12125807.
- Troen BR (2006). "The regulation of cathepsin K gene expression". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1068 (1): 165–72. Bibcode:2006NYASA1068..165T. doi:10.1196/annals.1346.018. PMID 16831915. S2CID 8117602.
- Del Nery E, Chagas JR, Juliano MA, et al. (1996). "Evaluation of the extent of the binding site in human tissue kallikrein by synthetic substrates with sequences of human kininogen fragments". The Biochemical Journal. 312 (1): 233–8. doi:10.1042/bj3120233. PMC 1136249. PMID 7492318.
- Brömme D, Okamoto K (1995). "Human cathepsin O2, a novel cysteine protease highly expressed in osteoclastomas and ovary molecular cloning, sequencing and tissue distribution". Biological Chemistry Hoppe-Seyler. 376 (6): 379–84. doi:10.1515/bchm3.1995.376.6.379. PMID 7576232.
- Gelb BD, Edelson JG, Desnick RJ (1995). "Linkage of pycnodysostosis to chromosome 1q21 by homozygosity mapping". Nature Genetics. 10 (2): 235–7. doi:10.1038/ng0695-235. PMID 7663521. S2CID 24297764.
- Polymeropoulos MH, Ortiz De Luna RI, Ide SE, et al. (1995). "The gene for pycnodysostosis maps to human chromosome 1cen-q21". Nature Genetics. 10 (2): 238–9. doi:10.1038/ng0695-238. PMID 7663522. S2CID 11723845.
- Shi GP, Chapman HA, Bhairi SM, et al. (1995). "Molecular cloning of human cathepsin O, a novel endoproteinase and homologue of rabbit OC2" (PDF). FEBS Letters. 357 (2): 129–34. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)01349-6. PMID 7805878. S2CID 28099876.
- Inaoka T, Bilbe G, Ishibashi O, et al. (1995). "Molecular cloning of human cDNA for cathepsin K: novel cysteine proteinase predominantly expressed in bone". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 206 (1): 89–96. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.1013. PMID 7818555.
- Velasco G, Ferrando AA, Puente XS, et al. (1994). "Human cathepsin O. Molecular cloning from a breast carcinoma, production of the active enzyme in Escherichia coli, and expression analysis in human tissues". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 269 (43): 27136–42. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)47135-9. PMID 7929457.
- Li YP, Alexander M, Wucherpfennig AL, et al. (1996). "Cloning and complete coding sequence of a novel human cathepsin expressed in giant cells of osteoclastomas". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 10 (8): 1197–202. doi:10.1002/jbmr.5650100809. PMID 8585423. S2CID 41832979.
- Bossard MJ, Tomaszek TA, Thompson SK, et al. (1996). "Proteolytic activity of human osteoclast cathepsin K. Expression, purification, activation, and substrate identification". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (21): 12517–24. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.21.12517. PMID 8647860.
- Gelb BD, Shi GP, Chapman HA, Desnick RJ (1996). "Pycnodysostosis, a lysosomal disease caused by cathepsin K deficiency". Science. 273 (5279): 1236–8. Bibcode:1996Sci...273.1236G. doi:10.1126/science.273.5279.1236. PMID 8703060. S2CID 7188076.
- Johnson MR, Polymeropoulos MH, Vos HL, et al. (1997). "A nonsense mutation in the cathepsin K gene observed in a family with pycnodysostosis". Genome Research. 6 (11): 1050–5. doi:10.1101/gr.6.11.1050. PMID 8938428.
- Littlewood-Evans A, Kokubo T, Ishibashi O, et al. (1997). "Localization of cathepsin K in human osteoclasts by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry". Bone. 20 (2): 81–6. doi:10.1016/S8756-3282(96)00351-1. PMID 9028530.
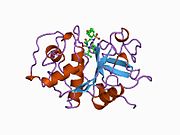
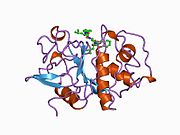
- McGrath ME, Klaus JL, Barnes MG, Brömme D (1997). "Crystal structure of human cathepsin K complexed with a potent inhibitor". Nature Structural Biology. 4 (2): 105–9. doi:10.1038/nsb0297-105. PMID 9033587. S2CID 22175354.
- Rood JA, Van Horn S, Drake FH, et al. (1997). "Genomic organization and chromosome localization of the human cathepsin K gene (CTSK)". Genomics. 41 (2): 169–76. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4614. PMID 9143491.
- Gelb BD, Shi GP, Heller M, et al. (1997). "Structure and chromosomal assignment of the human cathepsin K gene". Genomics. 41 (2): 258–62. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4631. PMID 9143502.
- Gomes RA, Juliano L, Chagas JR, Hial V (1997). "Characterization of kininogenase activity of an acidic proteinase isolated from human kidney". Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 75 (6): 757–61. doi:10.1139/cjpp-75-6-757. PMID 9276160.
- Thompson SK, Halbert SM, Bossard MJ, et al. (1998). "Design of potent and selective human cathepsin K inhibitors that span the active site". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 94 (26): 14249–54. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.26.14249. PMC 24926. PMID 9405598.
- Gelb BD, Willner JP, Dunn TM, et al. (1998). "Paternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 1 revealed by molecular analysis of a patient with pycnodysostosis". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 62 (4): 848–54. doi:10.1086/301795. PMC 1377035. PMID 9529353.
Additional images
External links
- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: C01.036
- Cathepsin+K at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| PDB gallery | |
|---|---|
|
| Proteases: cysteine proteases (EC 3.4.22) | |
|---|---|
| Caspase | |
| Fruit-derived | |
| Calpain | |
| Cathepsin | |
| Other | |
| Enzymes | |
|---|---|
| Activity | |
| Regulation | |
| Classification | |
| Kinetics | |
| Types |
|
Categories: