| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| This article may be a rough translation from Spanish. It may have been generated, in whole or in part, by a computer or by a translator without dual proficiency. Please help to enhance the translation. The original article is under "español" in the "languages" list.
See this article's entry on Pages needing translation into English for discussion. (June 2022) |
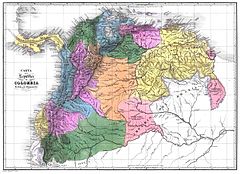 Departments of Gran Colombia in 1824 Departments of Gran Colombia in 1824 | |
| Date | April 30, 1826 – November 21, 1831 (1826-04-30 – 1831-11-21) |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Type | Dissolution of an administrative territorial entity |
| Outcome | Dissolution of Gran Colombia into the republics of Venezuela, Ecuador and New Granada |
The dissolution of Gran Colombia and the disintegration of its political structures and central government created three independent countries: the Republic of Venezuela, the Republic of Ecuador and the Republic of New Granada.
The main ideological leader of Gran Colombia was Simón Bolívar, known as the Liberator, who had wanted to create a nation strong enough to maintain its independence and compete economically with the European powers. It was the most ambitious dream of unity in Latin America.
Background
Gran Colombia was created in 1819 with the union of New Granada (today Colombia), Venezuela, Ecuador and Panama in an attempt to unite the peoples of northern South America into a single nation. Its constituent nations saw the new republic as a joining of forces to prevent the re-establishment of viceregal power, not a social, economic and political union of societies that were markedly dissimilar in their composition and the structure of their social power.

Before the union, some constituent countries had already tried other forms of government, notably federalism in the United Provinces of New Granada and the United Provinces of Venezuela. These experiments and their ensuing confrontations with other groups that were pro-Spanish or advocated a more centralized government caused them to fail and be reconquered by viceregal forces. Simón Bolívar concluded that a nation should be built with a solid unitary base in his Jamaica Letter.
After the Republic was formed, the differences of opinions between federalists and centralists, as well as the disparities between the regions and their differing interests, accelerated the dispute over Gran Colombia's form of government. As a form of concertation, he decided on the centralist system headed by Bolívar.
Quito and Panama had not had real representation in the 1821 constitutional deliberations in Villa del Rosario, because they didn't formally become part of Gran Colombia until 1822. Despite support for the Constitution of 1821 in Guayaquil, Quito and Caracas, many supported a federalist constitution that allowed regional control and freedom; in particular, the Venezuelan military hoped to exert more power in its region. Likewise, the heroes and leaders of Panama were businessmen linked to shipping and international traffic. Anglophiles for mercantile reasons, they professed Manchester liberalism and therefore supported state abstentionism, free trade and an essentially commercial economy.
The union of the four nations had never been solid due to their uneven economic development and the lack of connecting routes between the three regions of the country, in which cohesion was only maintained during the war years thanks to the prestige and will of Bolivar.
Members of the military had been given the right to vote in the Constitution of 1821 as recognition for their effort in Bolívar's campaign to liberate New Granada. In 1827 Congress made a constitutional change so that only officers could vote.
La Cosiata
As a result of the constant onslaught of royalist guerrillas and the prevailing fear of a supposed "Holy Alliance" between France and Spain to recover the American colonies, Francisco de Paula Santander decreed on 31 August 1824 a general enlistment of all citizens between 16 and 50 years old, demanding from the department of Venezuela a contingent of 50,000 men to be sent to Bogotá. General José Antonio Páez, who had been General Commander of the department since 1822, delayed the execution of the decree for almost a year, fearful not only of a general mutiny, but also to demonstrate his displeasure with the decisions of the central government.
After several uprisings in Venezuela due to forced enlistment, the continuous pressure from Bogotá to abide by the decree and also the intervention of influential leaders, including Miguel Peña, finally, José Antonio Páez declared a mutiny on 30 April 1826, assumed the government of Venezuela and committed himself to refusing orders from the central government in Bogotá.
Bolívar had been re-elected President and upon learning of the rebellion, left Lima for Venezuela on 4 September, arriving in Guayaquil on 12 September and Bogotá on 16 November, then heading to Cartagena and from there arrived by sea in Puerto Cabello on 31 December. Days later Bolívar met with Páez, reaffirmed the union, granted him a general amnesty and ratified him as civil and military chief of Venezuela. However, the divisions between Venezuelans and New Granadans grew in view of the delay in the constitutional reforms requested by the citizens, and intensified in subsequent years.
Bolívar returned to Santafé at the beginning of 1827, encountering strong resistance in the political circles around General Santander. The trust that he placed in his closest military collaborators, mostly Venezuelans and British, and their frequent excesses, added to the differences between Bolívar and the Congress, which convened a new Constituent Assembly. This assembly met on 9 April 1828 in Ocaña to elect the Constituent Congress that would reform the Constitution of Cúcuta, and was made up of representatives from the parishes. The inevitable confrontation between Bolivarians and Santander's followers took place: the Santanderistas (federalists) achieved a large representation while the Bolivarians decided to abandon the deliberations, for which a quorum was not achieved. Three months later the convention was closed without result.
This inability to exercise democracy and to resolve conflicts through dialogue, negotiation and voting, opting rather for abandonment, was a behavior that haunted the traditional parties during the 19th and 20th centuries, and generated violence. Despite everything, the members were appointed in the elections of 1 July 1828.
The Septembrine Conspiracy
Main article: Septembrine Conspiracy

On 27 August 1828, Bolivar assumed legislative powers and began a dictatorship, abolishing the vice presidency. Santander joined the opposition when he was removed from the government. Bolivar issued emergency economic decrees restoring abolished taxes and making customs tariffs more protectionist. He removed the teaching of Jeremy Bentham from education and dissolved Masonic organizations in an effort to appease belligerent opposition from the Catholic media. He also projected a constitution that included Peru and Bolivia (since the latter had already seceded from the Río de la Plata), with a strong central government and a presidency with dictatorial powers.
These measures created an atmosphere of tension, which finally set the Santanderistas on fire because they saw in that proposal a return to monarchy. Santander wrote to him expressing his disagreement
- "Furthermore, I have not fought fourteen years against Fernando VII to now have a king called Simón I". One faction reached the point of trying to assassinate the liberator on September 25 of the same year, a conspiracy in which a group of Granadan intellectuals participated, including the poet Luis Vargas Tejada [es], Florentino González [es], Mariano Ospina and Wenceslao Zulabair, accompanied by the Venezuelan military officer Pedro Carujo, Frenchman Agustín Horment and Portuguese adventurer Dr. Arganil, who entered the Palace of San Carlos, killed the soldiers of the guard and Bolívar's personal aide-de-camp. He, half-naked, protected by members of the servants and by Manuelita Sáenz, remained hidden for several hours under a bridge over the San Francisco River.
As a result of the Septembrine conspiracy, fourteen conspirators were put to death, among them Admiral José Prudencio Padilla, naval hero of the war of emancipation. Santander, to whom the intellectual authorship of the attack was attributed, was also sentenced to death, but his sentence was commuted to exile. He went to Europe as a political exile, from where he returned to assume the Presidency of New Granada in 1833, once the dissolution of Gran Colombia had been completed.
War with Peru and death of Bolivar
Main article: Gran Colombia–Peru WarTerritorial disputes over old, unclear colonial decrees led to the Gran Colombo-Peruvian war. Bolivar marched south and left the Council of Ministers, chaired by Domingo Caicedo, in power. Congress, meeting at the end of 1828, appointed General Antonio José de Sucre as interim president despite the merit that General Rafael Urdaneta had for the position. On June 4, 1830 Sucre was assassinated in the jungles of Berruecos, a premature end for a hero considered the political heir of the Liberator. His death caused great confusion, especially in politics. The constitution for Gran Colombia was also left without great defenders. Caicedo asked Congress not to ratify it without first making sure of its acceptance in Venezuela. However, it was sanctioned by Caicedo on May 15 (without consulting Caracas), three days after it was issued. The constitution triggered insubordination and agitation: battalions began due to ignorance of Bolívar's mandate over them, and the municipal councils of Pasto and Buenaventura, as well as that of Cauca, asked to be annexed by Ecuador. Cúcuta, Casanare and Pamplona also requested to be annexed, but by Venezuela. Criticism abounded from the inhabitants of Peru, who refused to be part of the dictatorship. Bolívar then resigned the presidency on May 4, 1830, leaving Domingo Caicedo as interim president. The next day, May 5, Congress approved a new constitution that maintained the unity of Gran Colombia but never entered into force.
Discontented military and liberal groups confronted government forces in the Funza savannah on August 27, 1830, which led to the dictatorship of General Urdaneta and the overthrow of Joaquín Mosquera. Finally, after being exiled from Venezuela and seeing his dream of a united America fall into disgrace, Simón Bolívar died on December 17, 1830.
Separation of Venezuela
After several years of attempts to reconcile the positions of the federalists and centralists, the separation of Venezuela began to materialize in 1826 with the La Cosiata movement of José Antonio Páez. Bolívar, seeing an imminent separation of that region from Gran Colombia, called a constituent assembly on 20 March 1830 in order to reconcile the different factions that were created in the Republic and avoid dissolution. This was called the Admirable Congress after the group of eminent persons who attended; Despite reconciling the various ideologies in a certain way, it was not possible to achieve the union of the regions around the command of Bogotá.
Before the Congress was held, popular assemblies in the cities of Valencia and Caracas on 23 and 25 November 1829 expressed their opinion on the form of government that the republic should have, the type of constitution and the form of election of the president of the nation. They agreed on the definitive secession of Venezuela from Bogotá and disregard of Bolívar's authority. A constituent congress was then called and installed in Valencia on 6 May 1830, characterized by its anti-Bolivarian tendency; This congress confirmed José Antonio Páez as president of Venezuela, declared the total autonomy of Venezuela and promulgated election regulations for the constituent congress.
On 22 September, the Congress of Valencia sanctioned the new constitution, and the separation of Venezuela from Gran Colombia was definitively consummated. Bolívar, sick and dying, passed from Cartagena to Soledad and from there to Barranquilla. On 1 December, he arrived by sea at Santa Marta, where on the 6th he was taken to the Quinta San Pedro Alejandrino, where he died on 17 December at the age of 47.
Separation of Ecuador
Quito, knowing that Venezuela had separated and that Bolívar was withdrawing definitively, decided to secede. With this, Gran Colombia vanished after 11 years of existence.
On 13 May 1830, the Southern District declared its independence from Colombia, forming the State of Ecuador. That day an Assembly of Notables met in Quito to resolve the separation of this region from Gran Colombia and form an independent State, although initially federated. From it emerged General Juan José Flores, originally from Venezuela, as Supreme Head of the Government.
The Quito Assembly arranged for Flores to manage the integration of the other southern departments since their governors were military under his command; so on 19 and 20 May, the Departments of Guayaquil and Azuay separated from Colombia to form the new State. For 14 August, Flores called a Constituent Assembly in the city of Riobamba to issue the Political Constitution of Ecuador; the assembly was made up of his supporters who named him Provisional President.
On 22 September 1830, the first Ecuadorian constitution was promulgated, which declared, among other articles, that the departments of Azuay, Guayaquil and Ecuador were united, and formed a single independent body with the name of the State of Ecuador. Juan José Flores assumed power as President of the new state and José Joaquín de Olmedo as Vice President.
With the definitive disappearance, in 1831, of Gran Colombia, Ecuador proclaimed itself a Republic with the Constitution of 1835.
Separations of Panama
See also: Separation of Panama from Colombia
After these dismemberments, Gran Colombia was made up only of the central region, which at that time included the departments of Boyacá, Cauca, Cundinamarca, Magdalena and Isthmus.
On 26 September 1830, the Department of the Isthmus (Panama) also separated from the Gran Colombian State. Its manager was the Panamanian General José Domingo Espinar [es], a mulatto of popular origin who did not share the preferences of the Panamanian oligarchy and was a great supporter of Bolívar, whose secretary he had been. Due to the crisis caused by the resignation of the liberator and the dismemberment of Gran Colombia, Espinar, supported by the masses of the capital's suburbs, rebelled against the prevailing government, waiting for Bolívar's return to power.
In consequence of what was proclaimed, a Panamanian delegation went to Barranquilla, where Bolívar was located, to invite him to the isthmus to resume power and rebuild the dismembered Gran Colombia. Bolívar declined the offer and advised his former secretary to reincorporate the isthmus into Colombia. This is how José Domingo Espinar proceeded, although soon another secessionist movement would take place.
The second separation was conceived by Venezuelan colonel Juan Eligio Alzuru [es] on 9 July 1831, who initially had the approval of the Panamanian oligarchy, both in the capital and in the interior. However, the methods of Alzuru were cruel and arbitrary, and endangered the interests of the Panamanian ruling class. To appease this movement and return order to the isthmus, the government of New Granada entrusted General Tomás de Herrera with confronting Alzuru and reincorporating the provinces under his mandate into the Republic, investing him with the rank of "Commander General of the Isthmus." Herrera managed to capture Alzuru and shot him on 29 August. Once Herrera was victorious, he was entrusted with the said territory.
Consequences
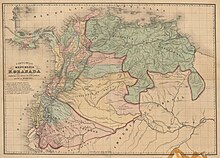
From 1830 in the middle of the separations of Ecuador (1830), Panama (1830 and 1831) and Venezuela (1830); the disintegration of the government of Gran Colombia and its political structures was precipitated. Being born as a consequence the State of Ecuador and the State of Venezuela; while Panama remained under dictatorial military governments that failed to organize the basic institutions of a State.
Through the Apulo Agreement (carried out on 28 April 1831), General Rafael Urdaneta, the last president of Gran Colombia, handed over command to Domingo Caicedo (3 May). He presided over it until 21 November, when it was legally abolished.
On 7 May, a convention was convened in the central departments of the former Gran Colombia, in which representatives from Cundinamarca, Cauca, Antioquia, Isthmus (Panama), Magdalena and Boyacá were to gather. They were to meet in Bogotá on 15 October. Panama joined the initiative after the fall of the dictatorial regime at the end of August 1831. The objective of this convention was to agree on a constitution for the central departments of the late Gran Colombia and elect the magistrates who should govern it. At the convention held on 20 October 1831, the State of New Granada was created, which with the Constitution of 1832 was officially called the Republic of New Granada.
References
- ^ "La Red Cultural del Banco de la República".
- ^ Blanco, Jacqueline (18 October 2007). "De La Gran Colombia a La Nueva Granada, Contexto Histórico - Político de La Transición Constitucional" (PDF). New Granada Military University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 December 2019. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- Bolivar, Simon (1 January 1965). Carta de Jamaica (in Spanish). NoBooks Editorial.
- Navarro, Alfredo Figueroa (1982). Dominio y sociedad en el Panamá colombiano (1821-1903): escrutinio sociológico (in Spanish). Editorial Universitaria.
- ^ "Etapas y Sentido de la Historia de Colombia" (PDF).
- Bolívar, Antonio Ecarri (2017). Miguel Peña y la Cosiata: Bolívar, Santander, Páez, Peña : relectura de una controversia histórica (in Spanish). IPAPEDI. ISBN 978-980-12-9713-0.
- The Last Dictatorship: Betrayal or Consummation?, David Bushnell, The Hispanic American Historical Review Vol. 63, No. 1 (Feb., 1983), pp. 65-105 (41 pages), Duke University Press https://doi.org/10.2307/2515359
- "cap2". www4.congreso.gob.pe. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- "Historia de Colombia - Colombia Info". www.colombia.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- ^ "leosociales - DISOLUCIÓN DE LA GRAN COLOMBIA.docx - Detail". 24 July 2018. Archived from the original on 24 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- "Proclamación de la separación de Venezuela de la Gran Colombia | banrepcultural.org". 16 October 2013. Archived from the original on 16 October 2013. Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- Picón, Delia (1999). Historia de la diplomacia venezolana: (1811-1985) (in Spanish). Universidad Catolica Andres. ISBN 978-980-244-204-1.
- ^ "13 de mayo de 1830; Nacimiento de la República del Ecuador". 7 June 2013. Archived from the original on 7 June 2013. Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- ^ Sosa, Juan Bautista (2003). Compendio de historia de Panamá: edición corregida del libro original de 1911 con un estudio preliminar de Carlos Manuel Gasteazoro (in Spanish). Editorial Universitaria. ISBN 978-9962-53-118-0.