Star in the constellation Boötes
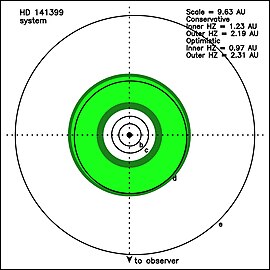 Habitable zone in the HD 141399 system | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Boötes |
| Right ascension | 15 46 53.8135 |
| Declination | 46° 59′ 10.5407″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.20 |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | main-sequence star |
| Spectral type | K0 |
| B−V color index | 0.73±0.04 |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | -21.9±0.2 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: -108.119 mas/yr Dec.: 6.040 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 26.9888 ± 0.0146 mas |
| Distance | 120.85 ± 0.07 ly (37.05 ± 0.02 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.09±0.08 M☉ |
| Radius | 1.46±0.15 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.59±0.39 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.24±0.05 cgs |
| Temperature | 5602±34 K |
| Metallicity | 0.36±0.03 dex |
| Rotation | 49±12 |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 2.9±1.0 km/s |
| Other designations | |
| BD+47 2267, Gaia DR2 1398218223733415552, HIP 77301, TYC 3490-928-1, GSC 03490-00928, 2MASS J15465382+4659105 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
HD 141399 is a K-type main-sequence star 121 light-years away in the constellation of Boötes. Its surface temperature is 5602 K. HD 141399 is enriched in heavy elements compared to the Sun, with a metallicity Fe/H index of 0.36±0.03. Its age is unknown. The star has very low starspot activity.
Planetary system
In 2014, four planets orbiting HD 141399 were discovered by the radial velocity method. Planet HD 141399c is possibly located within the habitable zone. The planetary orbits are close to high-order mean-motion resonance and closely conform to the Titius–Bode law. Two additional planets, one with a period of 462.9 days, are suspected by analogy with the orbits of the Solar System planets. The planetary orbits around HD 141399 are expected to "jump" periodically on a timescale of a few million years between several quasi-stable configurations due to planet-planet interactions. HD 141399 is one of only two known planetary systems consisting of at least four massive gas giants (the other is the system of planets around the young star HR 8799).
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 0.451±0.030 MJ | 0.415±0.011 | 94.44±0.05 | 0.04±0.02 | — | — |
| c | 1.33±0.08 MJ | 0.689±0.02 | 201.99±0.08 | 0.048±0.009 | — | — |
| d | 1.18±0.08 MJ | 2.09±0.06 | 1069.8±6.7 | 0.074±0.025 | — | — |
| e | 0.66±0.10 MJ | 5.0±1.5 | 3370±90 | <0.1 | — | — |
References
- Kane, Stephen R. (2023). "Surrounded by Giants: Habitable Zone Stability within the HD 141399 System". The Astronomical Journal. 166 (5) 187. arXiv:2310.00860. Bibcode:2023AJ....166..187K. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/acfb01.
- ^ "HD 141399". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 6 May 2021.
- ^ Hébrard, Guillaume; Arnold, Luc; Forveille, Thierry; Correia, Alexandre C. M.; Laskar, Jacques; Bonfils, Xavier; Boisse, Isabelle; Díaz, Rodrigo F.; Hagelberg, Janis; Sahlmann, Johannes; Santos, Nuno C.; et al. (1 April 2016). "The SOPHIE search for northern extrasolar planets. X. Detection and characterization of giant planets by the dozen". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 588: A145. arXiv:1602.04622. Bibcode:2016A&A...588A.145H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201527585. ISSN 0004-6361. S2CID 55138055.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 649: A1. arXiv:2012.01533. Bibcode:2021A&A...649A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. S2CID 227254300. (Erratum: doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657e). Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ Sousa, S. G.; Adibekyan, V.; Delgado-Mena, E.; Santos, N. C.; Andreasen, D. T.; Ferreira, A. C. S.; Tsantaki, M.; Barros, S. C. C.; Demangeon, O.; Israelian, G.; Faria, J. P.; Figueira, P.; Mortier, A.; Brandão, I.; Montalto, M.; Rojas-Ayala, B.; Santerne, A. (2018), "SWEET-Cat updated", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 620: A58, arXiv:1810.08108, Bibcode:2018A&A...620A..58S, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833350, S2CID 119374557
- ^ Vogt, Steven S.; Butler, R. Paul; Rivera, Eugenio J.; Kibrick, Robert; Burt, Jennifer; Hanson, Russell; Meschiari, Stefano; Henry, Gregory W.; Laughlin, Gregory (2014), "A Four-Planet System Orbiting the K0V Star Hd 141399", The Astrophysical Journal, 787 (2): 97, arXiv:1404.7462, Bibcode:2014ApJ...787...97V, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/787/2/97, S2CID 10477331
- ^ Agnew, Matthew T.; Maddison, Sarah T.; Horner, Jonathan (2018), "Prospecting for exo-Earths in multiple planet systems with a gas giant", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 481 (4): 4680–4697, arXiv:1809.03730, doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2509
- Allen, Christine; Cordero-Tercero, Guadalupe; Lara, Patricia (2020), "The reliability of the Titius–Bode relation and its implications for the search for exoplanets", Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan, 72 (2), arXiv:2003.05121, doi:10.1093/pasj/psz146
- Staff, News (31 October 2023). "Giant Exoplanets Are Potential 'Agents of Chaos' in Multiplanet Systems, Astronomers Say | Sci.News". Sci.News: Breaking Science News. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
{{cite web}}:|first=has generic name (help)
This main-sequence-star-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |