| Frontonia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Frontonia sp., specimen is digesting cyanobacteria, the mouth (cytostome) is at the bottom right. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| (unranked): | SAR |
| (unranked): | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Ciliophora |
| Subphylum: | Intramacronucleata |
| Class: | Oligohymenophorea |
| Order: | Peniculida |
| Family: | Frontoniidae |
| Genus: | Frontonia Ehrenberg, 1838 |
| Species | |
| See text | |
Frontonia is a genus of free-living unicellular ciliate protists, belonging to the order Peniculida. As Peniculids, the Frontonia are closely related to members of the genus Paramecium. However, whereas Paramecia are mainly bacterivores, Frontonia are capable of ingesting large prey such as diatoms, filamentous algae, testate amoebas, and even, in some circumstances, members of their own species. In bacteria-rich saprobic conditions, Frontonia leucas can live as a facultative bacterivore.
Frontonia are widely dispersed, and members of the genus can be found in marine and freshwater environments on every continent.
Appearance and characteristics
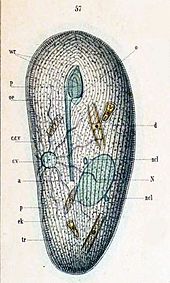

Frontonia species vary in length from 50 to 600 micrometres. Cell bodies are typically ovoid or elongate, and somewhat flattened from back to front. They are flexible, uniformly ciliated, and usually surrounded by trichocysts. The small oral aperture is pear-shaped, and located in the anterior half of the cell. Along the left side of the opening there are three membranelles, and the right has a single paroral membrane. The mouth is supported by inconspicuous microtubular rods (nematodesmata), and may expand during feeding to as much as two-thirds of the cell's length.
The cytoplasm of some species, such as Frontonia atra and Frontonia acuminata, can be darkly pigmented.
Classification
The genus Frontonia, created by C. G. Ehrenberg in 1838, includes some thirty named and described species.
In 2008, analysis of small subunit rRNA gene sequences confirmed the close relationship of several members of the genus: Frontonia leucas, F. vernalis, F. tchibisovae, F. lynni. However, Frontonia didieri was found to be related more closely to a species from another genus, Apofrontonia dohrni. This result calls into question the monophyly of the genus Frontonia, and also casts doubt on the morphological criteria used to distinguish Apofrontonia from it.
Image gallery
Video gallery
- Frontonia leucas ingesting a diatom
- Frontonia atra has symbiotic bacteria in its cytoplasm
- Frontonia leucas, radiating canals around contractile vacuole
- Frontonia vernalis carries symbiotic algae in its cytoplasm
List of accepted species names
- Frontonia aberrans Dragesco, 1960
- Frontonia acuminata (Ehrenberg, 1834) Bütschli, 1889
- Frontonia acuta Fromentel, 1876
- Frontonia acutissima Dumas, 1930
- Frontonia alba Fromentel, 1876
- Frontonia algivora Kahl, 1931
- Frontonia ambigua Dragesco, 1972
- Frontonia angusta Kahl, 1931
- Frontonia arenaria Kahl, 1933
- Frontonia atra (Ehrenberg, 1834) Bütschli, 1889
- Frontonia branchiostomae Codreanu, 1928
- Frontonia canadensis
- Frontonia caneti Dragesco, 1960
- Frontonia curva Fromentel, 1876
- Frontonia cypraea Zacharias, 1904
- Frontonia depressa (Stokes, 1886) Kahl, 1931
- Frontonia didieri Long, Song, AL-Rasheid, Wang, Yi, Al-Quraishy, Lin & AL-Farraj, 2008
- Frontonia elliptica Beardsley, 1902
- Frontonia frigida Petz, Song & Wilbert, 1995
- Frontonia fusca Quennerstedt, 1869
- Frontonia lacrimula Dumas, 1930
- Frontonia leucas (Ehrenberg, 1834) Ehrenberg, 1838
- Frontonia longaria Dumas, 1930
- Frontonia lurida Blochmann, 1895
- Frontonia lynni Long, Song, Gong, Hu, Ma, Zhu & Wang, 2005
- Frontonia macrostoma Srámek-Husek, 1957
- Frontonia magnistoma Foissner, 1987
- Frontonia marina Fabre-Domergue, 1891
- Frontonia marisalbi Burkovsky, 1970
- Frontonia microstoma Kahl, 1931
- Frontonia minuta Dragesco, 1970
- Frontonia multinucleata Long, Song, AL-Rasheid, Wang, Yi, Al-Quraishy, Lin & AL-Farraj, 2008
- Frontonia nassuloides Lepsi, 1926
- Frontonia nigricans Penard, 1922
- Frontonia obtusa
- Frontonia ocularis Bullington, 1940
- Frontonia ovalis Fromentel, 1876
- Frontonia parameciiformis Wenzel, 1953
- Frontonia parva Fromentel, 1876
- Frontonia parvula Penard, 1922
- Frontonia perna Fromentel, 1876
- Frontonia piriformis Dumas, 1930
- Frontonia roqueae Dragesco, 1970
- Frontonia rostrata Fromentel, 1876
- Frontonia rotunda Gelei, 1954
- Frontonia salmastra Dragesco & Dragesco-Kernéis, 1986
- Frontonia schaeferi Bullington, 1940
- Frontonia solea Foissner, 1987
- Frontonia tanganyikae Dragesco & Dragesco-Kernéis, 1991
- Frontonia subtropica
- Frontonia tchibisovae Burkovsky, 1970
- Frontonia terricola Foissner, 1987
- Frontonia undulata Dumas, 1929
- Frontonia vacuolata Dragesco, 1960
- Frontonia vernalis (Ehrenberg, 1834) Kahl, 1931
- Frontonia vesiculosa Cunha, 1913
References
- Dias, Roberto Júnio P.; D'Agosto, Marta (September 2006). "Feeding behavior of Frontonia leucas (Ehrenberg) (Protozoa, Ciliophora, Hymenostomatida) under different environmental conditions in a lotic system". Revista Brasileira de Zoologia. 23 (3): 758–763. doi:10.1590/S0101-81752006000300021.
- Devi, R. Vimala (August 1964). "Cannibalism in Frontonia leucas Ehr". The Journal of Protozoology. 11 (3): 304–307. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.1964.tb01758.x.
- Dias, Roberto Júnio P.; D'Agosto, Marta (September 2006). "Feeding behavior of Frontonia leucas (Ehrenberg) (Protozoa, Ciliophora, Hymenostomatida) under different environmental conditions in a lotic system". Revista Brasileira de Zoologia. 23 (3): 758–763. doi:10.1590/S0101-81752006000300021.
- Petz, Wolfgang; Valbonesi, Alessandro; Schiftner, Uwe; Quesada, Antonio; Cynan Ellis-Evans, J. (2007). "Ciliate biogeography in Antarctic and Arctic freshwater ecosystems: Endemism or global distribution of species?". FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 59 (2): 396–408. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2006.00259.x. PMID 17313584. S2CID 13117002.
- Long, Hongan; Song, Weibo; Al-Rasheid, Khaled A. S.; Wang, Yangang; Yi, Zhenzhen; Al-Quraishy, Saleh A.; Lin, Xiaofeng; Al-Farraj, Saleh A. (23 January 2008). "Taxonomic studies on three marine species of Frontonia from northern China: F. didieri n. sp., F. multinucleata n. sp. and F. tchibisovae Burkovsky, 1970 (Ciliophora: Peniculida)". Zootaxa. 1687 (1): 35. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.1687.1.2.
- Patterson, D.J. Free-Living Freshwater Protozoa: A Colour Guide. Manson, 1992,1996. p. 133. ISBN 1-874545-40-5
- Carey, Philip G., Marine interstitial ciliates: an illustrated key. Chapman and Hall, 1992, ISBN 978-0-412-40610-2 p. 129
- Gil, Rosario (1981). "Cortical fine structure of Frontonia leucas (Ciliata: Holotricha)". Transactions of the American Microscopical Society. 100 (4): 373–383. doi:10.2307/3226150. JSTOR 3226150.
- Goldsmith, William M. (October 1922). "The process of ingestion in the ciliate, Frontonia". Journal of Experimental Zoology. 36 (3): 332–351. doi:10.1002/jez.1400360305.
- Long, Hongan; Song, Weibo; Gong, Jun; Hu, Xiaozhong; Ma, Honggang; Zhu, Mingzhuang; Wang, Mei (3 June 2005). "Frontonia lynni n. sp., a new marine ciliate (Protozoa, Ciliophora, Hymenostomatida) from Qingdao, China". Zootaxa. 1003 (1): 57. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.1003.1.4.
- Gao, Shan; Chen, Zi-Gui; Shao, Chen; Long, Hong-An; Al-Rasheid, Khaled A. S.; Song, Wei-Bo (1 March 2008). "Reconsideration of the phylogenetic position of Frontonia-related Peniculia (Ciliophora, Protozoa) inferred from the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences". Acta Protozoologica. 47 (1). NAID 10029826287.
| Eukaryote classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incertae sedis |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Frontonia | |

