You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. (January 2021) Click for important translation instructions.
|
| Goryōkaku | |
|---|---|
| 五稜郭 | |
| Part of Boshin War | |
| Near Hakodate in Japan | |
 Goryōkaku viewed from Goryōkaku Tower Goryōkaku viewed from Goryōkaku Tower | |
 | |
| Coordinates | 41°47′49″N 140°45′25″E / 41.79694°N 140.75694°E / 41.79694; 140.75694 |
| Type | Star fort |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1866 |
| Built by | Takeda Ayasaburō |
| Battles/wars | Boshin War |
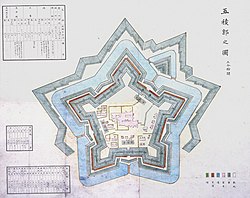 19th century map of Goryōkaku 19th century map of Goryōkaku | |
Goryōkaku (五稜郭, lit. 'five-point fort') is a star fort in the Japanese city of Hakodate on the island of Hokkaido. The fortress was completed in 1866. It was the main headquarters of the short-lived Republic of Ezo.
History
Goryōkaku was designed in 1855 by Takeda Ayasaburō, a scholar of Dutch. He studied the fortified cities of Europe in the early modern period to design a fort that could protect against battles using guns and cannons. It took nearly seven years for the construction. The fortress was completed in 1866, two years before the collapse of the Tokugawa shogunate. It is shaped like a five-pointed star. This allowed for greater numbers of gun emplacements on its walls than a traditional Japanese fortress, and reduced the number of blind spots where a cannon could not fire.
The fort was built by the Tokugawa shogunate, he ordered Takeda Ayasaburō to design the fort for the purpose of protecting Tsugaru Strait. It became the capital of the Republic of Ezo, a state that existed only in 1869. It was the site of the last battle of the Boshin War between the Republic and the Empire of Japan. The fighting lasted for a week (June 20–27, 1869).
Park
Today, Goryōkaku is a park declared as a Special Historical Site, being a part of the Hakodate city museum and a citizens' favorite spot for cherry-blossom viewing in spring.
See also
- List of Special Places of Scenic Beauty, Special Historic Sites and Special Natural Monuments
- Benten Daiba, another key fortress of the Republic of Ezo
- Citadel Hill, a similar shaped fortress in Nova Scotia, Canada
- Fort Bourtange, a similarly shaped fortress in the Netherlands
- List of foreign-style castles in Japan
- Palmanova
References
- Hinago, Motoo (1986). Japanese Castles. Kodansha International Ltd. and Shibundo. pp. 131–133. ISBN 0870117661.
- Schmorleitz, Morton S. (1974). Castles in Japan. C. E. Tuttle Company. p. 144. ISBN 0-8048-1102-4.
- ^ url=https://www.goryokaku-tower.co.jp/en/history/
Further reading
- Benesch, Oleg and Ran Zwigenberg (2019). Japan's Castles: Citadels of Modernity in War and Peace. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 374. ISBN 9781108481946.
- De Lange, William (2021). An Encyclopedia of Japanese Castles. Groningen: Toyo Press. p. 600. ISBN 978-9492722300.
- Schmorleitz, Morton S. (1974). Castles in Japan. Tokyo: Charles E. Tuttle Co. p. 144. ISBN 0-8048-1102-4.
External links
| 100 Fine Castles of Japan by region | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hokkaidō |  | |
| Tōhoku | ||
| Kantō | ||
| Chūbu | ||
| Kansai | ||
| Chūgoku | ||
| Shikoku | ||
| Kyūshū | ||
| including Okinawa. | ||