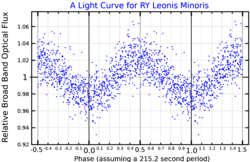
 A light curve for RY Leonis Minoris, plotted from data published by Chote et al. (2014) | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Leo Minor |
| Right ascension | 09 24 15.25 |
| Declination | +35° 16′ 51.4″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 15.5 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | DAV4 |
| U−B color index | −0.6 |
| B−V color index | +0.2 |
| Variable type | DAV |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −145.181 mas/yr Dec.: −0.053 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 17.3947 ± 0.0452 mas |
| Distance | 187.5 ± 0.5 ly (57.5 ± 0.1 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 11.79 |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.69 M☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 8.14 cgs |
| Temperature | 12,400 K |
| Other designations | |
| RY LMi, EGGR 65, WD 0921+354 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
G117-B15A is a small, well-observed variable white dwarf star of the DAV, or ZZ Ceti, type in the constellation of Leo Minor.
G117-B15A was found to be variable in 1974 by Richer and Ulrych, and this was confirmed in 1976 by McGraw and Robinson. In 1984 it was demonstrated that the star's variability is due to nonradial gravity wave pulsations. As a consequence, its timescale for period change is directly proportional to its cooling timescale, allowing its cooling rate to be measured using astroseismological techniques. Its age is estimated at 400 million years. Its light curve has a dominant period of 215.2 seconds, which is estimated to increase by approximately one second each 14 million years. G117-B15A has been claimed to be the most stable optical clock ever found, much more stable than the ticks of an atomic clock. It is also the first pulsating white dwarf to have its main pulsation mode index identified.
An X-ray source in the constellation Leo Minor is the white dwarf G117-B15A.
Notes
- Chote, P.; Sullivan, D. J.; Brown, R.; Harrold, S. T.; Winget, D. E.; Chandler, D. W. (May 2014). "Puoko-nui: a flexible high-speed photometric system". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 440 (2): 1490–1497. arXiv:1412.5724. doi:10.1093/mnras/stu348.
- ^ Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ McCook, George P.; Sion, Edward M. (March 1999). "A Catalog of Spectroscopically Identified White Dwarfs". Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 121 (1): 1–130. Bibcode:1999ApJS..121....1M. doi:10.1086/313186. S2CID 122286998. CDS ID III/210.
- ^ Gianninas, A.; Bergeron, P.; Ruiz, M. T. (2011). "A Spectroscopic Survey and Analysis of Bright, Hydrogen-rich White Dwarfs". The Astrophysical Journal. 743 (2): 138. arXiv:1109.3171. Bibcode:2011ApJ...743..138G. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/743/2/138. S2CID 119210906.
- Kepler, S. O.; Winget, D. E.; Vanderbosch, Zachary P.; Castanheira, Barbara Garcia; Hermes, J. J.; Bell, Keaton J.; Mullally, Fergal; Romero, Alejandra D.; Montgomery, M. H.; Degennaro, Steven; Winget, Karen I.; Chandler, Dean; Jeffery, Elizabeth J.; Fritzen, Jamile K.; Williams, Kurtis A.; Chote, Paul; Zola, Staszek (2020). "The Pulsating White Dwarf G117-B15A: Still the Most Stable Optical Clock Known". The Astrophysical Journal. 906 (1): 7. arXiv:2010.16062. Bibcode:2021ApJ...906....7K. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abc626. S2CID 226222216.
- "V* RY LMi". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2023-01-30.
- ^ Kepler, S. O.; et al. (2000-05-10). "Evolutionary Timescale of the Pulsating White Dwarf G117-B15A: The Most Stable Optical Clock Known". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 534 (2): L185 – L188. arXiv:astro-ph/0003478. Bibcode:2000ApJ...534L.185K. doi:10.1086/312664. PMID 10813678. S2CID 14540467.
- High-frequency optical variables. II. Luminosity-variable white dwarfs and maximum entropy spectral analysis, H. B. Richer and T. J. Ulrych, Astrophysical Journal 192 (September 1974), pp. 719–730.
- High-speed photometry of luminosity-variable DA dwarfs: R808, GD 99, and G 117-B15A, J. T. McGraw and E. L. Robinson, Astrophysical Journal 205 (May 1976), pp. L155–L158.
- Pivetta, Marcos (January 2006). "The star of the moment". Retrieved 2007-06-06.
- From Ṗ=2.3·10 in Kepler et al.
- McDonald Observatory. "Astronomers Find Most Stable Optical Clock in Heavens; Aids Understanding of Stars' Lives". McDonald Observatory. Retrieved 2007-06-06.
- Kepler SO (December 5, 2005). "Astronomers Find Most Stable Optical Clock In Heavens".
See also
| Constellation of Leo Minor | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stars |
| ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Galaxies |
| ||||||||||||