| Danishmend | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1071/1075–1178 | |||||||||
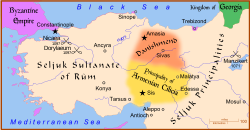 Anatolia in 1097, before the Siege of Nicaea Anatolia in 1097, before the Siege of Nicaea | |||||||||
| Capital | Sivas Niksar | ||||||||
| Common languages | Old Anatolian Turkish Medieval Greek | ||||||||
| Religion | Islam | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Bey, Ghazi, Melik | |||||||||
| • 1071/1075–1084 | Danishmend Gazi | ||||||||
| • 1175–1178 | Nasreddin Muhammed | ||||||||
| Historical era | High Medieval | ||||||||
| • Established | 1071/1075 | ||||||||
| • Disestablished | 1178 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Danishmendids or Danishmends (Turkish: Dânişmendliler) was a Turkoman Chepni founded beylik that ruled in north-central and eastern Anatolia from 1071/1075 to 1178. The dynasty centered originally around Sivas, Tokat, and Niksar in central-northeastern Anatolia, they extended as far west as Ankara and Kastamonu for a time, and as far south as Malatya, which they captured in 1103. In early 12th century, Danishmends were rivals of the Seljuk Sultanate of Rum, which controlled much of the territory surrounding the Danishmend lands, and they fought extensively against the Crusaders.
The dynasty was established by Danishmend Gazi for whom historical information is rather scarce and was generally written long after his death. His title or name, Dānishmand (دانشمند) means "wise man" or "one who searches for knowledge" in Persian.
Origins
The Turkoman Chepni Danishmendid dynasty was founded by Danishmend Gazi. Sources about Danishmend Gazi's origins however, are steeped in "legendary flavor". According to Robert Irwin, Danishmend Gazi was a "Turkoman emir of impenetrably obscure origins". For instance, according to Niketas Choniates, a Byzantine government official and historian and a near-contemporary of Danishmend Gazi, he was of Arsacid descent. According to the medieval Armenian historians Matthew of Edessa and Vardan Areveltsi, Danishmend Gazi was of Armenian origin, which, as Tahsin Yazici explains, "is not incompatible with Niketas' report". Yazici adds that other historians explained his origins differently. Some identified him as a nephew of Malik-Shah I (r. 1072–1092), Sultan of the Great Seljuk Empire. According to this narrative, Danishmend Gazi was sent by Malik-Shah to conquer Cappadocia. Others viewed Danishmend Gazi as a maternal uncle of Suleiman ibn Qutulmish (r. 1077–1086), the first ruler of the Sultanate of Rum. In addition, some historians believed he was one of the Seljuq commanders who fought at the Battle of Manzikert in 1071. According to Yazici: "Osman Turan's suggestion that he was a Seljuq envoy to the Ghaznavid court was based on a misunderstanding of a passage in Abu'l Fazl Bayhaqi's Tarikh-i Bayhaqi and is thus totally erroneous". According to Robert Gregory Bedrosian (citing Suren Yeremian and Halil Yinanc), Danishmend Gazi was an Armenian Muslim. The Danishmendnâme, a 14th century (i.e. posthumous) epic romance based on oral traditions dealing with Danishmend Gazi, is likewise filled with "legendary material". According to the Danishmendnâme, Danishmend Gazi was a native of Malatya.
History
The dynasty

As of 1134, Danishmend dynasty leaders also held the title Melik (the King) bestowed in recognition of their military successes by the Abbasid caliph Al-Mustarshid, although the Beys (Emirs) of Danishmend prior to 1134 may also be retrospectively referred to as Melik. Danishmend Gazi himself was alternatively called "Danishmend Taylu".
The Danishmends established themselves in Anatolia in the aftermath of the Battle of Manzikert in 1071, in which the Seljuks defeated the Byzantine Empire and captured most of Anatolia. Gazi took advantage of the dynastic struggles of the Seljuks upon the death of the Sultan Suleyman I of Rûm in 1086 to establish his own dynasty in central Anatolia. The capital was likely first established in Amasia.
In 1100, Gazi's son, Emir Gazi, captured Bohemond I of Antioch, who remained in their captivity until 1103. A Seljuk-Danishmend alliance was also responsible for defeating the Crusade of 1101.
In 1116, the Danishmends helped Mesud I become the Seljuk sultan.

In 1130, Bohemond II of Antioch was killed in a battle with Emir Gazi, after coming to the aid of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, which Gümüshtigin had invaded. Gümüshtigin died in 1134 and his son and successor Melik Mehmed Gazi did not have the martial spirit of his father and grandfather. He is nevertheless considered the first builder of Kayseri as a Turkish city, despite his relatively short period of reign.
When Mehmed died in 1142, the Danishmend lands were divided between his two brothers, Melik Yaghibasan, who maintained the title of "Melik" and ruled from Sivas, and Ayn el-Devle, who ruled from Malatya.
In 1155, Seljuk Sultan Kilij Arslan II attacked Melik Yaghibasan, who sought help from Nur ad-Din, the Zengid emir of Mosul. However, when Nur ad-Din died in 1174, the Sivas lands were incorporated into the Sultanate.
Following the death of Fahreddin in a riding accident in 1172, he was succeeded by his brother Afridun. By 1175, Nasreddin Muhammed had returned to power, and ruled as a Seljuk vassal. In 1178, Malatya was occupied. This event marked the end of the Danishmend rule, while the remaining Danishmends joined Seljuk service.
Culture and legend
Danishmend Gazi, the founder of the dynasty, is the central figure of a posthumous romance epic, Danishmendnâme, in which he is misidentified with an 8th-century Arab warrior, Sidi Battal Gazi, and their exploits intertwined.
Virtually all Danishmend rulers entered the traditions of the Turkish folk literature, where they are all referred to as "Melik Gazi". Hence, there are "tombs of Melik Gazi", many of which are much visited shrines and belong in fact to different Danishmend rulers, in the cities of Niksar, Bünyan, Kırşehir, along the River Zamantı near the castle of the same name (Zamantı) and elsewhere in Anatolia, and Melikgazi is also the name of one of the central districts of the city of Kayseri. The same uniformity in appellations in popular parlance may also apply to other edifices built by Danishmends.
The official title of the Danishmendids was Malik of All Romania and the East/Anatolia, was always inscribed in the local currency in Greek, indication of Byzantine influence. The Danishmend's coins, along with being bilingual, included an image of a figure slaying a dragon, thought to represent St. George.
Rulers
| Danishmends | Reign | Notes |
| Danishmend Gazi | 1075 -d. 1084 | Also called Danishmend Taylu |
| Gazi Gümüshtigin | 1084-d. 1104 | Son of Danishmend Gazi |
| Emir Gazi | 1104-d. 1134 | |
| Melik Mehmed Gazi | 1134-d. 1142 | |
| Sivas branch (Meliks - The Kings) | 1142–1175 | Incorporated to Anatolian Seljuks |
| Melik Zünnun (first rule) | 1142–1143 | Son of Melik Mehmed Gazi |
| Yağıbasan | 1143–1164 | Son of Emir Gazi |
| Melik Mücahid Gazi | 1164–1166 | |
| Melik İbrahim | 1166-1166 | |
| Melik İsmail | 1166-1172 | Killed in palace revolt. |
| Melik Zünnun (second rule) | 1172–1174 | Son of Melik Mehmed Gazi |
| Malatya branch (Emirs) | 1142–1178 | Incorporated to Anatolian Seljuks |
| Ayn el-Devle | 1142–1152 | |
| Zülkarneyn | 1152–1162 | |
| Nasreddin Muhammed | 1162–1170 | |
| Fahreddin | 1170–1172 | |
| Efridun | 1172–1175 | |
| Nasreddin Muhammed | 1175–1178 | Second reign |
See also
Notes
- According to Yeremyan, Danishmend Gazi was originally named Hrahat/Rat/Rati, supposedly a scion of the Armeno-Georgian Liparitid and Orbelian noble houses. Yinanc, who according to Bedrosian "probably" followed an 18th century Armenian historian, suggested that Danishmend Gazi was possibly an Armenian captive of war.
References
- The New Islamic Dynasties: A Chronological and Genealogical Manual, Clifford Edmund Bosworth, Edinburgh University Press, p.215, Online
- ^ Yazici 1993, pp. 654–655.
- ^ Irwin 2014, p. 304.
- Eddé, Anne-Marie (2005). "Seljuks". In Vauchez, André (ed.). Oxford Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages. doi:10.1093/acref/9780227679319.001.0001. ISBN 9780227679319.
- Morton, Nicholas (2010). "Crusades". In Rogers, Clifford J. (ed.). The Oxford Encyclopedia of Medieval Warfare and Military Technology. p. 466. doi:10.1093/acref/9780195334036.001.0001. ISBN 9780195334036.
- Bedrosian 1979, p. 85.
- ^ Bedrosian 1979, p. 85 (note 2).
- Anetshofer 2015.
- Claude Cahen cited in Donald Sidney Richards (2006). The Chronicle of Ali ibn al-Athir for the Crusading Period. Ashgate Publishing Inc. ISBN 978-0-7546-4077-6.
- Fisher, p. 8.
- "Turkmen Ruling Dynasties in Asia Minor".
- "Copper alloy dirham of Nasir al-Din Muhammad, Malatya, 557-73 H. 1917.215.840". numismatics.org. American Numismatic Society.
- ^ Danishmendids, I. Melikoff, The Encyclopaedia of Islam, ed. B. Lewis, C. Pellat and J. Schacht, (Brill, 1986), 111.
- Dr. Mürselin Güney. "History of Ünye" (in Turkish).
All Danishmend rulers are referred to as "Melik Gazi" by the general public
- Bryer, Anthony (1980). The Empire of Trebizond and the Pontos. Historical Journal, University of Birmingham. p. 170.
- Ocak, Murat (2002). The Turks: Middle ages. p. 202. ISBN 9789756782576.
- Christian Elements in the Identity of the Anatolian Turkmens (12th-13th Centuries), Rustam Shukurov, Cristianità d'occidente e cristianità d'oriente (secoli VI-XI), CISAM. Spoleto, 2004), 707-64; Khidr and the Changing Frontiers of the Medieval World, Ethel Sara Wolper, Confronting the Borders of Medieval Art, ed. Jill Caskey, Adam S. Cohen, Linda Safran, (Brill, 2011), 136.
Sources
- Anetshofer, Helga (2015). "Danişmendname". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam (3rd ed.). Brill Online. doi:10.1163/1573-3912_ei3_COM_27712. ISSN 1873-9830.
- Oktay Aslanapa (1991). Anadolu'da ilk Türk mimarisi: Başlangıcı ve gelişmesi (Early Turkish architecture in Anatolia: Beginnings and development) (in Turkish). AKM Publications, Ankara. ISBN 978-975-16-0264-0. Archived from the original on 2007-09-30.
- Bedrosian, Robert Gregory (1979). The Turco-Mongol Invasions and the Lords of Armenia in the 13th-14th Centuries. Columbia University Press.
- Clifford Edmund Bosworth (2004). The New Islamic Dynasties: A Chronological and Genealogical Manual. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0-7486-2137-8.
- Fisher, Sydney Nettleton (2000). The Foreign Relations of Turkey 1481-1512. Electronic Journal of Oriental Studies.
- Irwin, Robert (2014). "The Impact of the Early Crusades on the Muslim World". In Stuckey, Jace (ed.). The Eastern Mediterranean Frontier of Latin Christendom. Routledge. ISBN 978-1472422750.
- "Turkmen Ruling Dynasties in Asia Minor"
- Yazici, Tahsin (1993). "DĀNEŠMAND". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. VI, Fasc. 6. pp. 654–655.
External links
- "Danishmend Gazi (Melik Gazi) Tomb in Niksar (fact sheet)". ArchNet. Archived from the original on 2007-04-05.
- Prof. Dr. Mehmet Eti. "Specimens of Danishmend numismatics". Archived from the original on 2007-07-21.
- Mustafa Güler, İlknur Aktuğ Kolay. "12. yüzyıl Anadolu Türk Camileri (12th century Turkish mosques in Anatolia)" (PDF) (in Turkish). Istanbul Technical University Magazine (İtüdergi). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-07-04.
| History |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geography |
| ||||||||||||
| Government |
| ||||||||||||
| Economy | |||||||||||||
| Demographics | |||||||||||||
| Society |
| ||||||||||||
| Seljuk Sultanate of Rum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History of Anatolia | |
|---|---|
 |
| States in late medieval Anatolia (after 1071) | |
|---|---|
| Muslim states |
|
| Christian states | |
Categories: