| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Hellschreiber" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

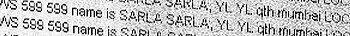

Problems playing this file? See media help.
The Hellschreiber, Feldhellschreiber or Typenbildfeldfernschreiber (also Hell-Schreiber named after its inventor Rudolf Hell) is a facsimile-based teleprinter invented by Rudolf Hell. Compared to contemporary teleprinters that were based on typewriter systems and were mechanically complex and expensive, the Hellschreiber was much simpler and more robust, with far fewer moving parts. It has the added advantage of being capable of providing intelligible communication even over very poor quality radio or cable links, where voice or other teledata would be unintelligible.
The device was first developed in the late 1920s, and saw use starting in the 1930s, chiefly being used for landline press services. During World War II it was sometimes used by the German military in conjunction with the Enigma encryption system. In the post-war era, it became increasingly common among newswire services, and was used in this role well into the 1980s. Today, the Hellschreiber is used as a means of communication by amateur radio operators using computers and sound cards; the resulting mode is referred to as Hellschreiber, Feld-Hell, or simply Hell.
Operation
Hellschreiber sends a line of text as a series of vertical columns. Each column is broken down vertically into a series of pixels, normally using a 7 by 7 pixel grid to represent characters. The data for a line is then sent as a series of on-off signals to the receiver, using a variety of formats depending on the medium, but normally at a rate of 112.5 baud.
At the receiver end, a paper tape is fed at a constant speed over a roller. Located above the roller is a spinning cylinder with small bumps in a helical pattern on the surface. The received signal is amplified and sent to a magnetic actuator that pulls the cylinder down onto the roller, hammering out a dot into the surface of the paper. A Hellschreiber will print each received column twice, one below the other. This is to compensate for slight timing errors that are often present in the equipment, and causes the text to slant. The received text can look like two identical texts coming out one below the other, or a line of text coming out in the middle, with chopped-off lines above and below. In either case, at least one whole letter can be read at all times.
The original Hellschreiber machine was a mechanical device, so therefore it was possible to send "half-pixels". The right ends of the loops in B, for instance, could be shifted a little, so as to improve the readability. Any on-signal could in any case last no shorter than 8 ms, however, both because of having to restrict the occupied bandwidth on the radio, but also for reasons having to do with the mechanical makeup of the receiving machinery.
Improvements that came as a result of software implementation:
- Depicting the received signal as shades of gray instead of monochrome, thereby making it much easier to read weak signals.
- Changing to a different font. Here is one mode that is truly international and independent of character sets: any thing that can be depicted as markings within a 7 pixels high grid, can be transmitted over the air.
Variants

Hellschreiber has also spawned a number of variants over the years, many of them due to radio amateur efforts in the 1990s. Examples of them are:
- PSK Hell encodes a pixel's brightness in the carrier phase instead of the amplitude. Strictly speaking, it's encoded in the change of the phase (differential phase shift keying): an unchanged phase in the beginning of a pixel means white, and a reversed phase means black. It operates at 105 or 245 baud.
- FM Hell (or FSK Hell) uses frequency modulation with a careful control of phase, essentially minimum-shift keying. The most common variant is FSK Hell-105.
- Duplo Hell is a dual tone mode which sends two columns at a time at different frequencies (980 Hz and 1225/1470 Hz).
- C/MT Hell or concurrent multitone Hell sends all rows at the same time using tones at different frequencies. The transmission can be read using an FFT display or a waterfall plot. It allows for high resolutions.
- S/MT Hell or sequential multitone Hell is like C/MT but it sends only one tone (for one row) at a time. As a result, characters received have a bit of slant, they look like an oblique font.
Slowfeld
Slowfeld is an experimental narrow band communication program that makes use of the Hellschreiber principle – requiring that the transmitter and receiver both use the same column-scan speed. Data is sent at a very slow rate and received via a Fast Fourier Transform routine giving a bandwidth of several Hz. As long as tuning is within several signal bandwidths, the result will appear. The transmission rate is around 3, 1.5 and 0.75 characters per second. Slowfeld, along with similar modes such as very slow QRSS Morse code, may be used when all other communication methods fail.
Media
-
 Hellschreiber on display at Bletchley Park, United Kingdom (March 2010)
Hellschreiber on display at Bletchley Park, United Kingdom (March 2010)
-
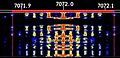 Spectrogram of a Feld-Hell transmission centered on 7072.0 kHz (at ~200 Hz bandwidth)
Spectrogram of a Feld-Hell transmission centered on 7072.0 kHz (at ~200 Hz bandwidth)
-
 QSL card confirming an amateur radio FeldHell contact (2018)
QSL card confirming an amateur radio FeldHell contact (2018)
See also
References
- Freek Simon, Kijkje achter de schermen bij het ANP, 1974: 1:31 ‘Zoals het nu gaat: Via de Hell-zenders komen de berichten uit Parijs, Londen en Berlijn binnen en zonder dat iemand zich hiermee bemoeit worden de uitgezonden ethertrillingen onmiddelijk in leesbaar schrift op de papierband vastgelegd.’ How it's done today: Via the Hell-transmitters the messages from Paris, London and Berlin come in and without any human intervention the broadcast vibrations of the ether are instantly recorded in readable writing on the paper tape.
- "The Hellschreiber - what it is and how it works".
- "VHF Communication via Aircraft Reflections". Archived from the original on 12 April 2015.
External links
- Feld Hell Club website
- Hellschreiber on Signal Identification Wiki
- FELD HELL, WWII Hellschreiber and Hagenuk Ha5K39b in use (Using WWII equipment)
| Amateur radio digital modes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Frequency-shift keying (FSK) |  | |
| Multiple frequency-shift keying (MFSK) | ||
| Phase-shift keying (PSK) | ||
| COFDM |
| |
| Non-traditional digital modes | ||