You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (March 2016) Click for important translation instructions.
|
 Company flag Company flag | |
 Coat of arms Coat of arms Motto: Florebo quocumque ferar Latin for "I will flourish wherever I will be brought" | |
| Native name | Compagnie française pour le commerce des Indes orientales |
|---|---|
| Company type | Public State-owned enterprise |
| Industry | Trade |
| Founded | 1 September 1664 |
| Founder | Jean-Baptiste Colbert |
| Defunct | 1794 |
| Fate | Dissolved and activities absorbed by the French Crown in 1769; reconstituted 1785, bankrupt 1794 |
| Headquarters | Lorient |
| Colonial India | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Map of colonial India, distributed by the British Information Services (1942) Map of colonial India, distributed by the British Information Services (1942) | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
Portuguese India (1505–1961) | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
British India (1600–1947) | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
The French East India Company (French: Compagnie française pour le commerce des Indes orientales) was a joint-stock company founded in France on 1 September 1664 to engage in trade in India and other Asian lands. It competed with the English (later British) and Dutch trading companies in the East Indies. Planned by Jean-Baptiste Colbert, it was chartered by King Louis XIV for the purpose of trading in the Eastern Hemisphere. It resulted from the fusion of three earlier companies, the 1660 Compagnie de Chine, the Compagnie d'Orient and Compagnie de Madagascar. The first Director General for the Company was François de la Faye, who was adjoined by two Directors belonging to the two most successful trading organizations at that time: François Caron, who had spent 30 years working for the Dutch East India Company, including more than 20 years in Japan, and Marcara Avanchintz, an Armenian trader from Isfahan, Persia.
History
In 1604, King Henry IV of France authorized the establishment of the Compagnie des Indes Orientales (East India Company), granting the new firm a 15-year monopoly on French trade with the East Indies. This company was a precursor to a firm of the same name founded Jean-Baptiste Colbert, though the first business was not a joint-stock company, and was funded by the French Crown. The seventeenth century saw several French efforts to trade with the East Indies. They were influenced by the successful business ventures of the Dutch East India Company. Between the 1630s and early 1660s, French efforts were smaller in scale, but they enjoyed some success. French merchant ships traversed the Persian Gulf, Red Sea, and the northwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. These accomplishments paled France in comparison with England and Dutch Republic. France's Atlantic ports pursued to compete and amalgamate with each other. The commercial and capital expertise was disbursed around the coastal regions of Brittany and Normandy. Like other nationally-chartered trading companies of the time, the Company was based on a mercantilist model of trade, and complemented a colonialist foreign policy.
The initial capital of the revamped Compagnie des Indes Orientales was 15 million livres, divided into shares of 1000 livres apiece. Louis XIV funded the first 3 million livres of investment, against which losses in the first 10 years were to be charged. The initial stock offering quickly sold out, as courtiers of Louis XIV recognized that it was in their interests to support the King's overseas initiative. The Compagnie des Indes Orientales was granted a 50-year monopoly on French trade in the Indian and Pacific Oceans, a region stretching from the Cape of Good Hope to the Straits of Magellan. The French monarch also granted the company a concession in perpetuity for the island of Madagascar, as well as any other territories it could conquer. The company possessed greater resources and better political banking than France's previous ventures in the Indian Ocean. Colbert's obsession with VOC led to series of early letdowns. One of France's main aims was to establish a French entrepôt in Madagascar to rival the Dutch colony of Batavia.
By the 1680s, the company went insolvent and they had little choice but to rent out its monopoly to a group of merchants. The Indian trade remained under the company for approximately thirty years. In 1716, Scottish financier John Law arrived at the French royal court. The French court were in deep misery and were impotent to cover their debts caused due to War of Spanish Succession. Law approached the Crown with a scheme to construct a national bank and introduce paper currency, which would facilitate France's shift to credit economy. The company failed to found a successful colony on Madagascar, but was able to establish ports on the nearby islands of Bourbon and Île-de-France (today's Réunion and Mauritius). By 1719, it had established itself in India, but the firm was near bankruptcy. In the same year the Compagnie des Indes Orientales was merged under Law's direction with other French trading companies to form the Compagnie Perpétuelle des Indes. This merger resulted in the company being involved in importing slaves to Louisiana, as the colony operated on a plantation economy. The French economy crashed drastically in 1721 due to Law's reforms. Following this event, the company again started trading and settling in India. The reorganized corporation resumed its operating independence in 1723.
The company's interest in the Mughal Empire was to prove no easier. The French arrived at the Indian subcontinent decades after the English, Portuguese and Dutch in establishing trade in India. On 4 September 1666, the French secured a royal mandate from Emperor Aurangzeb that granted them to trade on the port of Surat. By 1683, the French had directed their attention toward the prominent site of Pondicherry, however the shift did little to offset the company's chronic shortage of capital. By 1738, the company owned 1,432 slaves, 630 of whom resided in the French colony of Isle de France. Many slaves in the colony were imported by the company from the West African region of Senegambia; these included laptots, African slaves who forcibly served onboard the company's ships. With the decline of the Mughal Empire, the French decided to intervene in Indian political affairs to protect their interests, notably by forging alliances with local rulers in south India. From 1741 the French under Joseph François Dupleix pursued an aggressive policy against both the Indians and the British until they ultimately were defeated by Robert Clive. Several Indian trading ports, including Pondichéry and Chandernagore, remained under French control until 1954.

France's main rivalry came from the British. As a result of constant wars in Europe, notably the War of the Austrian Succession and the Seven Years' War the British were able to exert control over French territories in India. With the Treaty of Paris in 1763, the territories were returned to France. The company was not able to maintain itself financially, and it was abolished in 1769. King Louis XV issued a 1769 edict that required the company to transfer to the state all its properties, assets and rights, which were valued at 30 million livres. The King agreed to pay all of the company's debts and obligations, though holders of company stock and notes received only an estimated 15 percent of the face value of their investments by the end of corporate liquidation in 1790.
The company was reconstituted in 1785 and issued 40,000 shares of stock, priced at 1,000 livres apiece. It was given monopoly on all trade with countries beyond the Cape of Good Hope for an agreed period of seven years. The agreement, however, did not anticipate the French Revolution, and on 3 April 1790 the monopoly was abolished by an act of the new French Assembly which enthusiastically declared that the lucrative Far Eastern trade would henceforth be "thrown open to all Frenchmen". The company, accustomed neither to competition nor official disfavor, fell into steady decline and was finally liquidated in 1794.
Map gallery
-
 Carte de L'Indoustan. Bellin, 1770.
Carte de L'Indoustan. Bellin, 1770.
-
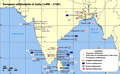 French and other European settlements in India.
French and other European settlements in India.
-
 Acme of French influence, 1741–1754.
Acme of French influence, 1741–1754.
Liquidation scandal
Even as the company was headed consciously toward extinction, it became embroiled in its most infamous scandal. The Committee of Public Safety had banned all joint-stock companies on 24 August 1793, and specifically seized the assets and papers of the East India Company. While its liquidation proceedings were being set up, directors of the company bribed various senior state officials to allow the company to carry out its own liquidation, rather than be supervised by the government. When this became known the following year, the resulting scandal led to the execution of key Montagnard deputies like Fabre d'Églantine and Joseph Delaunay, among others. The infighting sparked by the episode also brought down Georges Danton and can be said to have led to the downfall of the Montagnards as a whole.
Coins
-
 French-issued copper coin, minted in Pondichéry, used for internal Indian trade.
French-issued copper coin, minted in Pondichéry, used for internal Indian trade.
-
 French-issued "Gold Pagoda" for Southern India trade, cast in Pondichéry 1705–1780.
French-issued "Gold Pagoda" for Southern India trade, cast in Pondichéry 1705–1780.
-
 French-issued rupee in the name of Mohammed Shah (1719–1748) for Northern India trade, cast in Pondichéry.
French-issued rupee in the name of Mohammed Shah (1719–1748) for Northern India trade, cast in Pondichéry.
-
 Silver Rupee issued by the French East India Company, Arkat Mint, AH 1221 and Regnal Year 45, having the "Saya-e-fazle elah" couplet, struck in the name of Mughal emperor Shah Alam II.
Silver Rupee issued by the French East India Company, Arkat Mint, AH 1221 and Regnal Year 45, having the "Saya-e-fazle elah" couplet, struck in the name of Mughal emperor Shah Alam II.
See also

- British East India Company, founded in 1600
- Portuguese East India Company, founded 1628
- Carnatic Wars
- Chanda Sahib
- Dutch East India Company, founded in 1602
- Dutch West India Company, founded in 1621
- European chartered companies founded around the 17th century (in French)
- France-Asia relations
- French colonial empire
- French India
- List of trading companies
- Lorient
- Muzaffar Jang
- Salabat Jang
- Swedish East India Company, founded in 1731
- Whampoa anchorage
Notes
- Mole 2016, p. 24.
- Rogala 2001, p. 31. Caron lived in Japan from 1619 to 1641.
- McCabe 2008, p. 104.
- ^ Shakespeare, Howard (2001). "The Compagnie des Indes". Archived from the original on 25 December 2007. Retrieved 6 March 2008.
- Mole 2016, p. 27.
- ^ Mole 2016, p. 28.
- Mole 2016, pp. 34–35.
- ^ Mole 2016, p. 14.
- Kleen 2017, p. 41.
- Mole 2016, p. 14–15.
- Mole 2016, p. 35.
- Mole 2016, p. 36.
- Danley & Speelman 2012.
- ^ Mole 2016, p. 15.
- ^ Soboul 1975, p. 192.
- ^ Soboul 1975, pp. 360–363.
- Doyle 1990, pp. 273–274.
Bibliography
- Ames, Glenn J. (1996). Colbert, Mercantilism, and the French Quest for Asian Trade. DeKalb, IL: Northern Illinois University Press. ISBN 0-87580-207-9.
- Boucher, P. (1985). The Shaping of the French Colonial Empire: A Bio-Bibliography of the Careers of Richelieu, Fouquet and Colbert. New York: Garland.
- Danley, Mark H.; Speelman, Patrick J., eds. (2012). The Seven Years' War: Global Views. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-23644-8.
- Doyle, William (1990). The Oxford History of the French Revolution (2 ed.). Oxford; New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-925298-5.
- Greenwald, Erin M. (2016). Marc-Antoine Caillot and the Company of the Indies in Louisiana: Trade in the French Atlantic World. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 9780807162859
- Kleen, Michael (2017). Witchcraft in Illinois: A Cultural History. Charleston, South Carolina: The History Press. ISBN 978-1-62585-876-4.
- Lokke, C. L. (1932). France and the Colonial Question: A Study of Contemporary French Public Opinion, 1763–1801. New York: Columbia University Press.
- Malleson, G. B. (1893). History of the French in India. London: W.H. Allen & Co.
- Rogala, Jozef (2001). A Collector's Guide to Books on Japan in English: A Select List of Over 2500 Titles. Richmond, Surrey: Japan Library. ISBN 1-873410-90-5.
- Sen, S. P. (1958). The French in India, 1763–1816. Calcutta: Firma K.L. Mukhopadhyay. ASIN B000HINRSC.
- Sen, S. P. (1947). The French in India: First Establishment and Struggle. Calcutta: University of Calcutta Press.
- Soboul, Albert (1975). The French Revolution 1787–1799. New York: Vintage. ISBN 0-394-71220-X. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- Subramanian, Lakshmi, ed. (1999). French East India Company and the Trade of the Indian Ocean: A Collection of Essays by Indrani Chatterjee. Delhi: Munshiram Publishers.
- McCabe, Ina Baghdiantz (2008). Orientalism in early Modern France. Berg. ISBN 978-1-84520-374-0. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- Wellington, Donald C. (2006). French East India Companies: A Historical Account and Record of Trade. Lanham, Maryland: Hamilton Books.
- Mole, Gregory (2016). Privileging Commerce: The Compagnie des Indes and the politics of trade in old Regime France. Carolina Digital Repository.
External links
- Museum of the French East India Company at Lorient (archived 25 April 2014)
- The French East India Company (1785–1875) – history of the last French East India Company on the site dedicated to its business lawyer Jean-Jacques Regis of Cambaceres.
- French East Indies Company nowadays
- Frenchbooksonindia.com – an open access multilingual discovery tool with book data from 1531 to 2020, full-text ebooks from 1531 to 1937 and in-text search from c. 1830–1920]
| French overseas empire | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Former |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Present |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- French East India Company
- Yanam
- Colonial Indian companies
- 1664 establishments in France
- Companies established in 1664
- 1769 disestablishments in France
- Companies disestablished in 1769
- Trading companies of France
- 1785 establishments in France
- 1794 disestablishments in France
- 1794 disestablishments in French India
- French companies established in 1785
- Trade monopolies
- French slave trade