| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Deadweight loss" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In economics, deadweight loss is the loss of societal economic welfare due to production/consumption of a good at a quantity where marginal benefit (to society) does not equal marginal cost (to society) – in other words, there are either goods being produced despite the cost of doing so being larger than the benefit, or additional goods are not being produced despite the fact that the benefits of their production would be larger than the costs. The deadweight loss is the net benefit that is missed out on. While losses to one entity often lead to gains for another, deadweight loss represents the loss that is not regained by anyone else. This loss is therefore attributed to both producers and consumers.
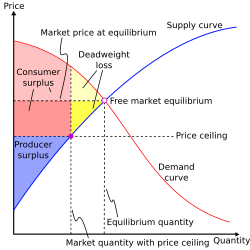
Deadweight loss can also be a measure of lost economic efficiency when the socially optimal quantity of a good or a service is not produced. Non-optimal production can be caused by monopoly pricing in the case of artificial scarcity, a positive or negative externality, a tax or subsidy, or a binding price ceiling or price floor such as a minimum wage.
Examples
Assume a market for nails where the cost of each nail is $0.10. Demand decreases linearly; there is a high demand for free nails and zero demand for nails at a price per nail of $1.10 or higher. The price of $0.10 per nail represents the point of economic equilibrium in a competitive market.
Monopoly
If market conditions are perfect competition, producers would charge a price of $0.10, and every customer whose marginal benefit exceeds $0.10 would buy a nail. A monopoly producer of this product would typically charge whatever price will yield the greatest profit for themselves, regardless of lost efficiency for the economy as a whole. In this example, the monopoly producer charges $0.60 per nail, thus excluding every customer from the market with a marginal benefit less than $0.60. The deadweight loss due to monopoly pricing would then be the economic benefit foregone by customers with a marginal benefit of between $0.10 and $0.60 per nail. The monopolist has "priced them out of the market", even though their benefit exceeds the true cost per nail.
Subsidy
Conversely, deadweight loss can also arise from consumers buying more of a product than they otherwise would based on their marginal benefit and the cost of production. For example, if in the same nail market the government provided a $0.03 subsidy for every nail produced, the subsidy would reduce the market price of each nail to $0.07, even though production actually still costs $0.10 per nail. Consumers with a marginal benefit of between $0.07 and $0.10 per nail would then buy nails, even though their benefit is less than the real production cost of $0.10. The difference between the cost of production and the purchase price then creates the "deadweight loss" to society.
Tax
A tax has the opposite effect of a subsidy. Whereas a subsidy entices consumers to buy a product that would otherwise be too expensive for them in light of their marginal benefit (price is lowered to artificially increase demand), a tax dissuades consumers from a purchase (price is increased to artificially lower demand). This excess burden of taxation represents the lost utility for the consumer. A common example of this is the so-called sin tax, a tax levied against goods deemed harmful to society and individuals. For example, "sin taxes" levied against alcohol and tobacco are intended to artificially lower demand for these goods; some would-be users are priced out of the market, i.e. total smoking and drinking are reduced. Products such as alcohol and tobacco have historically been highly taxed and incur excise duties which are one of the categories of indirect tax. Indirect tax (VAT), weighs on the consumer, is not a cause of loss of surplus for the producer, but affects consumer utility and leads to deadweight loss for consumers. Indirect taxes are usually paid by large entities such as corporations or manufacturers but are partially shifted towards the consumer. Furthermore, indirect taxes can be charged based on the unit price of a said commodity or can be calculated based on a percentage of the final retail price. Additionally, indirect taxes can either be collected at one stage of the production and retail process or alternatively can be charged and collected at multiple stages of the overall production process of a commodity.
Harberger's triangle

Harberger's triangle, generally attributed to Arnold Harberger, shows the deadweight loss (as measured on a supply and demand graph) associated with government intervention in a perfect market. Mechanisms for this intervention include price floors, caps, taxes, tariffs, or quotas. It also refers to the deadweight loss created by a government's failure to intervene in a market with externalities.
In the case of a government tax, the amount of the tax drives a wedge between what consumers pay and what producers receive, and the area of this wedge shape is equivalent to the deadweight loss caused by the tax.
The area represented by the triangle results from the fact that the intersection of the supply and the demand curves are cut short. The consumer surplus and the producer surplus are also cut short. The loss of such surplus is never recouped and represents the deadweight loss.
Some economists like Martin Feldstein maintain that these triangles can seriously affect long-term economic trends by pivoting the trend downwards and causing a magnification of losses in the long run but others like James Tobin have argued that they do not have a huge impact on the economy.
Hicks vs. Marshall
The Hicksian (per John Hicks) and the Marshallian (per Alfred Marshall) demand function differ about deadweight loss. After the consumer surplus is considered, it can be shown that the Marshallian deadweight loss is zero if demand is perfectly elastic or supply is perfectly inelastic. However, Hicks analyzed the situation through indifference curves and noted that when the Marshallian demand curve is perfectly inelastic, the policy or economic situation that caused a distortion in relative prices has a substitution effect, i.e. is a deadweight loss.
In modern economic literature, the most common measure of a taxpayer's loss from a distortionary tax, such as a tax on bicycles, is the equivalent variation, the maximum amount that a taxpayer would be willing to forgo in a lump sum to avoid the tax. The deadweight loss can then be interpreted as the difference between the equivalent variation and the revenue raised by the tax. The difference is attributable to the behavioral changes induced by a distortionary tax that are measured by the substitution effect. However, that is not the only interpretation, and Pigou did not use a lump sum tax as the point of reference to discuss deadweight loss (excess burden).
Taxation

When a tax is levied on buyers, the demand curve shifts downward in accordance with the size of the tax. Similarly, when tax is levied on sellers, the supply curve shifts upward by the size of tax. When the tax is imposed, the price paid by buyers increases, and the price received by seller decreases. Therefore, buyers and sellers share the burden of the tax, regardless of how it is imposed. Since a tax places a "wedge" between the price buyers pay and the price sellers get, the quantity sold is reduced below the level that it would be without tax. To put it another way, a tax on a good causes the size of market for that good to decrease.
For example, suppose that Will is a cleaner who is working in the cleaning service company and Amie hired Will to clean her room every week for $100. The opportunity cost of Will's time is $80, while the value of a clean house to Amie is $120. Hence, each of them get same amount of benefit from their deal. Amie and Will each receive a benefit of $20, making the total surplus from trade $40.
However, if the government were to decide to impose a $50 tax upon the providers of cleaning services, their trade would no longer benefit them. Amie would not be willing to pay any price above $120, and Will would no longer receive a payment that exceeds his opportunity cost. As a result, not only do Amie and Will both give up the deal, but Amie has to live in a dirtier house, and Will does not receive his desired income. They have thus lost amount of the surplus that they would have received from their deal, and at the same time, this made each of them worse off to the tune of $40 in value.
Government revenue is also affected by this tax: since Amie and Will have abandoned the deal, the government also loses any tax revenue that would have resulted from wages. This $40 is referred to as the deadweight loss. It causes losses for both buyers and sellers in a market, as well as decreasing government revenues. Taxes cause deadweight losses because they prevent buyers and sellers from realizing some of the gains from trade.
In the graph, the deadweight loss can be seen as the shaded area between the supply and demand curves. While the demand curve shows the value of goods to the consumers, the supply curve reflects the cost for producers. As the example above explains, when the government imposes a tax upon taxpayers, the tax increases the price paid by buyers to and decreases price received by sellers to . Buyers and sellers (Amie and Will) give up the deal between them and exit the market. Thus, the quantity sold reduces from to . The deadweight loss occurs because the tax deters these kinds of beneficial trades in the market.
Determinants
Price elasticities of supply and demand determine whether the deadweight loss from a tax is large or small. This measures to what extent quantity supplied and quantity demanded respond to changes in price. For instance, when the supply curve is relatively inelastic, quantity supplied responds only minimally to changes in the price. However, when the supply curve is more elastic, quantity supplied responds significantly to changes in price. In other words, when the supply curve is more elastic, the area between the supply and demand curves is larger. Similarly, when the demand curve is relatively inelastic, deadweight loss from the tax is smaller, comparing to more elastic demand curve.
A tax results in deadweight loss as it causes buyers and sellers to change their behaviour. Buyers tend to consume less when the tax raises the price. When the tax lowers the price received by sellers, they in turn produce less. As a result, the overall size of the market decreases below the optimum equilibrium. The elasticities of supply and demand determine to what extent the tax distorts the market outcome. As the elasticities of supply and demand increase, so does the deadweight loss resulting from a tax.
Variation based on taxes
Taxes may be changed by the government or policymakers at different levels. For instance, when a low tax is levied, the deadweight loss is also small (compared to a medium or high tax). An important consideration is that the deadweight loss resulting from a tax increases more quickly than the tax itself; the area of the triangle representing the deadweight loss is calculated using the area (square) of its dimension. Where a tax increases linearly, the deadweight loss increases as the square of the tax increase. This means that when the size of a tax doubles, the base and height of the triangle double. Thus, doubling the tax increases the deadweight loss by a factor of 4.
The varying deadweight loss from a tax also affects the government's total tax revenue. Tax revenue is represented by the area of the rectangle between the supply and demand curves. When a low tax is levied, tax revenue is relatively small. As the size of the tax increases, tax revenue expands. However, when a much higher tax is levied, tax revenue eventually decreases. The higher tax reduces the total size of the market; Although taxes are taking a larger slice of the "pie", the total size of the pie is reduced. Just as in the nail example above, beyond a certain point, the market for a good will eventually decrease to zero.
Monopolies
A deadweight loss occurs with monopolies in the same way that a tax causes deadweight loss. When a monopoly, as a "tax collector", charges a price in order to consolidate its power above marginal cost, it drives a "wedge" between the costs born by the consumer and supplier. Imposing this effective tax distorts the market outcome, and the wedge causes a decrease in the quantity sold, below the social optimum. It is important to remember the difference between the two cases: whereas the government receives the revenue from a genuine tax, monopoly profits are collected by a private firm.
See also
References
- Dickson, Vaughan; He, Jian (1997). "Optimal Concentration and Deadweight Losses in Canadian Manufacturing". Review of Industrial Organization. 12 (5/6): 719–732. doi:10.1023/A:1007714502964. S2CID 150473969.
- "Negative Externality". Retrieved February 11, 2012.
- Gruber, Jonathan (2013). Public Finance and Public Policy. New York: Worth Publishers. ISBN 978-1-4292-7845-4.
- Lind and Granqvist (2010)
- ^ N. Mankiw-David Hakes (2012). Principles of microeconomics. South-Western Cengage Learning.
Further reading
- Case, Karl E.; Fair, Ray C. (1999). Principles of Economics (5th ed.). Prentice-Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-961905-2.
- Hines, James R. Jr. (1999). "Three Sides of Harberger Triangles" (PDF). Journal of Economic Perspectives. 13 (2): 167–188. doi:10.1257/jep.13.2.167..
- Lind, H.; Granqvist, R. (2010). "A Note on the Concept of Excess Burden". Economic Analysis and Policy. 40 (1): 63–73. doi:10.1016/S0313-5926(10)50004-3.
 and decreases price received by sellers to
and decreases price received by sellers to  and the quantity sold reduces from
and the quantity sold reduces from  to
to  .
.