| Crooked Creek | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Country | Tioga County, Pennsylvania, United States |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Chatham Township |
| • elevation | 1,979 ft (603 m) |
| Mouth | |
| • location | Tioga River Tioga, |
| Length | 26.3 mi (42.3 km) |
| Basin size | 123 sq mi (320 km) |
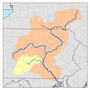
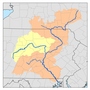
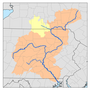
Crooked Creek is a 26.3-mile-long (42.3 km) tributary of the Tioga River located entirely in Tioga County, Pennsylvania in the United States.
Geography
The source is southwest of the unincorporated village of Little Marsh in Chatham Township at an elevation of 1,979 feet (603 m). The creek first flows east for 15 miles (24 km), then northeast for 9 miles (14 km). The mouth is at the confluence with the Tioga River, just north of the borough of Tioga, at an elevation of 1,018 ft (310 m).
The difference in elevation (961 ft (293 m) divided by the length of the creek of gives the average drop in elevation per unit length of creek or relief ratio of 39.1 ft/mi (7.4 m/km ). The meander ratio is 1.07, so despite its name, the creek is fairly straight in its bed.
Watershed
The watershed area is 123 sq mi (320 km), with a population of 4,570 as of 2000. Of that area, 79 sq mi (200 km) are forested, 51 sq mi (130 km) are given to agricultural uses, and 1 sq mi (2.6 km) is open water. The watershed accounts for 12.2% of Tioga County by area.
Hammond Reservoir
Crooked Creek has one major impoundment, the Hammond Reservoir, formed by a dam just before it enters the Tioga River. The lake has a surface area of 685 acres (2.77 km) and is administered by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, who built the Hammond Dam from 1973 to 1979. Built together with the adjoining Tioga Dam and Tioga Lake (on the Tioga River), the total project cost $200 million.
The dam projects were initially authorized by the United States Congress in the Flood Control Act of July 3, 1958 (Public Law 85-500). A channel connects the two lakes so that Hammond Lake (which has greater storage capacity) may be used to store excess (flood) water from Tioga Lake.
However, in addition to flood control on the Chemung and North Branch Susquehanna Rivers, the dams are also meant to help decrease the acidity of water in the Tioga River downstream of the dams by dilution with the more neutral waters of Crooked Creek. The Tioga River's acidity is caused by acid mine drainage.
The lakes also offer recreational opportunities, including camping, boating, fishing, swimming, and hiking on area trails.
See also
References
- U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map Archived 2012-03-29 at the Wayback Machine, accessed August 8, 2011
- Shaw, Lewis C. Pennsylvania Gazetteer of Streams Part II (Water Resources Bulletin No. 16). Prepared in Cooperation with the United States Department of the Interior Geological Survey (1st ed.). Harrisburg, PA: Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, Department of Environmental Resources (no ISBN).
- "Chesapeake Bay Program: Watershed Profiles: The Crooked Creek Watershed". Chesapeake Bay Program Office, 10 Severn Avenue, Suite 109, Annapolis, MD 21403. Archived from the original on 2011-05-16. Retrieved 2006-06-02.
External links
- U.S. Geological Survey: PA stream gaging stations
- Pennsylvania Department of Transportation Map of Tioga County showing Crooked Creek
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers page on Tioga-Hammond Lakes
- History of the Hammond-Tioga Dam Project
41°52′55″N 77°24′41″W / 41.88184°N 77.41138°W / 41.88184; -77.41138