
The United States federal earned income tax credit or earned income credit (EITC or EIC) is a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income working individuals and couples, particularly those with children. The amount of EITC benefit depends on a recipient's income and number of children. Low-income adults with no children are eligible. For a person or couple to claim one or more persons as their qualifying child, requirements such as relationship, age, and shared residency must be met.
EITC phases in slowly, has a medium-length plateau, and phases out more slowly than it was phased in. Since the credit phases out at 21% (more than one qualifying child) or 16% (one qualifying child), it is always preferable to have one more dollar of actual salary or wages considering the EITC alone. However, investment income is handled far less gracefully, as one more dollar of income can result in a sudden and complete loss of the credit. If the EITC is combined with multiple other means-tested programs such as Medicaid or Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, it is possible that the marginal tax rate approaches or exceeds 100% in rare circumstances depending on the state of residence; conversely, under certain circumstances, net income can rise faster than the increase in wages because the EITC phases in.
The earned income tax credit has been part of political debates in the United States over whether raising the minimum wage or increasing EITC is a better idea. In a random survey of 568 members of the American Economic Association in 2011, roughly 60% of economists agreed (31.7%) or agreed with provisos (30.8%) that the earned income tax credit program should be expanded. In 2021, when the survey was done again, the percentage of economists that agreed to expanding the credit increased to 90%.
Overview
In 1969, Richard Nixon proposed the Family Assistance Plan, which included a guaranteed minimum income in the form of a negative income tax. The House of Representatives passed this plan, but the Senate did not. During his 1972 Presidential campaign, George McGovern proposed a demogrant of $1,000 for every American. Critics during this time complained about implying people don't have to work for a living, and saw the program as having too little stigma; during this time, Hawaii had an established residency requirement for public aid, which one Hawaii State Senator suggested was necessary to discourage "parasites in paradise".
Proposed by Russell Long and signed into law by President Gerald Ford as part of the Tax Reduction Act of 1975, the EITC provides an income tax credit to certain individuals. Upon enactment, the EITC gave a tax credit to individuals who had at least one dependent, maintained a household, and had earned income of less than $8,000 during the year. The tax credit was $400 for individuals with earned income of less than $4,000. The tax credit was an amount less than $400 for individuals whose income was between $4,000 and $7,999 during the year.
The initial EITC was expanded by tax legislation on a number of occasions, including the widely publicized Tax Reform Act of 1986, and it was further expanded in 1990, 1993, 2001, and 2009, regardless of whether the act in general raised taxes (1990, 1993), lowered taxes (2001), or eliminated other deductions and credits (1986). In 1993, President Clinton tripled the EITC. Today, the EITC is one of the largest anti-poverty tools in the United States, and is mainly used to "promote and support work". Most income measures, including the poverty rate, do not account for the credit.
A qualifying child can be a person's daughter, son, stepchild, or any further descendant (such as grandchild, great grandchild, etc.) or a person's brother, sister, half sister, half brother, stepbrother, stepsister, or any further descendant (such as niece, nephew, great-nephew, great-great-niece, etc.). A qualifying child can also be in the process of being adopted provided he or she has been lawfully placed. Foster children also count provided either the child has been officially placed or is a member of one's extended family. A younger single parent cannot claim EITC if he or she is also claimable as a qualifying child of their parent or another older relative, which can happen in some extended family situations. This restriction does not apply to a married couple who is claiming EITC with a child, even if one or both spouses are under the age of 19.
A person claiming EITC must be older than his or her qualifying child unless the “child” is classified as "permanently and totally disabled" for the tax year (physician states one year or more). A qualifying "child" can be up to and including age 18. A qualifying "child" who is a full-time student (one long semester or equivalent) can be up to and including age 23. And a person classified as "permanently and totally disabled" (one year or more) can be any age and count as one's qualifying "child" provided the other requirements are met. Parents claim their own child(ren) if eligible unless they are waiving this year's credit to an extended family member who has higher adjusted gross income. There is no support test for EITC. There is a six-month plus one day shared residency test.
In the 2009 American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, the EITC was temporarily expanded for two specific groups: married couples and families with three or more children; this expansion was extended through December 2012 by H.R. 4853, the Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of 2010. Effective for the 2010, 2011, 2012 and 2013 filing seasons, the EITC supported these taxpayers by:
- Increasing benefits for larger families by creating a new category or “third tier” of the EITC for families with three or more children. In this tier, the credit phases in at 45 percent of income (up from 40 percent), effectively increasing the maximum credit for these families by almost $600.
- Increasing marriage penalty relief by raising the income threshold at which the EITC begins to phase out for married couples to $5,000 above the amount for unmarried filers, thereby giving MFJ filers a longer plateau. The combined plateau and phase-out range for married filing jointly is still not double that for single filers, and thus there still is a marriage penalty, just less than there used to be.
As of 2022, 30 states and DC have enacted state EITCs: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia, Hawaii, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, and Wisconsin. Some of these state EICs are refundable, and some are not. In addition, a few small local EITCs have been enacted in San Francisco, New York City, and Montgomery County, Maryland.
Earned income
Earned income is defined by the United States Internal Revenue Code as income received through personal effort, with the following as the main sources:
- Wages, salaries, tips, commissions, and other taxable employee pay.
- Net earnings from self-employment.
- Gross income received as a statutory employee.
- Disability payments through a private employer's disability plan received prior to minimum retirement age (62 in 2011).
- Nontaxable combat pay received by a member of the U.S. armed services which he or she elects to include for purposes of EIC calculation. This is an all-or-none election. For each tax year, the service member must elect to include either all of the combat pay or none of it.
Income that does not qualify as earned includes investment income, rental income (since it is passive), alimony, pensions, social security, worker's comp, etc.
Qualifying children
If an adult's income is very low they may be eligible for EITC even if they have no children, for the 2021 that was less than $21,430 ($27,380 if married filing jointly).
A person or couple claiming EITC with one or more qualifying children need to fill out and attach Schedule EITC to their 1040 or 1040A. This form asks for the child(ren)'s name, social security number, year of birth, whether an older "child" age 19 to 23 was classified as a student for the year (full-time status for at least one long semester or equivalent time period), whether an older "child" is classified as disabled during the year (doctor states one year or more), the child's relationship to claimant, and the number of months the child lived with the claimant in the United States.
To claim a person as qualifying child, the following requirements of relationship, age, and shared residence must be met.
Relationship
In the case of a married couple filing jointly, if one spouse is related to the child by any of the below relationships, both spouses are considered related to the child.
The claimant must be related to their qualifying child through blood, marriage, or law. The qualifying child can be:
- a person's daughter, son, stepchild, or any further descendant (such as grandchild, great grandchild, etc.),
- or a person's brother, sister, half sister, half brother, stepbrother, stepsister, or any further descendant (such as niece, nephew, great-nephew, great-great-niece, etc.),
- or a foster child officially placed by an agency, court, or Indian tribal government. Authorized placement agencies include tax-exempt organizations licensed by states as well as organizations authorized by Indian tribal governments to place Native American children.
- or an adopted child, including a child in the process of being adopted provided he or she has been lawfully placed.
A child might classify as the qualifying child of more than one adult family member, at least initially. For example, in an extended family situation, both a parent and an uncle may meet the initial standards of relationship, age, and residency to claim a particular child. In such a case, there is a further rule: If a single parent or both parents, whether married or not, can claim the child (residency and age) but choose to waive the child to a non-parent, such as a grandparent or uncle or aunt, this non-parent can claim the child only if they have a higher adjusted gross income (AGI) than any parent who has lived with the child for at least six months.
This still remains the parent's choice. Provided the parent has lived with the child for at least six months and one day, the parent can always choose to claim his or her child for purposes of the earned income credit. In a tiebreaker situation between two unmarried parents, the tiebreak goes to the parent who lived with the child for the longest. In a tiebreaker between two non-parents, the tiebreak goes to the person with the higher AGI. And in a tiebreaker between a parent and non-parent, the parent wins by definition. These tiebreaker situations only occur if more than one family member actually file tax returns in which they claim the same child. On the other hand, if the family can agree, per the above and following rules, they can engage in a limited amount of tax planning as to which family member claims the child.
Age
A single parent younger than age 19 living in an extended family situation is potentially claimable as the qualifying "child" of an older relative. And a single parent under age 24 who is also a full-time college student (one long semester or equivalent) living in an extended family situation is also potentially claimable. If so, the younger single parent cannot claim EIC. This rule does not apply to a married couple who are claiming EIC with a child, even if one or both spouses are under the age of 19. (This rule also does not apply if the older relative is not required to file a tax return, and subsequently either does not file or only files to receive a full refund of taxes withheld.)
Generally, one sibling claiming another as their qualifying child must be older. In the case of a married couple filing a joint return, only one of the spouses must be older. An exception to the must-be-older-rule is the case of a qualifying child who is classified as "permanently and totally disabled" (physician states one year or more). Such a "child" can be any age and the age requirement is considered to be automatically met (of course the relationship and shared residency requirements must still be met).
The standard rule is that the qualifying "child" must be under the age of 19 at the end of the tax year. That is, the younger person can be 18 years and 364 days old on December 31 and the age requirement is met.
This age limit is extended for a qualifying "child" who is also a full-time student during some part of five calendar months. This young adult merely needs to be under age 24 at the end of the tax year for the age requirement to be met (relationship and residency requirements must still be met). That is, the young adult who is full-time for at least part of five different months can be 23 years and 364 days on December 31 and meet the age requirement to be someone else's qualifying "child." The standard Fall semester of a university, in which classes start in late August and continue through September, October, November, and early December, counts as part of five calendar months. And a similar conclusion applies to the standard Spring semester. However, the five months need not be consecutive and can be obtained with any combination of shorter periods. A full-time student is a student who is enrolled for the number of hours or courses the school considers to be full-time attendance. High school students who work in co-op jobs or who are in a vocational high school program are classified as full-time students. Schools include technical, trade, and mechanical schools.
A person who is classified as "permanently and totally disabled" (physician states one year or more) can be any age and the age requirement is automatically met. More fully, the definition of "permanently and totally disabled" is that a person has a mental or physical disability, cannot engage in substantial gainful activity, and a physician has determined that the condition has lasted or is expected to last one year or more (or that it can lead to death).
Shared residence
The claimant must live with their qualifying child(ren) within the fifty states and/or District of Columbia of the United States for more than half the tax year (per instructions, six months and one day is listed as 7 months on Schedule EIC). U.S. military personnel stationed outside the United States on extended active duty are considered to live in the U.S. for purposes of the EIC. Extended active duty means the person is called to duty for an indefinite period or for a period of more than 90 days (which is still considered to be extended active even if the period ends up being less than 90 days).
Temporary absences, for either the claimant or the child, due to school, hospital stays, business trips, vacations, shorter periods of military service, or jail or detention, are ignored and instead count as time lived at home. "Temporary" is perhaps unavoidably vague and generally hinges or whether the claimant and/or the child are expected to return, and the IRS does not provide any substantial guidance past this. If the child was born or died in the year and the claimant's home was the child's home, or potential home, for the entire time the child was alive during the year, this counts as living with the claimant, and per instructions, 12 months is entered on Schedule EIC.
Unlike the rules for claiming a dependent, there is no rule that a qualifying child not support herself or himself. A child who supports himself or herself can still qualify as a qualifying child for purposes of the EIC. There is an exception for older married "children." If an otherwise qualifying child is married, the claimant needs to be able to claim this child as a dependent (and the married couple must have low enough income so that they are not required to file a return and are either not filing or are filing only for the purpose of claiming a refund on withheld taxes).
Other requirements
Investment income cannot be greater than $3,650 for the 2020 tax year. As a result of the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021, the investment income limit was increased to $10,000 effective the 2021 tax year and will be adjusted for inflation. Investment income includes interest, dividends, capital gains, rental income, and passive activities."
A claimant must be either a United States citizen or resident alien. In the case of married filing jointly where one spouse is and one isn't, the couple can elect to treat the nonresident spouse as resident and have their entire worldwide income subject to U.S. tax, and will then be eligible for EITC.
Filers both with and without qualifying children must have lived in the 50 states and/or District of Columbia of the United States for more than half the tax year (six months and one day). Puerto Rico, American Samoa, the Northern Mariana Islands, and other U.S. territories do not count in this regard. However, a person on extended military duty is considered to have met this requirement for the period of the duty served.
Filers who are not claiming a qualifying child must be between the ages of 25 and 64 inclusive. For a married couple without a qualifying child, only one spouse must be within this age range. For a single person with a qualifying child, there is no age requirement per se other than the requirement that the single person not himself or herself be claimable as another relative's qualifying child (see Age section above). A married couple with at least one qualifying child is only occasionally classified as claimable by another relative, especially if the married couple has earned income and elects to claim EITC.
All filers and all children being claimed must have a valid social security number. This includes social security cards printed with "Valid for work only with INS authorization" or "Valid for work only with DHS authorization."
Single, Head of Household, Qualifying Widow(er), and Married Filing Jointly are all equally valid filing statuses for EITC. In fact, depending on the income of both spouses, Married Filing Jointly can be advantageous in some circumstances because, in 2009, the phase-out for MFJ for begins at $21,450 whereas phase-out begins at $16,450 for the other filing statuses. A couple who is legally married can file MFJ even if they lived apart the entire year and even if they shared no revenues or expenses for the year, as long as both spouses agree. However, if both spouses do not agree, or if there are other circumstances such as domestic violence, a spouse who lived apart with children for the last six months of the year and who meets other requirements can file as Head of Household. Or, for a couple that is split up but still legally married, they might consider visiting an accountant at separate times and perhaps even signing a joint return on separate visits. There is even an IRS form that can be used to request direct deposit into up to three separate accounts. In addition, if a person obtains a divorce by December 31, that will carry, since it is marital status on the last day of the year that controls for tax purposes. In addition, if a person is "legally separated" according to state law by December 31, that will also carry. The only disqualifying filing status for purposes of the EIC is married filing separately.
EIC phases out by the greater of earned income or adjusted gross income.
A married couple in 2018, whose total income was just shy of $24,350, of which exactly $3,500 was investment income, would receive the maximum credit for their number of qualifying children (i.e. $6,431 with 3 kids). But if this couple instead had $3,501 of investment income, then — because of the rule that for any claimant, whether single or married, with or without children, investment income cannot be greater than $3,500 — they will instead receive zero EIC. This is a loss of up to $6,431 due to one extra dollar of investment income, and the loss is nearly twice the entire amount of the couple's investment income. This is an edge case, but there are income ranges and situations in which an increase of investment dollars will result in a loss of after-tax dollars. (Instead of $24,350, the phase-out for Single, Head of Household, and Qualifying Widow(er) begins at $18,700.)
In normal circumstances, EIC phases out relatively slowly, at 16% or 21% depending on the number of children.
Disallowances for reckless or fraudulent claims
A person or couple will be disallowed EIC for two years if they claim EIC when not eligible and the IRS determines the "error is due to reckless or intentional disregard of the EIC rules." A person or couple will be disallowed for ten years if they make a fraudulent claim. Form 8862 is required after this time period in order to be reinstated. However, this form is not required if EIC was reduced solely because of mathematical or clerical error.
Example(s) for 2012 from IRS Pub. 596
Cynthia and Jerry Grey have two children ages 6 and 8. For tax year 2012, one spouse made $10,000 in wages and the other spouse made $15,000, plus the couple received $525 on interest from a savings account. Since they are into the phase-out range, their EIC will phase out by the greater of earned income or adjusted gross income. So, they will look up in the EIC table $25,525 for MFJ with two children, and this amount is $4,557. Since they are claiming children, the Greys will also need to attach Schedule EIC to their tax return which will ask for each child, the child's name, social security number, year of birth, relationship to couple, and months lived with couple in the United States during 2012. If the Greys use 1040A, they will enter $4,557 on line 38a. If they use form 1040, they will enter $4,557 on line 64a.
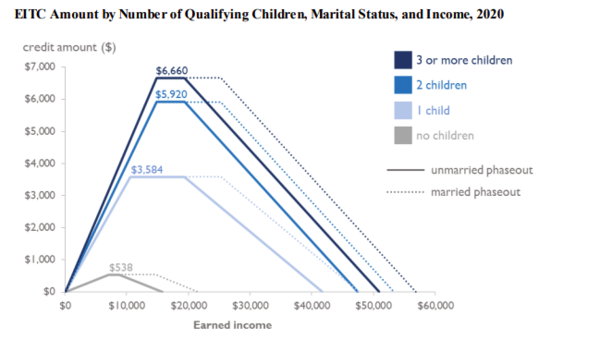
Graph, 2020
Tax Credit for case of one qualifying child
With one child and parent filing singly or as head of household, as of 2020:
- Tax credit equals $0.34 for each dollar of earned income for income up to $10,540.
- For income between $10,540 and $19,330, the tax credit is a constant "plateau" at $3,584.
- For income between $19,330 and $41,765, the tax credit decreases by $0.1598 for each dollar earned over $19,330.
- For income over $41,765, the tax credit is zero.
This is represented by the lightest blue, solid line (other lines are various other scenarios):
Impact
Welfare benefits

At a cost of $56 billion in 2013, the EITC is the third-largest social welfare program in the United States after Medicaid ($275 billion federal and $127 billion state expenditures) and food stamps ($78 billion). Almost 27 million American households received more than $56 billion in payments through the EITC in 2010. These EITC dollars had a significant impact on the lives and communities of the nation's lowest-paid working people largely repaying any payroll taxes they may have paid. The EITC is one of the most effective social welfare programs in the United States. The Census Bureau, using an alternative calculation of poverty, found that EITC lifted 5.4 million above the poverty line in 2010.
The stimulus effects of the EITC and other consumption-augmenting policies have been challenged by more recent and rigorous studies. Haskell (2006) finds that the unique spending patterns of lump-sum tax credit recipients and the increasingly global supply chain for consumer goods is counter-productive to producing high, localized multipliers. He places the local multiplier effect somewhere in the range of 1.07 to 1.15, more in line with typical economic returns. The lower multiplier is due to recipients emphasizing "big-ticket" durable-good purchases, which are typically produced elsewhere, versus locally produced products and services such as agricultural products or restaurant visits. However, Haskell points to a silver lining: there are perhaps more important benefits from recipients who use the credit for savings or investment in big-ticket purchases that promote social mobility, such as automobiles, school tuition, or health-care services.
Due to its structure, the EITC is effective at targeting assistance to low-income families in the bottom two quintiles—0–40% of households. By contrast, only 30% of minimum wage workers live in families near or below the federal poverty line, as most are teenagers, young adults, students, or spouses supplementing their studies or family income. Opponents of the minimum wage argue that it is a less efficient means to help the poor than adjusting the EITC.
EITC follows a graphical benefit pattern of going up a hill, traveling along a plateau, and then going back down the hill more slowly than it went up. For example, a married couple with two qualifying children and yearly income of seven thousand dollars will receive EITC of $2,810 (going up the hill). At fifteen thousand dollars, this couple will receive EITC of $5,036 (plateau). And at twenty-five and thirty-five thousand dollars, this same couple with their two children will receive EITC of $4,285 and $2,179, respectively.
A single person (such as a single parent, aunt, uncle, grandparent, older sibling, etc.) goes up the hill at the same rate and will receive the same maximum EITC for two qualifying children of $5,036 at plateau. But the single person has a shorter plateau. And thus, a single person with two qualifying children and income of twenty-five and thirty-five thousand will receive EITC of $3,230 and $1,124 respectively (going down the hill).
EITC phases out at 16% with one qualifying child and at 21% for two children and three or more children. Thus it is always preferable to have an extra fifty dollars of actual earned income (the table for EITC steps in increments of fifty dollars).
The GRAPHICAL plateau range for Married Filing Jointly continues for five thousand dollars longer than does the plateau for the other filing statuses and thus MFJ can be advantageous for some income ranges. Single, Head of Household, and Qualifying Widow(er) are all equally valid and eligible filing statuses for claiming EITC. The only disqualifying status is Married Filing Separately. However, a couple can file as Married Filing Jointly even if they lived apart for the entire year if legally married and both agree.
Impact on health
A 2016 review of the EITC and state-matches to the EITC found significant impacts on maternal mental health, low birth weight births, and other health indicators association with inflammation.
Working mothers
According to a 2020 study, the introduction of the EITC increased maternal employment by 6 percent. The EITC may explain why the United States has high levels of maternal employment, despite the absence of childcare subsidies or parental leave.
Cost
The direct cost of the EITC to the U.S. federal government was about $56 billion in 2012. The IRS has estimated that between 21% and 25% of this cost ($11.6 to $13.6 billion) is due to EITC payments that were issued improperly to recipients who did not qualify for the EITC benefit that they received. For the 2013 tax year the IRS paid an estimated $13.6 billion in bogus claims. The IRS overpaid as much as $132.6 billion in EITC between 2003 and 2013.
The direct fiscal cost of the EITC may be partially offset by two factors: any new taxes (such as payroll taxes paid by employers) generated by new workers drawn by the EITC into the labor force; and taxes generated on additional spending done by families receiving earned income tax credit.
Some economists have noted that the EITC might conceivably cause reductions in entitlement spending that result from individuals being lifted out of poverty by their EITC benefit check. However, because the pre-tax income determines eligibility for most state and federal benefits, the EITC rarely changes a taxpayer's eligibility for state or federal aid benefits.
Uncollected tax credits
Millions of American families who are eligible for the EITC do not receive it, essentially leaving billions of dollars unclaimed. The IRS estimates that about 20 percent of eligible taxpayers do not claim $7.3 billion of Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) each tax year.
Many nonprofit organizations around the United States, sometimes in partnership with government and with some public financing, have begun programs designed to increase EITC utilization by raising awareness of the credit and assisting with the filing of the relevant tax forms. One example is the Claim it! campaign in Minnesota that launched in 2006 to help Minnesotans claim the EITC.
The state of California requires employers to notify every employee about the EITC every year, in writing, at the same time W-2 forms are distributed.
Storefront tax prep, “RACs,” prep and account fees, third-party debt collection
RALs (Refund Anticipation Loans) are short term loans on the security of an expected tax refund, and RACs (Refund Anticipation Checks) are temporary accounts specifically to wait to receive tax refunds, which are then paid by a check or debit card from the bank less fees. The combination of Earned Income Credit, RALs, and RACs has created a major market for the storefront tax preparation industry. A 2002 Brookings Institution study of Cleveland taxpayers found that 47 percent of filers claiming EIC purchased RALs, as compared to 10 percent of those not claiming EIC. The tax preparation industry responded that at least one-half of RAL customers included in the IRS data actually received RACs instead.
These financial products have been criticized on various grounds, including inflated prices for tax preparation, account fees, RAL interest rates, as well as the practice of third-party debt collection (this used to be called "cross-collection" which hinted at the practice, but tax prep companies now to seem more vaguely refer to the practice merely as "previous debt"). This practice occurs when one RAL- or RAC-issuing bank collects for another. That is, such lenders may take all or part of a client's current year tax refund for purposes of third-party debt collection, and it is unclear how broad are the types of debts for which the banks collect. This contrasts with the more limited types of debt collected for by the IRS. This practice of one bank collecting debt for another may not be adequately disclosed to the tax preparation client; on the other hand, some clients may fail to disclose obligations that result a governmental seizure of their refunds. With both RALs and RACs, the client grants the bank first rights to their tax refund, and both carry the same risk of third-party bank collection.
Advertisement phrases such as "Rapid Refund" have been deemed deceptive and illegal, since these financial products do not speed remittances beyond the routine automation of tax return processing, and do not make it clear that these are loan applications. Beginning with 2011 tax season, the IRS announced that they would no longer provide preparers and financial institutions with the “debt indicator” that assisted banks in determining whether RAL applications were approved. Beginning with the 2013 tax season, major banks are no longer offering RALs but only RACs.
However, a March 2013 article in CNN Money reported that tax prep companies are offering a hodgepodge of financial products similar to RALs. The article further states that, "The NCLC also found that some shady tax preparers are even offering tax refund loans to lure taxpayers into their offices, but have no intention of lending them the money."
See also
- Capital gains tax
- Child tax credit (United States)
- Guaranteed minimum income
- Negative income tax
- Refund anticipation loan
- Taxation in the United States
- Unearned income
References
- ^ "Publication 596 (2021), Earned Income Credit (EIC)". IRS. Retrieved April 9, 2021.
See www.irs.gov/forms-pubs/about-publication-596 for further developments
- EITC IRS instructions Internal Revenue Service, "EITC Home Page--It’s easier than ever to find out if you qualify for EITC"
- Tax Year 2020 1040 and 1040-SR Instructions, including the instructions for Schedules 1 through 3, Rules for EIC begin on page 40 for 2020 Tax Year.
- Maag, Elaine; Steuerle, C. Eugene; Chakravarti, Ritadhi; Quakenbush, Caleb (December 2012). "How Marginal Tax Rates Affect Families at Various Levels of Poverty". National Tax Journal. 65 (4). National Tax Association: 759–782. doi:10.17310/ntj.2012.4.02. ISSN 0028-0283.
- Rizzo, Salvador (January 28, 2013). "Gov. Christie rejects minimum wage increase, offers alternative". NJ.com. Retrieved August 30, 2024.
- Saltsman, Michael (February 14, 2013). "The $9 Minimum Wage That Already Exists". The Wall Street Journal. ISSN 1042-9840. Retrieved August 30, 2024 – via Employment Policies Institute.
- Romer, Christina D. (March 2, 2013). "The Business of the Minimum Wage". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved August 30, 2024.
- Fuller, Dan; Geide-Stevenson, Doris (2014). "Consensus Among Economists—An Update". The Journal of Economic Education. 45 (2): 131–146. doi:10.1080/00220485.2014.889963. S2CID 143794347.
- Geide-Stevenson, Doris; La Parra Perez, Alvaro (December 2021). "Consensus among economists 2020 – A sharpening of the picture". Weber State University. Archived from the original on August 29, 2024. Retrieved August 31, 2024.
- Hamilton, Jonathan (April 2010). "Optimal Tax Theory: The Journey from the Negative Income Tax to the Earned Income Tax Credit". Southern Economic Journal. 76 (4). Southern Economic Association: 861–877. doi:10.4284/sej.2010.76.4.861. ISSN 0038-4038.
- ^ Dilworth, Kevin (November 3, 1975). "12,000 may get break in taxes". Democrat and Chronicle (Rochester, New York). p. 1B, 6B.
- Earned Income Tax Credit Parameters 1975–2010, at the Tax Policy Center, Urban Institute and Brookings Institution, 27 Oct. 2009. See footnote for the increases in the travel distance, but not the credit amount, for Married Filling Jointly for the years 2002 through 2010. For example, in 2010, the plateaus for MFJ extend $5,000 further than do the corresponding plateaus for Single, Head of Household, Qualifying Widow(er). For all filing statuses, the phase out for EIC with one child is 16% (15.98%), and the phaseout for two children and for three or more children is 21% (21.06%). Single, Head of Household, and Qualifying Widow(er) are all equally valid, equally advantageous filing statuses for the purposes of Earned Income Credit. Married filing Jointly can sometimes be more advantageous depending on the income level.
- ^ Sykes, Jennifer; Križ, Katrin; Edin, Kathryn; Halpern-Meekin, Sarah (October 10, 2014). "Dignity and Dreams". American Sociological Review. 80 (2): 243–267. doi:10.1177/0003122414551552. ISSN 0003-1224. S2CID 154685898.
- "Welfare Chart". House Ways and Means Committee. Retrieved April 25, 2016.
- "Alternative Measures of Income Definitions". US Census Bureau. 2012. Archived from the original on January 25, 2012. Retrieved August 31, 2024.
- ^ 1040 Instructions 2010, rules for EITC pages 45–48, optional worksheets pages 49–51, and the EITC Table itself on pages 52–68. The only required attachment is Schedule EITC if you are claiming one or more qualifying children.
- ^ IRS Publication 596, Earned Income Credit (EIC): For use in preparing 2012 Returns.
- "Tax Credits for Working Families, Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)". Retrieved February 17, 2012.
- "State and Local Governments with Earned Income Tax Credit". Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- "What is the Working Families Credit (WFC)?". www.sfhsa.org. Retrieved July 29, 2023.
- Assistance, New York State Office of Temporary and Disability. "Earned Income Tax Credits (EITC) | OTDA". otda.ny.gov. Retrieved May 22, 2016.
- "Montgomery County, MD 311 - Answering to You". www3.montgomerycountymd.gov. Retrieved May 22, 2016.
- Earned Income IRS Page defining Earned Income.
- Statutory Employee IRS Definition
- Disability and Earned Income Tax Credit, page last reviewed 22-Jan-2013. "Benefits such as Social Security Disability Insurance, SSI, or military disability pensions are not considered earned income and cannot be used to claim Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)."
- https://www.irs.gov/publications/p596#en_US_2023_publink1000297687 Income That Is Not Earned Income
- ^ IRS Schedule EIC. A person or couple claiming qualifying child(ren) need to attach this form to their 1040 or 1040A tax return.
- "Who is a qualifying child?". Retrieved January 6, 2017.
- In addition to being able to claim a married child as a dependent (or be waiving dependency to other parent), there is also the joint return test in which one's married child cannot be filing a joint return, unless it is solely to claim a refund. For example, if one's married child files a joint return in part to claim the Making Work Pay Credit, one cannot claim this child for purposes of the EIC. See page 15 of Pub. 596. Recall that a qualifying child can be up to and including age 18, up to and including age 23 if a full-time student for one long semester or equivalent, or any age if classified as "permanently and totally disabled" (physician states one year or more).
- "EITC Income Limits Maximum Credit Amounts Next Year | Internal Revenue Service".
- A person who is legally married can file as Head of Household if the following conditions are met: The person lived apart from his or her spouse for the last six months of the year, the person individually or jointly paid over half the costs of keeping up a home (or several homes) for the year, the home(s) were the main home of a child for more than half the year, and the person can claim the child as a dependent (or could claim, but are waiving the child to the other parent). See pages 15–16 of 1040 Instructions 2009. And again, Head of Household status is not a requirement for EIC, it’s not even particularly advantegeous. It is just one more option to consider in some circumstances.
- Mark Moreau, Low-Income Taxpayer Clinic, Southeast Louisiana Legal Services, New Orleans, March 23, 2005, presentation to President’s Advisory Panel on Federal Tax Reform, Index of /taxreformpanel/meetings, see Moreau.ppt and esp. pages 4 and 7. On page 7, Moreau bluntly states that domestic violence is the leading cause of female poverty.
- Form 8888 Allocation of Refund (Including Savings Bond Purchases) is used to request splitting a refund into up to three separate accounts. However, this form cannot be used simultaneously with Form 8379 Injured Spouse Allocation. And also, if the IRS reduces the amount of the refund, there are complicated rules regarding which of the bank accounts the remaining refund will be sent to (see the paragraphs “Past-due federal tax” and “Other offsets” on page 3). Additionally, a refund typically cannot be split with the loan and bank products offered by tax prep companies.
- From Pub. 501 Exemptions, Standard Deduction, and Filing Information “You are separated under an interlocutory (not final) decree of divorce. For purposes of filing a joint return, you are not considered divorced” (part of section “Considered married” on page 5). From 1040 Instructions 2009, “You were legally separated, according to your state law, under a decree of divorce or separate maintenance” (a rule for filing as Single on page 14). And apparently, the IRS does generally defer to state law and does not provide any more guidance than this.
- "IRS Publication 596 for use in preparing 2018 returns" (PDF).
- 1040 Instructions 2010, see caution note on page 45. See also "Form 8862, who must file" on page 48.
- ^ "The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): How It Works and Who Receives It" (PDF). January 12, 2021. Retrieved August 11, 2023.
- Federal spending by the Numbers 2013 accessed 22 Nov 2013
- "Government Programs Kept Millions Out of Poverty in 2010 - Center on Budget and Policy Priorities". September 13, 2011.
- "The State of the Earned-Income Tax Credit in Nashville" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December 29, 2009. Retrieved March 24, 2009.
- Haskell, John (2006). "EITC Boosts Local Economies". Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta. Archived from the original on October 20, 2012. Retrieved April 2, 2013.
- Turner, Mark (January 17, 2007). "The Low-Wage Labor Market".
- "Characteristics of Minimum Wage Workers: 2005". Bureau of Labor Statistics, US Department of Labor. January 17, 2007.
- "The Cost of a 'Living Wage'". N. Gregory Mankiw.
- Nichols, A, Rothstein, J (December 6, 2016). "The Earned Income Tax Credit" (PDF). Economics of Means-Tested Transfer Programs in the United States, Volume 1.
- Bastian, Jacob (2020). "The Rise of Working Mothers and the 1975 Earned Income Tax Credit". American Economic Journal: Economic Policy. 12 (3): 44–75. doi:10.1257/pol.20180039. ISSN 1945-7731. S2CID 168227352.
- "The Internal Revenue Service Was Not in Compliance With All Requirements of the Improper Payments Elimination and Recovery Act for Fiscal Year 2012".
- "IRS wastes billions in bogus claims for Earned Income Tax Credit". The Washington Times.
- "The Internal Revenue Service Should Consider Modifying the Form 1040 to Increase Earned Income Tax Credit Participation by Eligible Tax Filers" (PDF). April 2, 2018.
- "Claim it!".
- "Earned Income Tax Credit Notification". January 1, 2008.
- NATIONAL TAXPAYER ADVOCATE: 2005 ANNUAL REPORT TO CONGRESS, VOLUME 1, 31 December 2005, page 166 (174 in PDF file). See especially footnote 17.
- Connecting Cleveland’s Low-Income Workers to Tax Credits Archived November 2, 2014, at the Wayback Machine , The Brookings Institution, Metropolitan Policy Program, Alan Berube, Fellow, Levin College Forum, Jan. 13, 2005. See pages 17 and 18. See also Using the Earned Income Tax Credit to Stimulate Local Economies Archived November 2, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Brookings Institution, Alan Berube.
- National Taxpayer Advocate 2005 Annual Report to Congress, Executive Summary, The Most Serious Problems Encountered by Taxpayers, page I-3, item 8. Refund Anticipation Loans: Oversight of the Industry, Cross-Collection Techniques, and Payment Alternatives: " . . . It is also unclear if RAL customers fully understand the ramifications of cross-collection provisions in standardized RAL contracts . . . "
- RALs drain off millions in taxpayer refunds, National Consumer Law Center, published by consumer-action.org, February 5, 2007.
- National Taxpayer Advocate’s 2007 Objectives Report to Congress, Volume II, The Role Of The IRS In The Refund Anticipation Loan Industry, pages 10–12, June 30, 2006. In part, this report states: “ . . It is also interesting to note that federal law prohibits banks from exercising their right to offset Social Security benefits for the recipients’ defaulted loans to that bank. It would make sense to protect EITC funds in a similar manner. . ” (page 11, last three sentences). However, in many cases, tax preparation clients are not even informed of the practice of cross-collection (see second paragraph of “Debt Collection Offset Practice,” page 10).
- Attorney General Lockyer Files Lawsuit Against H&R Block for Illegally Marketing and Selling High-Cost Loans as ‘Instant' Tax Refunds, State of California, Office of Attorney General, news release, Feb. 15, 2006.
- IRS to end release of taxpayer debt information, EILEEN AJ CONNELLY (Associated Press), Friday, August 6, 2010.
- IRS Removes Debt Indicator for 2011 Tax Filing Season, (IRS press notice), IR-2010-89, Aug. 5, 2010. IRS Commissioner Doug Shulman said, “Refund Anticipation Loans are often targeted at lower-income taxpayers.”
- Refund Anticipation Loans Come With Risks, Better Business Bureau, 2/26/2013. ' . . The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation has forced all major national banks to discontinue these types of loans. Be wary of sketchy lenders, both online and off. . '
- Tax refund offers include extra fees, KGET , Feb. 7, 2013. ' . . "They have to disclose all the fees so make sure you carefully read any papers that you sign, giving them rights to your refund, because that's exactly what you're doing," said Hudson . . '
- New tax refund loans carry sky-high fees and rates, CNNMoney, Blake Ellis, March 6, 2013.
Further reading
- Chetty, Raj; Saez, Emmanuel (January 2013). "Teaching the Tax Code: Earnings Responses to an Experiment with EITC Recipients". American Economic Journal: Applied Economics. 5 (1): 1–31. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.231.1497. doi:10.1257/app.5.1.1. S2CID 9402981.
External links
| This article's use of external links may not follow Misplaced Pages's policies or guidelines. Please improve this article by removing excessive or inappropriate external links, and converting useful links where appropriate into footnote references. (August 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Taxpayer info/tools:
- IRS EITC Assistant, which can help determine if one qualifies for EITC
- IRS 1040 Instructions 2010, Earned Income Credit instructions on pages 45–48, optional worksheets 49–51, credit table itself 51–58. Only required attachment is Schedule EIC if one is claiming a qualifying child.
- IRS Schedule EIC. A person or couple claiming qualifying child(ren) needs to attach this form to the 1040 or 1040A tax return.
- IRS Publication 596 – Earned Income Credit, a publication aimed at people who will potentially be claiming the credit.
Organizations/campaigns:
Background:
- Section 13 ("Tax Provisions Related to Retirement, Health, Poverty, Employment, Disability, and Other Social Issues") of the House Ways and Means Committee's Green Book provides historical information, including previous EITC parameters. (The version linked to here is the 2004 edition. Note: it's not published annually.)
Policy analysis:
- New Research Findings on the Effects of the Earned Income Tax Credit, Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, March 11, 1998
- The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): An Economic Analysis Congressional Research Service
- The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): Percentage of Total Tax Returns and Credit Amount by State Congressional Research Service
- The Earned Income Tax Credit at Age 30: What We Know, Steve Holt, the Brookings Institution
- The Hidden Welfare State: Tax Expenditures and Social Policy in the United States, Christopher Howard, Princeton University Press, 1997. Howard discusses the mortgage interest deduction, employer pensions, EITC, and the targeted jobs tax credit as examples of tax expenditures.