| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Dioxobutanedioic acid | |
| Other names
Dioxosuccinic acid 2,3-Dioxosuccinic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 956740 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.622 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H2O6 |
| Molar mass | 146.054 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
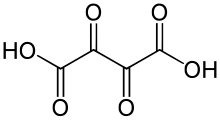
Dioxosuccinic acid or dioxobutanedioic acid is an organic compound with formula C4H2O6 or HO−(C=O)4−OH.
Removal of two protons from the molecule would yield the dioxosuccinate anion, C
4O
6 or O−(C=O)4−O. This is one of the oxocarbon anions, which consist solely of carbon and oxygen. The name is also used for salts containing that anion, and for esters with the moiety.
Removal of a single proton would result in the monovalent anion hydrogendioxosuccinate, C
4HO
6 or HO−(C=O)4−O.
Occurrence
Dioxosuccinic acid is one of the acids occurring naturally in wine, from the oxidation of tartaric acid via dihydroxyfumaric acid.
Reactions
The acid combines with two molecules of water to produce dihydroxytartaric acid, the ketone hydrate form, C4H6O8 or HO−(C=O)−(C(OH)2)2−(C=O)−OH. Indeed, the product traded under the name "dioxosuccinic acid hydrate" appears to be that substance.
Dihydroxytartaric acid behaves like dioxosuccinic acid in some reactions; for example, it reacts with ethanol in the presence of hydrogen chloride to yield the ester diethyl dioxosuccinate, upon isolation.
See also
- Mesoxalic acid
- Oxaloacetic acid (or oxosuccinic acid)
- Fumaric acid
References
- Ján Farkaš, Beatrix Farkaš (1988), Technology and Biochemistry of Wine. CRC Press, 744 pages. ISBN 2-88124-070-4.
- Victorian College of Pharmacy, Dept. of Chemistry (1959), Notes on qualitative analysis.