| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Finabel" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 Finabel member states marked blue Finabel member states marked blue | |
| Formation | January 1, 1953; 72 years ago (1953-01-01) |
|---|---|
| Type | International organisation |
| Headquarters | Brussels |
| Membership | 25 Member States |
| Website | www |
Finabel is a European organisation for the promotion of cooperation and interoperability between the national armies of the member states of the European Union (EU). Founded in 1953, Finabel is controlled by the chiefs of staff of its member states' armies, and the organisation's work agenda consists of studies and working groups. Finabel also has a relatively small permanent secretariat.
The studies carried out by Finabel take the form of reports resulting from studies and research, entrusted to the working groups, agreements relating to the military characteristics of equipment, as well as conventions on standardising procedures, testing methods and glossaries to facilitate exchanges between member states.
The Finabel coordination committee is a land forces organisation comprising 24 Member states of the European Union with a view to promote interoperability between the land forces of its Member states. Membership is open to all of the Member states of the European Union.
History
The organisation was founded in October 1953 under the acronym FINBEL by the Army Chiefs of Staff of France, Italy, the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg, and then became FINABEL with the arrival of West Germany (Allemagne) in 1956, shortly after West Germany was rearmed in 1955. Later, the name has been kept as a proper noun, written in lower-case, when membership further expanded. Finabel was founded by armies which belonged to both NATO and Western European Union.
Initially, French was the official language of Finabel. In the 2000s the use of English has increased progressively, and since 2011 is the language used across all levels. The Finabel Committee’s initial task focused on cooperation between armament programs. This task quickly developed into the harmonization of army doctrines.
Founding principles
The tasks of the Finabel Committee have a European perspective; their purpose is to ‘promote and facilitate interoperability between land forces across the full spectrum of military operations through the harmonisation of concepts, doctrines and procedures, whilst taking into account the joint military environment’, and to ‘develop a common European understanding of defence problems by seeking to complement and co-operate with NATO and EU military structures.’ The Finabel Committee takes its decisions based on consensus and equality between its Member states.
The organisation expresses itself through reports entrusted to working groups, which produce ‘studies’ and ‘agreements’ on the military characteristics of equipment or ‘conventions’ that normalise certain procedures and glossaries in order to facilitate discussion between countries.
The proposal and recommendations that result from Finabel’s work can be freely applied by the land components and its member states.
Since the creation of Finabel was not the result of an intergovernmental agreement, Finabel has the status of an informal international de facto association.
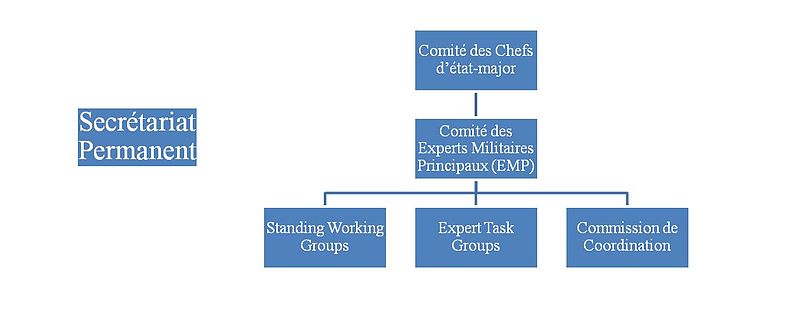
Structure
Army Chiefs of Staff/Land Force Commanders Committee
Executive, the highest level. It meets once a year to summarise work of the past year and to establish the objectives for the coming year. The chairmanship of the committee changes annually.
Principal Military Experts Committee
The Principal Military Experts (PME) Committee, made up primarily of officers responsible for doctrine, planning and studies within the staff of land components of Finabel member states. It meets twice a year to analyse the directives of the Chiefs of Staff and reformulates them.
Permanent Secretariat
Located in Brussels, the only permanent structure. It deals with administrative and organisational matters. Under the Permanent Secretariat's supervision, FINABEL publishes papers on European defence and legal-related matters. The Defence and Security, Legal, and Communication teams conduct the research and publish the articles on the FINABEL website.
Working Groups
1 Standing Working Group carries out studies (missions) distributed by the Principal Military Experts Committee in various areas of interest to the Armies and prepares the yearly COS meeting.
Actually, all Standing Working Groups are suspended.
Expert Task Groups
Ad Hoc working group of Subject Matter Experts, mounted on demand of a Finabel Member State.
Member states
As of 2024, membership consists of 25 countries:
| Country | Date |
|---|---|
| 1953 | |
| 1953 | |
| 1953 | |
| 1953 | |
| 1953 | |
| 1956 | |
| 1973 | |
| 1990 | |
| 1996 | |
| 1996 | |
| 2006 | |
| 2006 | |
| 2008 | |
| 2008 | |
| 2008 | |
| 2010 | |
| 2012 | |
| 2015 | |
| 2015 | |
| 2016 | |
| 2016 | |
| 2016 | |
| 2021 | |
| 2021 | |
| 2024 |
Symbols
The two crossed swords represent Finabel’s land identity. The twelve stars represent the strong link with Europe, maintained by Finabel since its creation. The shield represents the defence of peace, a key foundation of European military forces. On the left we can see Ares, Greek God of War, expressing its violence and, on the right we can see the Goddess Athena, who personifies wisdom and the ordered side of war, abiding by the rules which characterise our democracies.
This symbol is summarised by the Latin phrase, which means ‘reflexion serving military action’, Finabel’s essential purpose.
Observers
Finabel welcomes observer organisations from the EU and NATO: the EDA (European Defence Agency), the EUMS (European Union Military Staff), the NSO (NATO Standardization Office), the NAAG (NATO Army Armament Group), as well as the following bodies: CHENS (CHiefs of European NavieS), EAG European Air Group) and ELDIG (European Land Defence Industry Group; sectorial land component of ASD, the Aerospace and Defence Industries Association of Europe).
The objective is to consult on the different points of view and to prevent any duplication or contradiction of NATO’s doctrine or the concepts outlined by the military organisations of the EU.
Partners
- The European Union Military Staff (EUMS): early warning, strategic planning, and situation assessment
- NAAG: The NATO Army Armaments Group is responsible for promoting cooperation and standardisation in the area of land armaments via information exchange and collective activities.
- The European Defence Agency (EDA)
- The European Air Group (EAG)
References
- Finabel information folder: "Finabel: Contributing to European Army Interoperability since 1953" Archived 2011-07-20 at the Wayback Machine
- "Our Member States". Finabel. Retrieved 2024-04-23.
- "POLISH PRESIDENCY OF FINABEL". Wojska Ladowe. 24 April 2012. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 7 July 2012.
- ^ "Velitelia pozemných síl krajín Európskej únie rokovali v Trenčíne :: Ministerstvo obrany SR". Mod.gov.sk. 2015-04-22. Retrieved 2022-08-24.
External links
| Common Security and Defence Policy of the European Union | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leadership | |||||||||||
| Structure |
| ||||||||||
| Policies | |||||||||||
| Equipment | |||||||||||
| Decorations | |||||||||||
| Related | |||||||||||