| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Ethoxymethanedithioic acid | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
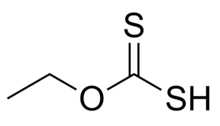
| Chemical formula | CH3CH2OCS2H |
| Molar mass | 122.20 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless oily liquid |
| Melting point | −53 °C (−63 °F; 220 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Solubility in water | Slightly |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.6 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Ethyl xanthic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH2−O−C(=S)−SH. It can be viewed as an O-ethyl ester of dithiocarbonic O,S-acid (the formula of that acid is S=C(OH)(SH)). Ethyl xanthic acid belongs to the category of thioacids, where the prefix thio- means that an oxygen atom in the compound is replaced by a sulfur atom.
Preparation
Ethyl xanthic acid is obtained by the action of dilute sulfuric acid on potassium ethyl xanthate at 0 °C.
Ethyl xanthic acid is a colorless, labile oil. In aqueous solution, it decomposes rapidly by a unimolecular pathway to give carbon disulfide and ethanol.
Esters of ethyl xanthic acid
The methyl and ethyl esters of ethyl xanthic acid are colorless, oily liquids with a penetrating odor.
 Methyl ethylxanthate or O-ethyl S-methyl dithiocarbonate, a methyl ester of ethyl xanthic acid
Methyl ethylxanthate or O-ethyl S-methyl dithiocarbonate, a methyl ester of ethyl xanthic acid Ethyl ethylxanthate or O,S-diethyl dithiocarbonate, an ethyl ester of ethyl xanthic acid
Ethyl ethylxanthate or O,S-diethyl dithiocarbonate, an ethyl ester of ethyl xanthic acid
Reactions
Ethyl xanthic acid reacts with water or moisture producing carbon disulfide.
Safety
In an experiment with white rats, chronically exposed rats by inhalation of ethyl xanthic acid revealed higher frequency of chromosomal rearrangements in lymphocytes of peripheral blood than the control rats.
References
- ^ "Ethylxanthate". PubChem.
- "Xanthic acid". merriam-webster.com.
- Millican, Robert J.; Sauers, Carol K. (1979). "General acid-catalyzed decomposition of alkyl xanthates". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 44 (10): 1664–1669. doi:10.1021/jo01324a018.
- ^ "Xanthic Acid" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 881.
- Iwasaki, Iwao; Cooke, Strathmore R. B. (1958). "The Decomposition of Xanthate in Acid Solution". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 80 (2): 285–288. Bibcode:1958JAChS..80..285I. doi:10.1021/ja01535a008.
- "Xanthic acid". dictionary.com.