The following Comparison of Prolog implementations provides a reference for the relative feature sets and performance of different implementations of the Prolog computer programming language. A comprehensive discussion of the most significant Prolog systems is presented in an article published in the 50-years of Prolog anniversary issue of the journal Theory and Practice of Logic Programming (TPLP).
Portability
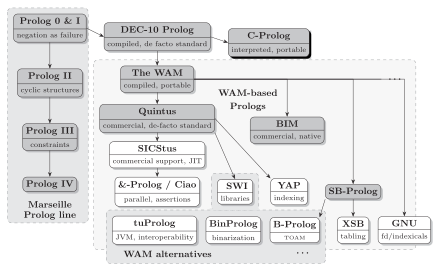
There are Prolog implementations that are radically different, with different syntax and different semantics (e.g. Visual Prolog) and sub-communities have developed around different implementations.
Code that strictly conforms to the ISO-Prolog core language is portable across ISO-compliant implementations. However, the ISO standard for modules is an extension which was not fully adopted in most Prolog systems.
Factors that can adversely affect portability include: use of bounded vs. unbounded integer arithmetic, additional types such as string objects, advanced numeric types (rationals, complex), feature extensions such as Unicode, threads, and tabling. Use of libraries unavailable in other implementations and library organisation:
Currently, the way predicates are spread over the libraries and system built-ins differs enormously. Fortunately, there are only few cases where we find predicates with the same name but different semantics (e.g.
delete/3)
Main features
| Platform | Features | Toolkit | Prolog Mechanics | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | OS | Licence | Native Graphics | Compiled Code | Unicode | Object Oriented | Native OS Control | Stand Alone Executable | C Interface | Java Interface | Interactive Interpreter | Debugger | Code Profiler | Syntax |
| AllegroProlog | Unix, Windows, Mac OS X | Proprietary (limited free edition available) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes, via Lisp | Yes | Yes, via Lisp | Yes, via Lisp | Yes | Yes | Yes, via Lisp | S-expressions. Full Common Lisp integration. | |
| BProlog | Unix, Windows, Mac OS X | Proprietary (free for non-commercial uses) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog, plus event-handling, CLP(FD), and tabling | |
| Ciao | Unix, Windows, Mac OS X | GPL, LGPL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog, plus extensions | ||
| DOS-Prolog | MS-DOS | Proprietary | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Edinburgh Prolog | |||||
| ECLiPSe | Linux, Windows, Solaris, macOS | MPL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Extended Prolog, Multi-dialect, including ISO | ||||
| GNU Prolog | Unix, Windows, Mac OS X | GPL, LGPL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog | |||||
| JIProlog | JVM, Android | AGPL (commercial support available) | Yes | Yes | Yes via Java | Yes | Yes via Java | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog | |||
| JLog | JVM | GPL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog | |||||||
| JScriptLog | Web Browser | GPL | Yes | ISO-Prolog | ||||||||||
| jTrolog | JVM | LGPL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog | |||||||
| WIN-Prolog | Windows | Proprietary | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Edinburgh Prolog with extensions |
| Open Prolog | Mac OS | Freeware | Yes | |||||||||||
| Poplog Prolog | Linux (32- and 64-bit), Unix, Windows | Free Open Source | Only through POP-11, on Linux | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Edinburgh Prolog, with interfaces to Poplog Common Lisp and Pop-11 | ||||
| Scryer Prolog | Linux, Windows, macOS | BSD License | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog | |||||||||
| SICStus Prolog | Unix, Linux, Windows, macOS | Proprietary | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog |
| Strawberry Prolog | Windows, Unix | Freeware | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Not ISO-Prolog + extensions | ||||||
| SWI-Prolog | Unix, Linux, Windows, macOS | BSD License | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog, Edinburgh Prolog | |
| tuProlog | JVM, Android | LGPL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog | |||||
| Visual Prolog | Windows | Freeware | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| XSB Prolog | Linux, Windows, Solaris, macOS | LGPL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ISO-Prolog, tabled WFS | ||
| YAP-Prolog | Linux, Windows, Solaris, Mac OS X, HP-UX | GPL or Artistic (user choice) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Edinburgh, ISO-Prolog, Quintus and SICStus Prolog compatible | |||
Operating system and web-related features
| OS-related | Web-related | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Conditional compilation | Sockets | Multi-threading | Tabling | HTTP client | HTTP server | HTML Parser | RDF Triple store |
| BProlog | Yes | |||||||
| Ciao | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| ECLiPSe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| GNU Prolog | Yes | |||||||
| WIN-Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Scryer Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| SICStus Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| SWI-Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Visual Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| XSB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| YAP-Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
Static analysis
| Name | Type checker | Determinacy checker | Call-pattern checker |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ciao | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| GNU Prolog | |||
| SICStus Prolog | Yes | ||
| SWI-Prolog | Yes | ||
| Visual Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| XSB | |||
| YAP-Prolog |
Optimizations
| Name | Tail-Call Optimization | Choice Point Elimination | Environment Trimming | Just-in-Time Indexing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ciao | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| ECLiPSe | Yes | Yes | Yes | multi-argument (compile time) |
| GNU Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| SICStus Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| SWI-Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Visual Prolog | Yes (compile time) | Yes (compile time) | N/A | N/A (compile time) |
| XSB | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| YAP-Prolog | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Release
| Name | Version | Date |
|---|---|---|
| AllegroProlog | 1.1.2 | 2018-12-12 |
| BProlog | 8.1 | 2014-02-23 |
| JIProlog | 4.1.7.1 | 2021-08-26 |
| Ciao | 1.22 | 2022-09-28 |
| DOS-Prolog | 8.0 | |
| ECLiPSe | 7.1 | 2023-01-01 |
| GNU Prolog | 1.5.0 | 2023-02-21 |
| JLog | 1.3.6 | 2007-09-13 |
| JScriptLog | 0.7.5 beta | 2007-09-10 |
| jTrolog | ||
| WIN-Prolog | 8.0 | 2022-07-14 |
| Open Prolog | ||
| Poplog Prolog | V16 | 2020-01-06 |
| Scryer Prolog | 0.9.3 | 2023-11-02 |
| SICStus Prolog | 4.9.0 | 2023-12-18 |
| Strawberry Prolog | 6.1 | 2023-08-23 |
| SWI-Prolog | 9.1.18 | 2023-11-01 |
| tuProlog | 2P-Kt 0.31.18 | 2023-10-24 |
| Visual Prolog | 10, Build 1000 | 2021-04-15 |
| XSB Prolog | 5.0 | 2022-05-15 |
| YAProlog | 7.1.0 | 2020-12-19 |
Benchmarks
- Benchmarking issues: Odd Prolog benchmarking, Performance differences.
- Benchmarking software: older, Dobry's Benchmarks, Aquarius benchmark suite, (Bothe, 1990), (Demoen et al. 2001), benchmark descriptions
- Benchmarking results: B-Prolog, SICStus, XSB, SICStus vs Yap vs hProlog
- Benchmarking results: Survey of java prolog engines by Michael Zeising
- Benchmarking results: OpenRuleBench yearly open-source benchmark of rule engines
Notes
References
- ^ Philipp Körner; Michael Leuschel; João Barbosa; Vítor Santos Costa; Verónica Dahl; Manuel V. Hermenegildo; Jose F. Morales; Jan Wielemaker; Daniel Diaz; Salvador Abreu; Giovanni Ciatto (November 2022), "Fifty Years of Prolog and Beyond", Theory and Practice of Logic Programming, 22 (6), doi:10.1017/S1471068422000102, hdl:10174/33387
- ^ Wielemaker, J.; Costa, V. T. S. (2011). "On the Portability of Prolog Applications". Practical Aspects of Declarative Languages. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 6539. pp. 69–83. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.1030.9396. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-18378-2_8. ISBN 978-3-642-18377-5.
- Jan Wielemaker and Vıtor Santos Costa: Portability of Prolog programs: theory and case-studies. CICLOPS-WLPE Workshop 2010 Archived 2010-07-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- "DOS-Prolog 8.0". Logic Programming Associates. 5 November 2023.
- ^ "JLog Homepage". jlogic.sourceforge.net. Retrieved 2023-11-03.
- "Jtrolog — Java.net". 2012-11-13. Archived from the original on 2012-11-13. Retrieved 2023-11-03.
- "WIN-Prolog 8.0". Logic Programming Associates. 5 November 2023.
- B. Demoen, and P. Nguyen, About unnecessary performance differences between Prolog implementations, Proceedings of the Colloquium on Implementation of Constraint and Logic Programming Systems (CICLOPS 2001)
- Bothe, K. (1990). "A prolog space benchmark suite". ACM SIGPLAN Notices. 25 (12): 54–60. doi:10.1145/122193.122197.
- A Summary of XSB Performance (1993)
- Demoen, B.; Nguyen, P. L.; Vandeginste, R. (2002). "Copying Garbage Collection for the WAM: to Mark or Not to Mark?". Logic Programming. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 2401. pp. 194–208. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.13.2586. doi:10.1007/3-540-45619-8_14. ISBN 978-3-540-43930-1.
External links
- Overview of Prolog Systems by Ulrich Neumerkel
- Conformity assessment I: Syntax