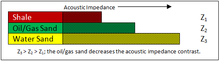
In reflection seismology, a dim spot is a local low-amplitude seismic attribute anomaly that can indicate the presence of hydrocarbons and is therefore known as a direct hydrocarbon indicator. It primarily results from the decrease in acoustic impedance contrast when a hydrocarbon (with a low acoustic impedance) replaces the brine-saturated zone (with a high acoustic impedance) that underlies a shale (with the lowest acoustic impedance of the three), decreasing the reflection coefficient.
Occurrence
For a dim spot to occur, the shale has to have a lower acoustic impedance than both the water sand and the oil/gas sand, which is the opposite situation required for a bright spot to occur. This is possible because compaction causes the acoustic impedances of sands and shales to increase with age and depth but it does not happen uniformly – younger shales have a higher acoustic impedance than younger sands, but this reverses at depth, with older shales having a lower acoustic impedance than older sands.
Similarly to bright spots, not all dim spots are caused by the presence of hydrocarbons and therefore they should not be treated as conclusive evidence hydrocarbon accumulations.
See also
References
- dim spot, Energy Glossary
- Brown, Alistar. R., (2010), "Dim Spots in Seismic Images as Hydrocarbon Indicators", AAPG Search and Discovery Article #40514.
- Hilterman, Fred J., (2001), "Seismic Amplitude Interpretation", SEG.
This seismology article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |