| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (March 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In mathematics, a comma category (a special case being a slice category) is a construction in category theory. It provides another way of looking at morphisms: instead of simply relating objects of a category to one another, morphisms become objects in their own right. This notion was introduced in 1963 by F. W. Lawvere (Lawvere, 1963 p. 36), although the technique did not become generally known until many years later. Several mathematical concepts can be treated as comma categories. Comma categories also guarantee the existence of some limits and colimits. The name comes from the notation originally used by Lawvere, which involved the comma punctuation mark. The name persists even though standard notation has changed, since the use of a comma as an operator is potentially confusing, and even Lawvere dislikes the uninformative term "comma category" (Lawvere, 1963 p. 13).
Definition
The most general comma category construction involves two functors with the same codomain. Often one of these will have domain 1 (the one-object one-morphism category). Some accounts of category theory consider only these special cases, but the term comma category is actually much more general.
General form
Suppose that , , and are categories, and and (for source and target) are functors:
We can form the comma category as follows:
- The objects are all triples with an object in , an object in , and a morphism in .
- The morphisms from to are all pairs where and are morphisms in and respectively, such that the following diagram commutes:

Morphisms are composed by taking to be , whenever the latter expression is defined. The identity morphism on an object is .
Slice category
Main article: OvercategoryThe first special case occurs when , the functor is the identity functor, and (the category with one object and one morphism). Then for some object in .
In this case, the comma category is written , and is often called the slice category over or the category of objects over . The objects can be simplified to pairs , where . Sometimes, is denoted by . A morphism from to in the slice category can then be simplified to an arrow making the following diagram commute:

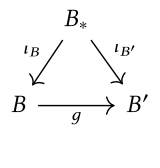
Coslice category
Main article: OvercategoryThe dual concept to a slice category is a coslice category. Here, , has domain and is an identity functor.
In this case, the comma category is often written , where is the object of selected by . It is called the coslice category with respect to , or the category of objects under . The objects are pairs with . Given and , a morphism in the coslice category is a map making the following diagram commute:
Arrow category
and are identity functors on (so ).
In this case, the comma category is the arrow category . Its objects are the morphisms of , and its morphisms are commuting squares in .

Other variations
In the case of the slice or coslice category, the identity functor may be replaced with some other functor; this yields a family of categories particularly useful in the study of adjoint functors. For example, if is the forgetful functor mapping an abelian group to its underlying set, and is some fixed set (regarded as a functor from 1), then the comma category has objects that are maps from to a set underlying a group. This relates to the left adjoint of , which is the functor that maps a set to the free abelian group having that set as its basis. In particular, the initial object of is the canonical injection , where is the free group generated by .
An object of is called a morphism from to or a -structured arrow with domain . An object of is called a morphism from to or a -costructured arrow with codomain .
Another special case occurs when both and are functors with domain . If and , then the comma category , written , is the discrete category whose objects are morphisms from to .
An inserter category is a (non-full) subcategory of the comma category where and are required. The comma category can also be seen as the inserter of and , where and are the two projection functors out of the product category .
Properties
For each comma category there are forgetful functors from it.
- Domain functor, , which maps:
- objects: ;
- morphisms: ;
- Codomain functor, , which maps:
- objects: ;
- morphisms: .
- Arrow functor, , which maps:
- objects: ;
- morphisms: ;
Examples of use
Some notable categories
Several interesting categories have a natural definition in terms of comma categories.
- The category of pointed sets is a comma category, with being (a functor selecting) any singleton set, and (the identity functor of) the category of sets. Each object of this category is a set, together with a function selecting some element of the set: the "basepoint". Morphisms are functions on sets which map basepoints to basepoints. In a similar fashion one can form the category of pointed spaces .
- The category of associative algebras over a ring is the coslice category , since any ring homomorphism induces an associative -algebra structure on , and vice versa. Morphisms are then maps that make the diagram commute.
- The category of graphs is , with the functor taking a set to . The objects then consist of two sets and a function; is an indexing set, is a set of nodes, and chooses pairs of elements of for each input from . That is, picks out certain edges from the set of possible edges. A morphism in this category is made up of two functions, one on the indexing set and one on the node set. They must "agree" according to the general definition above, meaning that must satisfy . In other words, the edge corresponding to a certain element of the indexing set, when translated, must be the same as the edge for the translated index.
- Many "augmentation" or "labelling" operations can be expressed in terms of comma categories. Let be the functor taking each graph to the set of its edges, and let be (a functor selecting) some particular set: then is the category of graphs whose edges are labelled by elements of . This form of comma category is often called objects -over - closely related to the "objects over " discussed above. Here, each object takes the form , where is a graph and a function from the edges of to . The nodes of the graph could be labelled in essentially the same way.
- A category is said to be locally cartesian closed if every slice of it is cartesian closed (see above for the notion of slice). Locally cartesian closed categories are the classifying categories of dependent type theories.
Limits and universal morphisms
Limits and colimits in comma categories may be "inherited". If and are complete, is a continuous functor, and is another functor (not necessarily continuous), then the comma category produced is complete, and the projection functors and are continuous. Similarly, if and are cocomplete, and is cocontinuous, then is cocomplete, and the projection functors are cocontinuous.
For example, note that in the above construction of the category of graphs as a comma category, the category of sets is complete and cocomplete, and the identity functor is continuous and cocontinuous. Thus, the category of graphs is complete and cocomplete.
The notion of a universal morphism to a particular colimit, or from a limit, can be expressed in terms of a comma category. Essentially, we create a category whose objects are cones, and where the limiting cone is a terminal object; then, each universal morphism for the limit is just the morphism to the terminal object. This works in the dual case, with a category of cocones having an initial object. For example, let be a category with the functor taking each object to and each arrow to . A universal morphism from to consists, by definition, of an object and morphism with the universal property that for any morphism there is a unique morphism with . In other words, it is an object in the comma category having a morphism to any other object in that category; it is initial. This serves to define the coproduct in , when it exists.
Adjunctions
William Lawvere showed that the functors and are adjoint if and only if the comma categories and , with and the identity functors on and respectively, are isomorphic, and equivalent elements in the comma category can be projected onto the same element of . This allows adjunctions to be described without involving sets, and was in fact the original motivation for introducing comma categories.
Natural transformations
If the domains of are equal, then the diagram which defines morphisms in with is identical to the diagram which defines a natural transformation . The difference between the two notions is that a natural transformation is a particular collection of morphisms of type of the form , while objects of the comma category contains all morphisms of type of such form. A functor to the comma category selects that particular collection of morphisms. This is described succinctly by an observation by S.A. Huq that a natural transformation , with , corresponds to a functor which maps each object to and maps each morphism to . This is a bijective correspondence between natural transformations and functors which are sections of both forgetful functors from .
References
- ^ Adámek, Jiří; Herrlich, Horst; Strecker, George E. (1990). Abstract and Concrete Categories (PDF). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-60922-6.
- Rydheard, David E.; Burstall, Rod M. (1988). Computational category theory (PDF). Prentice Hall.
- Mac Lane, Saunders (1998), Categories for the Working Mathematician, Graduate Texts in Mathematics 5 (2nd ed.), Springer-Verlag, p. 48, ISBN 0-387-98403-8
- Comma category at the nLab
- Lawvere, W (1963). "Functorial semantics of algebraic theories" and "Some algebraic problems in the context of functorial semantics of algebraic theories". http://www.tac.mta.ca/tac/reprints/articles/5/tr5.pdf
External links
- J. Adamek, H. Herrlich, G. Stecker, Abstract and Concrete Categories-The Joy of Cats
- Interactive Web page which generates examples of categorical constructions in the category of finite sets.
| Category theory | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|  | |||||||||||||||||
 ,
,  , and
, and  are categories, and
are categories, and  and
and  (for source and target) are
(for source and target) are 
 as follows:
as follows:
 with
with  an object in
an object in  an object in
an object in  a morphism in
a morphism in  are all pairs
are all pairs  where
where  and
and  are morphisms in
are morphisms in  to be
to be  , whenever the latter expression is defined. The identity morphism on an object
, whenever the latter expression is defined. The identity morphism on an object  .
.
 , the functor
, the functor  (the category with one object
(the category with one object  and one morphism). Then
and one morphism). Then  for some object
for some object  in
in 
 , and is often called the slice category over
, and is often called the slice category over  can be simplified to pairs
can be simplified to pairs  , where
, where  . Sometimes,
. Sometimes,  is denoted by
is denoted by  . A morphism
. A morphism  from
from  to
to  in the slice category can then be simplified to an arrow
in the slice category can then be simplified to an arrow  ,
,  and
and 
 , where
, where  is the object of
is the object of  , or the category of objects under
, or the category of objects under  with
with  . Given
. Given  , a morphism in the coslice category is a map
, a morphism in the coslice category is a map  ).
).

 . Its objects are the morphisms of
. Its objects are the morphisms of  is some fixed
is some fixed  has objects that are maps from
has objects that are maps from  , where
, where  is the free group generated by
is the free group generated by  is called a morphism from
is called a morphism from  or a
or a  and
and  , then the comma category
, then the comma category  , is the
, is the  and
and  are required. The comma category can also be seen as the inserter of
are required. The comma category can also be seen as the inserter of  and
and  , where
, where  and
and  are the two projection functors out of the
are the two projection functors out of the  .
.
 , which maps:
, which maps:
 ;
; ;
; , which maps:
, which maps:
 ;
; .
. , which maps:
, which maps:
 ;
; ;
; with
with  being (a functor selecting) any
being (a functor selecting) any  (the identity functor of) the
(the identity functor of) the  .
. is the coslice category
is the coslice category  , since any ring homomorphism
, since any ring homomorphism  induces an associative
induces an associative  that make the diagram commute.
that make the diagram commute. , with
, with  the functor taking a set
the functor taking a set  . The objects
. The objects  then consist of two sets and a function;
then consist of two sets and a function;  is an indexing set,
is an indexing set,  is a set of nodes, and
is a set of nodes, and  chooses pairs of elements of
chooses pairs of elements of  picks out certain edges from the set
picks out certain edges from the set  of possible edges. A morphism in this category is made up of two functions, one on the indexing set and one on the node set. They must "agree" according to the general definition above, meaning that
of possible edges. A morphism in this category is made up of two functions, one on the indexing set and one on the node set. They must "agree" according to the general definition above, meaning that  must satisfy
must satisfy  . In other words, the edge corresponding to a certain element of the indexing set, when translated, must be the same as the edge for the translated index.
. In other words, the edge corresponding to a certain element of the indexing set, when translated, must be the same as the edge for the translated index. is the category of graphs whose edges are labelled by elements of
is the category of graphs whose edges are labelled by elements of  , where
, where  a function from the edges of
a function from the edges of  is a
is a  is another functor (not necessarily continuous), then the comma category
is another functor (not necessarily continuous), then the comma category  and
and  are continuous. Similarly, if
are continuous. Similarly, if  is
is  the functor taking each object
the functor taking each object  to
to  and each arrow
and each arrow  . A universal morphism from
. A universal morphism from  to
to  consists, by definition, of an object
consists, by definition, of an object  with the universal property that for any morphism
with the universal property that for any morphism  there is a unique morphism
there is a unique morphism  with
with  . In other words, it is an object in the comma category
. In other words, it is an object in the comma category  having a morphism to any other object in that category; it is initial. This serves to define the
having a morphism to any other object in that category; it is initial. This serves to define the  and
and  are
are  and
and  , with
, with  and
and  the identity functors on
the identity functors on  and
and  . This allows adjunctions to be described without involving sets, and was in fact the original motivation for introducing comma categories.
. This allows adjunctions to be described without involving sets, and was in fact the original motivation for introducing comma categories.
 are equal, then the diagram which defines morphisms in
are equal, then the diagram which defines morphisms in  with
with  is identical to the diagram which defines a
is identical to the diagram which defines a  . The difference between the two notions is that a natural transformation is a particular collection of morphisms of type of the form
. The difference between the two notions is that a natural transformation is a particular collection of morphisms of type of the form  , while objects of the comma category contains all morphisms of type of such form. A functor to the comma category selects that particular collection of morphisms. This is described succinctly by an observation by S.A. Huq
that a natural transformation
, while objects of the comma category contains all morphisms of type of such form. A functor to the comma category selects that particular collection of morphisms. This is described succinctly by an observation by S.A. Huq
that a natural transformation  , with
, with  , corresponds to a functor
, corresponds to a functor  which maps each object
which maps each object  and maps each morphism
and maps each morphism