
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name Dichloronickel | |
| Other names 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propanenickel(II) chloride; NiCl2(dppp) | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.628 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C27H26Cl2NiP2 |
| Molar mass | 542.05 g·mol |
| Appearance | Orange to red-orange powder |
| Melting point | 213 °C (415 °F; 486 K) |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H315, H317, H319, H334, H335, H350 |
| Precautionary statements | P201, P261, P280, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313 |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External SDS |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Dichloronickel a coordination complex with the formula NiCl2(dppp); where dppp is the diphosphine 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane. It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. The compound is a bright orange-red crystalline powder.
Structure and properties
While the electronic and solid-state structure of the chloride congener is not known (due to low solubility in common analytical solvents), several studies have been carried out on the bromo and iodo derivatives. The complexes display a temperature-dependent interconversion between square-planar and tetrahedral geometries (diamagnetic and paramagnetic) in polar organic solvents (Keq between 1-3.68, depending on the solvent and temperature). In contrast, dichloro(1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane)nickel adopts a static square-planar (diamagnetic) structure in solution.
Preparation
NiCl2(dppp) is prepared by combining equal molar portions of nickel(II) chloride hexahydrate with 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane in 2-propanol.
- Ni(H2O)6Cl2 + dppp → NiCl2(dppp) + 6 H2O
Reactions
NiCl2(dppp) in an effective catalyst for coupling reactions such as the Kumada coupling and Suzuki reactions (example below). It also catalyzes other reactions that convert enol ethers, dithioacetals, and vinyl sulfides to olefins.
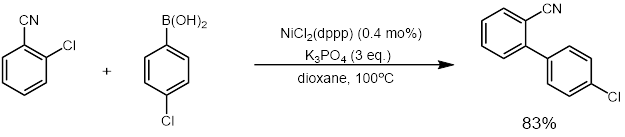
References
- ^ "1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane Nickel(II) Chloride". American Elements. Retrieved September 6, 2018.
- Van Hecke, Gerald R.; Horrocks, Jr., William DeW. (1966). "Ditertiary Phosphine Complexes of Nickel. Spectral, Magnetic, and Proton Resonance Studies. A Planar-Tetrahedral Equilibrium". Inorganic Chemistry. 5 (11): 1968–1974. doi:10.1021/ic50045a029.
- ^ Kumada, Makota; Tamao, Kohei; Sumitani, Koji (1978). "Phosphine-Nickel Complex Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Grignard Reagents with Aryl and Alkenyl Halides: 1,2-Dibutylbenzene". Org. Synth. 58: 127. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.058.0127.
- Zhao, Yu-Long; Li, You; Li, Shui-Ming; Zhou, Yi-Guo; Sun, Feng-Yi; Gao, Lian-Xun; Han, Fu-She (1 June 2011). "A Highly Practical and Reliable Nickel Catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling of Aryl Halides". Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis. 353 (9): 1543–1550. doi:10.1002/adsc.201100101.
- Tien-Yau Luh; Tien-Min Yuan. "Cross-Coupling Reactions". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd100.pub2.
- Ljungdahl, Thomas; Bennur, Timmanna; Dallas, Andrea; Emtenaes, Hans; Maartensson, Jerker (2008). "Two Competing Mechanisms for the Copper-Free Sonogashira Cross-Coupling Reaction". Organometallics. 27 (11): 2490–2498. doi:10.1021/om800251s.