| |||
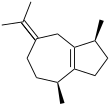
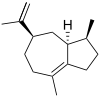 δ-Guaiene | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
α: (1S,4S,7R)-1,4-Dimethyl-7-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydroazulene β: (1S,4S)-1,4-Dimethyl-7-(propan-2-ylidene)-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydroazulene δ: (3S,3aS,5R)-3,8-Dimethyl-5-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1,2,3,3a,4,5,6,7-octahydroazulene | |||
| Other names Guajene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII |
| ||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C15H24 | ||
| Molar mass | 204.357 g·mol | ||
| Boiling point | α: 281-282 °C α: 78-79 °C (@ 2.5 Torr) β: 281 °C | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Guaienes are a series of closely related natural chemical compounds that have been isolated from a variety of plant sources. The guaienes are sesquiterpenes with the molecular formula C15H24. α-Guaiene is the most common and was first isolated from guaiac wood oil from Bulnesia sarmientoi. The guaienes are used in the fragrance and flavoring industries to impart earthy, spicy aromas and tastes.
See also
References
- ^ Alpha-guaiene, The Good Scents Company
- Takeda, Kenichi (1961). "Studies on sesquiterpenoids—III, Some derivatives of guaiol". Tetrahedron. 13 (4): 308–318. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)92224-0.
- Won, Mi-Mi (2009). "Analytica Chimica Acta". 631 (1): 54–61.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Bates, R. B.; Slagel, R. C. (1962). "Terpenoids. VI. β-Bulnesene, α-guaiene, β-patchoulene, and guaioxide in essential oils". Chemistry & Industry: 1715–1716.
- Guaiene, Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives