| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Tanais" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Τάναϊς Танаис | |
 The archaeological park of Tanais. May 2017 The archaeological park of Tanais. May 2017 | |
  | |
| Location | Nedvigovka, Rostov Oblast, Russia |
|---|---|
| Region | Maeotian marshes |
| Coordinates | 47°16′8″N 39°20′6″E / 47.26889°N 39.33500°E / 47.26889; 39.33500 |
| Type | Settlement |
| History | |
| Builder | Settlers from Miletus |
| Founded | Late 3rd century BC |
| Abandoned | Second half of the 5th century AD |
| Periods | Hellenistic to Late Antiquity |
| Cultures | Greek, Sarmatian |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | Ruined |
| Ownership | Public |
| Public access | Yes |
| Website | museum-tanais |

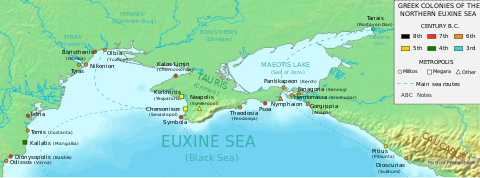
Tanais (Greek: Τάναϊς Tánaïs; Russian: Танаис) was an ancient Greek city in the Don river delta, called the Maeotian marshes in classical antiquity. It was a bishopric as Tana and remains a Latin Catholic titular see as Tanais.
Location
The delta reaches into the northeasternmost part of the Sea of Azov, which the Ancient Greeks called Lake Maeotis. The site of ancient Tanais is about 30 km west of modern Rostov-on-Don. The central city site lies on a plateau with a difference up to 20 m in elevation in the south. It is bordered by a natural valley to the east, and an artificial ditch to the west.
History
See also: Greeks in pre-Roman CrimeaThe site of Tanais was occupied long before the Milesians founded an emporium there. A necropolis of over 300 burial kurgans near the ancient city shows that the site had already been occupied since the Bronze Age, and that kurgan burials continued through Greek and into the Roman era.
Greek traders seem to have been meeting nomads in the district as early as the 7th century BC without a formal, permanent settlement. Greek colonies had two kinds of origins, apoikiai of citizens from the mother city-state, and emporia, which were strictly trading stations. Founded late in the 3rd century BC, by merchant adventurers from Miletus, Tanais quickly developed into an emporium at the farthest northeastern extension of the Hellenic cultural sphere. It was a natural post, first for the trade of the steppes reaching away eastwards in an unbroken grass sea to the Altai, the Scythian Holy Land, second for the trade of the Black Sea, ringed with Greek-dominated ports and entrepots, and third for trade from the impenetrable north, with furs and slaves brought down the Don. Strabo mentions Tanais in his Geography (11.2.2).
The site for the city, ruled by an archon, was at the eastern edge of the territory of the kings of Bosporus. A major shift in social emphasis is represented in the archaeological site when the propylaea gate that linked the port section with the agora was removed, and the open center of public life was occupied by a palatial dwelling in Roman times for the kings of Bosporus. For the first time there were client kings at Tanais: Sauromates (AD 175-211) and his son Rescuporides (c. AD 220), who both left public inscriptions.
In AD 330 Tanais was devastated by the Goths, but the site was occupied continuously up to the second half of the 5th century AD. Increasingly, the channel silted up, probably the result of deforestation, and the center of active life shifted, perhaps to the small city of Azov, halfway to Rostov.
The city was refounded around the 14th century by the Venetians. Later it was acquired by the maritime Republic of Genoa, who administered it 1332-1471 as Tana nel Mare Maggiore, being an important place for trade with the Golden Horde, like all their Black Sea colonies controlled by the Genoese Consul at Kaffa. It decayed again after 1368. In 1392 it was conquered by Timur, by the Ottoman Turks in 1471, by the Russians in 1696, again by the Turks in 1711 and by the Russian Empire in 1771.

Archaeology
See also: Russian cultural heritage registerIn 1823, I. A. Stempkovsky first made a connection between the visible archaeological remains, which were mostly Roman in date, and the "Tanais" mentioned in the ancient Greek sources.
Systematic modern excavations began in 1955. A joint Russian-German team has recently been excavating at the site of Tanais, with the aim of revealing the heart of the city, the agora, and defining the extent of Hellenistic influence on the urbanism of the Bosporan Greek city, as well as studying defensive responses to the surrounding nomadic cultures.
In the book Jakten på Odin, author Thor Heyerdahl advanced a highly controversial idea postulating connections between Tanais and ancient Scandinavia. In preparation of the book, he conducted some archaeological research on the site of Tanais. Heyerdal`s idea was based on the old Norse sagas of Snorri Sturlason. (1178 - 1241)
Tanais Tablets are the most important historical discoveries in region of Tanais.
Genetics
9 Y-chromosome markers were obtained from a skeleton. The result was 389I=13, 389II=30, 458=15, 385=11, 393=13, 391=11, 635=23, 437=14, 448=19. This result is characteristic for haplogroup R1a.
See also
- List of ancient Greek cities
- List of Catholic dioceses in Russia
- Tanais Tablets
- Tanais Archaeological Reserve Museum
Notes
- "The Population of Southern Russia Across the Ages (The Don Readings in Physical Anthropology): Collection of papers" (PDF). Russian academy of sciences.
References
- Crowley, Roger (2011). City of Fortune - How Venice Won and lost a Naval Empire. London: Faber and Faber. ISBN 978-0-571-24594-9.
External links
- (in Russian) Official website of the Tanais Archeological Reserve Museum
- GCatholic
- Information about the museum on the Russian Cultural Heritage Web Portal
- Bibliography
- Pius Bonifacius Gams, Series episcoporum Ecclesiae Catholicae, Leipzig 1931, p. 432
- Konrad Eubel, Hierarchia Catholica Medii Aevi, vol. 1, p. 471; vol. 2, p.
- Populated places established in the 3rd century BC
- Khazar towns
- Bosporan Kingdom
- Sarmatians
- Greek colonies on the Black Sea coast
- Archaeological sites in Russia
- Milesian Pontic colonies
- Defunct towns in Russia
- Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Russia
- Former populated places in Russia
- Stato da Màr
- Territories of the Republic of Genoa
- World Heritage Tentative List
- History of Rostov Oblast
- Cultural heritage monuments of federal significance in Rostov Oblast