| Denticulate ligaments | |
|---|---|
 The medulla spinalis and its membranes. (Ligamentum denticulatum labeled vertically at bottom left.) The medulla spinalis and its membranes. (Ligamentum denticulatum labeled vertically at bottom left.) | |
 Diagrammatic transverse section of the medulla spinalis and its membranes. (Denticulate ligament not labeled, but region is visible.) Diagrammatic transverse section of the medulla spinalis and its membranes. (Denticulate ligament not labeled, but region is visible.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamentum denticulatum |
| TA98 | A14.1.01.310 |
| TA2 | 5411 |
| FMA | 71245 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
Denticulate ligaments (also known as dentate ligaments) are lateral projections of the spinal pia mater forming triangular-shaped ligaments that anchor the spinal cord along its length to the dura mater on each side. There are usually 21 denticulate ligaments on each side, with the uppermost pair occurring just below the foramen magnum, and the lowest pair occurring between spinal nerve roots of T12 and L1. The denticulate ligaments are traditionally believed to provide stability for the spinal cord against motion within the vertebral column.
Their tooth-like appearance originates the word which derives from Latin denticulatus, from denticulus (meaning ‘small tooth’).
Anatomy
The bases of denticulate ligaments arise in the pia mater and are firmly attached to the arachnoid mater and dura mater at the apex. The denticulate ligaments extend across the subarachnoid space between anterior nerve roots and posterior nerve roots, piercing the intervening spinal arachnoid mater to reach the dura.
Structure
Each denticulate ligament is composed of a single narrow fibrous strip that extends from the craniovertebral junction to T12. Each ligament features 18-20 triangular extensions that attach to the dura at their apices in between successive nerve roots. The triangular extensions are smaller and more numerous at the cervical levels, and are larger and less numerous at the thoracic levels. The apices of the extensions attach to the dura via fibrous bands at cervical levels (each band 3–5 mm (0.12–0.20 in) long) and lower thoracic levels (21–26 mm (0.83–1.02 in) long), whereas they attach directly to the dura at upper thoracic levels.
These ligaments may be affected by altered motion and position of the vertebral segments.
Microanatomy/histology
The narrow fibrous strip of the denticulate ligament features longitudinally oriented collagen fibers, whereas the triangular extensions are composed of transverse and obliquely oriented collagen fibers. The collagen fibers are thicker and more abundant at the cervical than at the thoracic levels.
Biomechanics
Denticulate ligaments are characterised by high extensibility (on average 50% of their initial length) and relatively low force necessary to rupture them (around 1 N). Their strength, especially in cervical region, decreases in caudal orientation.
Clinical significance
From a clinical standpoint, denticulate ligaments do not play a significant role in lumbar spinal stenosis when compared to issues such as disc herniations, facet hypertrophy, shape of spinal canal, size of spinal canal, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, or degenerative joint disease resulting in bony osteophyte formation.
Additional images
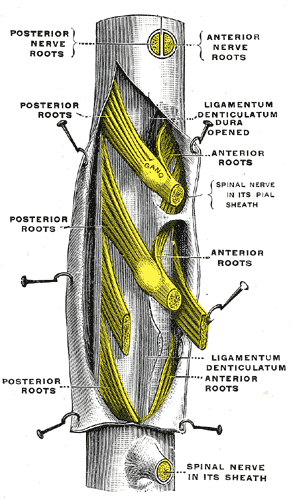 A portion of the spinal cord, showing its right lateral surface. The dura is opened and arranged to show the nerve roots.
A portion of the spinal cord, showing its right lateral surface. The dura is opened and arranged to show the nerve roots.
Sources
| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (May 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
- Polak K, Czyż M, Ścigała K, Jarmundowicz W, Będziński R (June 2014). "Biomechanical characteristics of the porcine denticulate ligament in different vertebral levels of the cervical spine — Preliminary results of an experimental study". Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. 34: 165–170. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.02.010. PMID 24583921.
- Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Moore, Keith and Arthur F. Dalley. Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2006.
- Tubbs RS, Salter G, Grabb PA, Oakes WJ (April 2001). "The denticulate ligament: anatomy and functional significance". Journal of Neurosurgery. 94 (2 Suppl): 271–5. doi:10.3171/spi.2001.94.2.0271. PMID 11302630.
- RC Schafer DC. Basic Principles of Chiropractic Neuroscience - Chapter 5; Neuroconceptual Models of Chiropractic ACA Press 1998.
- Ceylan D, Tatarlı N, Abdullaev T, et al. (July 2012). "The denticulate ligament: anatomical properties, functional and clinical significance". Acta Neurochirurgica. 154 (7): 1229–34. doi:10.1007/s00701-012-1361-x. PMID 22555553. S2CID 24391896.
See also
This article uses anatomical terminology.References
- ^ Sinnatamby, Chummy (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 453. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ Carpenter, Malcolm (1984). Core text of neuroanatomy (3rd ed.). Williams & Wilkins. p. 2. ISBN 978-0683014556.
- Denticulate. (n.d.) The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary. (2007). Retrieved March 8, 2021 from
- Polak (2014). "Biomechanical characteristics of the porcine denticulate ligament in different vertebral levels of the cervical spine—Preliminary results of an experimental study". J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 34: 165–70. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.02.010. PMID 24583921.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 02:05-03 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Coverings of the spinal cord."
| Meninges of the brain and spinal cord | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layers |
| ||||||||||||
| Spaces | |||||||||||||