| Relative key | F-flat major (theoretical) →enharmonic: E major |
|---|---|
| Parallel key | D-flat major |
| Dominant key | A-flat minor |
| Subdominant | G-flat minor (theoretical) →enharmonic: F-sharp minor |
| Enharmonic | C-sharp minor |
| Component pitches | |
| D♭, E♭, F♭, G♭, A♭, B | |
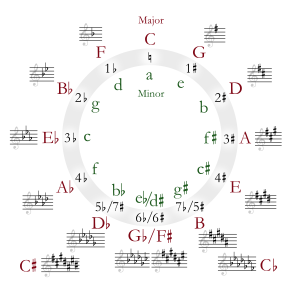
D-flat minor is a theoretical key based on D♭, consisting of the pitches D♭, E♭, F♭, G♭, A♭, B![]() , and C♭. Its key signature has eight flats, requiring one double flat and six single flats. Its relative major is F-flat major, which is usually replaced by E major. Its parallel major is D-flat major. Its direct enharmonic equivalent, C-sharp minor, is normally used.
, and C♭. Its key signature has eight flats, requiring one double flat and six single flats. Its relative major is F-flat major, which is usually replaced by E major. Its parallel major is D-flat major. Its direct enharmonic equivalent, C-sharp minor, is normally used.
The D-flat natural minor scale is:
Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The D-flat harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are:
D-flat minor is usually notated as the enharmonic key of C-sharp minor, as in the second and third measures of Amy Beach's Canticle of the Sun. However, unusually, two of Verdi's most well-known operas, La traviata and Rigoletto, both end in D-flat minor (although written with the five-flat key signature of the parallel major). Mahler's thematic motif "der kleine Appell" ("call to order") from his Fourth and Fifth Symphonies uses both notations: in his Symphony No. 4 (first movement) it is in D-flat minor, but in his Symphony No. 5 it is in C-sharp minor. In the Adagio of his Symphony No. 9, a solo bassoon interpolation following the main theme appears first in D-flat minor, returning twice more notated in C-sharp minor. Likewise, in the Adagio of Bruckner's Symphony No. 8, phrases that are tonally in D-flat minor are notated as C-sharp minor.
However, D-flat minor is used on Max Reger's On the Theory of Modulation on pp. 42–45, using the key signature.
Scale degree chords
The scale-degree chords of D-flat minor are:
- Tonic – D-flat minor
- Supertonic – E-flat diminished
- Mediant – F-flat major
- Subdominant – G-flat minor
- Dominant – A-flat minor
- Submediant – B-double-flat major
- Subtonic – C-flat major
See also
References
- Amy Beach & Betty Buchanan (2006). The Canticle of the Sun. A-R Editions, Inc. p. xiii. ISBN 0-89579-583-3.
- Ernst Levy (1985). A Theory of Harmony. SUNY Press. p. 62. ISBN 0-87395-993-0.
- James L. Zychowicz (2005). "Structural Considerations". Mahler's Fourth Symphony. Oxford University Press. p. 28. ISBN 0-19-816206-5.
- Eero Tarasti (1996). "Music history revisited". In Eero Tarasti; Paul Forsell; Richard Littlefield (eds.). Musical Semiotics in Growth. Indiana University Press. pp. 14–15. ISBN 0-253-32949-3.
- Theodor W. Adorno (1992). Mahler: A Musical Physiognomy. Translated by Edmund Jephcott. University of Chicago Press. pp. 165–166. ISBN 0-226-00769-3.
- Max Reger (1904). Supplement to the Theory of Modulation. Translated by John Bernhoff. Leipzig: C. F. Kahnt Nachfolger. pp. 42–45.
| Diatonic scales and keys | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||