| flmB | |
|---|---|
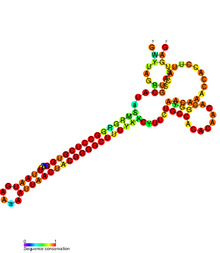 Conserved secondary structure of flmB RNA. Conserved secondary structure of flmB RNA. | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | FlmB |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | antisense RNA |
| Domain(s) | E. coli, S. enterica |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
The FlmA-FlmB toxin-antitoxin system consists of FlmB RNA (F leading-region maintenance B), a family of non-coding RNAs and the protein toxin FlmA. The FlmB RNA transcript is 100 nucleotides in length and is homologous to sok RNA from the hok/sok system and fulfills the identical function as a post-segregational killing (PSK) mechanism.
flmB is found on the F-plasmid of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. It is responsible for stabilising the plasmid. If the plasmid is not inherited, long-lived FlmA mRNA and protein will be highly toxic to the cell, possibly to the point of causing cell death. Daughter cells which inherit the plasmid inherit the FlmB gene, coding for FlmB RNA which binds the leader sequence of FlmA mRNA and represses its translation.
See also
References
- ^ Loh SM, Cram DS, Skurray RA (June 1988). "Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of a third function (Flm) involved in F-plasmid maintenance". Gene. 66 (2): 259–268. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(88)90362-9. PMID 3049248.
- ^ Kobayashi M, Kurusu Y, Yukawa H (February 1991). "High-expression of a target gene and high-stability of the plasmid". Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 27 (2): 145–162. doi:10.1007/BF02921523. PMID 2029184. S2CID 41601297.
Further reading
- Fozo EM, Makarova KS, Shabalina SA, Yutin N, Koonin EV, Storz G (June 2010). "Abundance of type I toxin–antitoxin systems in bacteria: searches for new candidates and discovery of novel families". Nucleic Acids Res. 38 (11): 3743–3759. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq054. PMC 2887945. PMID 20156992.
- Fozo EM, Hemm MR, Storz G (December 2008). "Small Toxic Proteins and the Antisense RNAs That Repress Them". Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 72 (4): 579–589, Table of Contents. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00025-08. PMC 2593563. PMID 19052321.
- Gerdes K, Wagner EG (April 2007). "RNA antitoxins". Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 10 (2): 117–124. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2007.03.003. PMID 17376733.
- Hayes F (September 2003). "Toxins-antitoxins: plasmid maintenance, programmed cell death, and cell cycle arrest". Science. 301 (5639): 1496–1499. doi:10.1126/science.1088157. PMID 12970556. S2CID 10028255.