
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of the moment often form a loop or hysteresis curve, where there are different values of one variable depending on the direction of change of another variable. This history dependence is the basis of memory in a hard disk drive and the remanence that retains a record of the Earth's magnetic field magnitude in the past. Hysteresis occurs in ferromagnetic and ferroelectric materials, as well as in the deformation of rubber bands and shape-memory alloys and many other natural phenomena. In natural systems, it is often associated with irreversible thermodynamic change such as phase transitions and with internal friction; and dissipation is a common side effect.
Hysteresis can be found in physics, chemistry, engineering, biology, and economics. It is incorporated in many artificial systems: for example, in thermostats and Schmitt triggers, it prevents unwanted frequent switching.
Hysteresis can be a dynamic lag between an input and an output that disappears if the input is varied more slowly; this is known as rate-dependent hysteresis. However, phenomena such as the magnetic hysteresis loops are mainly rate-independent, which makes a durable memory possible.
Systems with hysteresis are nonlinear, and can be mathematically challenging to model. Some hysteretic models, such as the Preisach model (originally applied to ferromagnetism) and the Bouc–Wen model, attempt to capture general features of hysteresis; and there are also phenomenological models for particular phenomena such as the Jiles–Atherton model for ferromagnetism.
It is difficult to define hysteresis precisely. Isaak D. Mayergoyz wrote "...the very meaning of hysteresis varies from one area to another, from paper to paper and from author to author. As a result, a stringent mathematical definition of hysteresis is needed in order to avoid confusion and ambiguity.".
Etymology and history
The term "hysteresis" is derived from ὑστέρησις, an Ancient Greek word meaning "deficiency" or "lagging behind". It was coined in 1881 by Sir James Alfred Ewing to describe the behaviour of magnetic materials.
Some early work on describing hysteresis in mechanical systems was performed by James Clerk Maxwell. Subsequently, hysteretic models have received significant attention in the works of Ferenc Preisach (Preisach model of hysteresis), Louis Néel and Douglas Hugh Everett in connection with magnetism and absorption. A more formal mathematical theory of systems with hysteresis was developed in the 1970s by a group of Russian mathematicians led by Mark Krasnosel'skii.
Types
Rate-dependent
One type of hysteresis is a lag between input and output. An example is a sinusoidal input X(t) that results in a sinusoidal output Y(t), but with a phase lag φ:
Such behavior can occur in linear systems, and a more general form of response is
where is the instantaneous response and is the impulse response to an impulse that occurred time units in the past. In the frequency domain, input and output are related by a complex generalized susceptibility that can be computed from ; it is mathematically equivalent to a transfer function in linear filter theory and analogue signal processing.
This kind of hysteresis is often referred to as rate-dependent hysteresis. If the input is reduced to zero, the output continues to respond for a finite time. This constitutes a memory of the past, but a limited one because it disappears as the output decays to zero. The phase lag depends on the frequency of the input, and goes to zero as the frequency decreases.
When rate-dependent hysteresis is due to dissipative effects like friction, it is associated with power loss.
Rate-independent
Systems with rate-independent hysteresis have a persistent memory of the past that remains after the transients have died out. The future development of such a system depends on the history of states visited, but does not fade as the events recede into the past. If an input variable X(t) cycles from X0 to X1 and back again, the output Y(t) may be Y0 initially but a different value Y2 upon return. The values of Y(t) depend on the path of values that X(t) passes through but not on the speed at which it traverses the path. Many authors restrict the term hysteresis to mean only rate-independent hysteresis. Hysteresis effects can be characterized using the Preisach model and the generalized Prandtl−Ishlinskii model.
In engineering
Control systems
In control systems, hysteresis can be used to filter signals so that the output reacts less rapidly than it otherwise would by taking recent system history into account. For example, a thermostat controlling a heater may switch the heater on when the temperature drops below A, but not turn it off until the temperature rises above B. (For instance, if one wishes to maintain a temperature of 20 °C then one might set the thermostat to turn the heater on when the temperature drops to below 18 °C and off when the temperature exceeds 22 °C).
Similarly, a pressure switch can be designed to exhibit hysteresis, with pressure set-points substituted for temperature thresholds.
Electronic circuits
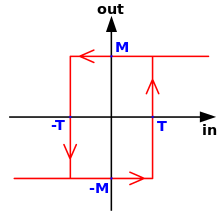
Often, some amount of hysteresis is intentionally added to an electronic circuit to prevent unwanted rapid switching. This and similar techniques are used to compensate for contact bounce in switches, or noise in an electrical signal.
A Schmitt trigger is a simple electronic circuit that exhibits this property.
A latching relay uses a solenoid to actuate a ratcheting mechanism that keeps the relay closed even if power to the relay is terminated.
Some positive feedback from the output to one input of a comparator can increase the natural hysteresis (a function of its gain) it exhibits.
Hysteresis is essential to the workings of some memristors (circuit components which "remember" changes in the current passing through them by changing their resistance).
Hysteresis can be used when connecting arrays of elements such as nanoelectronics, electrochrome cells and memory effect devices using passive matrix addressing. Shortcuts are made between adjacent components (see crosstalk) and the hysteresis helps to keep the components in a particular state while the other components change states. Thus, all rows can be addressed at the same time instead of individually.
In the field of audio electronics, a noise gate often implements hysteresis intentionally to prevent the gate from "chattering" when signals close to its threshold are applied.
User interface design
A hysteresis is sometimes intentionally added to computer algorithms. The field of user interface design has borrowed the term hysteresis to refer to times when the state of the user interface intentionally lags behind the apparent user input. For example, a menu that was drawn in response to a mouse-over event may remain on-screen for a brief moment after the mouse has moved out of the trigger region and the menu region. This allows the user to move the mouse directly to an item on the menu, even if part of that direct mouse path is outside of both the trigger region and the menu region. For instance, right-clicking on the desktop in most Windows interfaces will create a menu that exhibits this behavior.
Aerodynamics
In aerodynamics, hysteresis can be observed when decreasing the angle of attack of a wing after stall, regarding the lift and drag coefficients. The angle of attack at which the flow on top of the wing reattaches is generally lower than the angle of attack at which the flow separates during the increase of the angle of attack.
Hydraulics
Hysteresis can be observed in the stage-flow relationship of a river during rapidly changing conditions such as passing of a flood wave. It is most pronounced in low gradient streams with steep leading edge hydrographs.
Backlash
Moving parts within machines, such as the components of a gear train, normally have a small gap between them, to allow movement and lubrication. As a consequence of this gap, any reversal in direction of a drive part will not be passed on immediately to the driven part. This unwanted delay is normally kept as small as practicable, and is usually called backlash. The amount of backlash will increase with time as the surfaces of moving parts wear.
In mechanics
Elastic hysteresis

In the elastic hysteresis of rubber, the area in the centre of a hysteresis loop is the energy dissipated due to material internal friction.
Elastic hysteresis was one of the first types of hysteresis to be examined.
The effect can be demonstrated using a rubber band with weights attached to it. If the top of a rubber band is hung on a hook and small weights are attached to the bottom of the band one at a time, it will stretch and get longer. As more weights are loaded onto it, the band will continue to stretch because the force the weights are exerting on the band is increasing. When each weight is taken off, or unloaded, the band will contract as the force is reduced. As the weights are taken off, each weight that produced a specific length as it was loaded onto the band now contracts less, resulting in a slightly longer length as it is unloaded. This is because the band does not obey Hooke's law perfectly. The hysteresis loop of an idealized rubber band is shown in the figure.
In terms of force, the rubber band was harder to stretch when it was being loaded than when it was being unloaded. In terms of time, when the band is unloaded, the effect (the length) lagged behind the cause (the force of the weights) because the length has not yet reached the value it had for the same weight during the loading part of the cycle. In terms of energy, more energy was required during the loading than the unloading, the excess energy being dissipated as thermal energy.
Elastic hysteresis is more pronounced when the loading and unloading is done quickly than when it is done slowly. Some materials such as hard metals don't show elastic hysteresis under a moderate load, whereas other hard materials like granite and marble do. Materials such as rubber exhibit a high degree of elastic hysteresis.
When the intrinsic hysteresis of rubber is being measured, the material can be considered to behave like a gas. When a rubber band is stretched it heats up, and if it is suddenly released, it cools down perceptibly. These effects correspond to a large hysteresis from the thermal exchange with the environment and a smaller hysteresis due to internal friction within the rubber. This proper, intrinsic hysteresis can be measured only if the rubber band is thermally isolated.
Small vehicle suspensions using rubber (or other elastomers) can achieve the dual function of springing and damping because rubber, unlike metal springs, has pronounced hysteresis and does not return all the absorbed compression energy on the rebound. Mountain bikes have made use of elastomer suspension, as did the original Mini car.
The primary cause of rolling resistance when a body (such as a ball, tire, or wheel) rolls on a surface is hysteresis. This is attributed to the viscoelastic characteristics of the material of the rolling body.
Contact angle hysteresis
The contact angle formed between a liquid and solid phase will exhibit a range of contact angles that are possible. There are two common methods for measuring this range of contact angles. The first method is referred to as the tilting base method. Once a drop is dispensed on the surface with the surface level, the surface is then tilted from 0° to 90°. As the drop is tilted, the downhill side will be in a state of imminent wetting while the uphill side will be in a state of imminent dewetting. As the tilt increases the downhill contact angle will increase and represents the advancing contact angle while the uphill side will decrease; this is the receding contact angle. The values for these angles just prior to the drop releasing will typically represent the advancing and receding contact angles. The difference between these two angles is the contact angle hysteresis.
The second method is often referred to as the add/remove volume method. When the maximum liquid volume is removed from the drop without the interfacial area decreasing the receding contact angle is thus measured. When volume is added to the maximum before the interfacial area increases, this is the advancing contact angle. As with the tilt method, the difference between the advancing and receding contact angles is the contact angle hysteresis. Most researchers prefer the tilt method; the add/remove method requires that a tip or needle stay embedded in the drop which can affect the accuracy of the values, especially the receding contact angle.
Bubble shape hysteresis
The equilibrium shapes of bubbles expanding and contracting on capillaries (blunt needles) can exhibit hysteresis depending on the relative magnitude of the maximum capillary pressure to ambient pressure, and the relative magnitude of the bubble volume at the maximum capillary pressure to the dead volume in the system. The bubble shape hysteresis is a consequence of gas compressibility, which causes the bubbles to behave differently across expansion and contraction. During expansion, bubbles undergo large non equilibrium jumps in volume, while during contraction the bubbles are more stable and undergo a relatively smaller jump in volume resulting in an asymmetry across expansion and contraction. The bubble shape hysteresis is qualitatively similar to the adsorption hysteresis, and as in the contact angle hysteresis, the interfacial properties play an important role in bubble shape hysteresis.
The existence of the bubble shape hysteresis has important consequences in interfacial rheology experiments involving bubbles. As a result of the hysteresis, not all sizes of the bubbles can be formed on a capillary. Further the gas compressibility causing the hysteresis leads to unintended complications in the phase relation between the applied changes in interfacial area to the expected interfacial stresses. These difficulties can be avoided by designing experimental systems to avoid the bubble shape hysteresis.
Adsorption hysteresis
Hysteresis can also occur during physical adsorption processes. In this type of hysteresis, the quantity adsorbed is different when gas is being added than it is when being removed. The specific causes of adsorption hysteresis are still an active area of research, but it is linked to differences in the nucleation and evaporation mechanisms inside mesopores. These mechanisms are further complicated by effects such as cavitation and pore blocking.
In physical adsorption, hysteresis is evidence of mesoporosity-indeed, the definition of mesopores (2–50 nm) is associated with the appearance (50 nm) and disappearance (2 nm) of mesoporosity in nitrogen adsorption isotherms as a function of Kelvin radius. An adsorption isotherm showing hysteresis is said to be of Type IV (for a wetting adsorbate) or Type V (for a non-wetting adsorbate), and hysteresis loops themselves are classified according to how symmetric the loop is. Adsorption hysteresis loops also have the unusual property that it is possible to scan within a hysteresis loop by reversing the direction of adsorption while on a point on the loop. The resulting scans are called "crossing", "converging", or "returning", depending on the shape of the isotherm at this point.
Matric potential hysteresis
The relationship between matric water potential and water content is the basis of the water retention curve. Matric potential measurements (Ψm) are converted to volumetric water content (θ) measurements based on a site or soil specific calibration curve. Hysteresis is a source of water content measurement error. Matric potential hysteresis arises from differences in wetting behaviour causing dry medium to re-wet; that is, it depends on the saturation history of the porous medium. Hysteretic behaviour means that, for example, at a matric potential (Ψm) of 5 kPa, the volumetric water content (θ) of a fine sandy soil matrix could be anything between 8% and 25%.
Tensiometers are directly influenced by this type of hysteresis. Two other types of sensors used to measure soil water matric potential are also influenced by hysteresis effects within the sensor itself. Resistance blocks, both nylon and gypsum based, measure matric potential as a function of electrical resistance. The relation between the sensor's electrical resistance and sensor matric potential is hysteretic. Thermocouples measure matric potential as a function of heat dissipation. Hysteresis occurs because measured heat dissipation depends on sensor water content, and the sensor water content–matric potential relationship is hysteretic. As of 2002, only desorption curves are usually measured during calibration of soil moisture sensors. Despite the fact that it can be a source of significant error, the sensor specific effect of hysteresis is generally ignored.
In materials
Magnetic hysteresis
Main article: Magnetic hysteresis
When an external magnetic field is applied to a ferromagnetic material such as iron, the atomic domains align themselves with it. Even when the field is removed, part of the alignment will be retained: the material has become magnetized. Once magnetized, the magnet will stay magnetized indefinitely. To demagnetize it requires heat or a magnetic field in the opposite direction. This is the effect that provides the element of memory in a hard disk drive.
The relationship between field strength H and magnetization M is not linear in such materials. If a magnet is demagnetized (H = M = 0) and the relationship between H and M is plotted for increasing levels of field strength, M follows the initial magnetization curve. This curve increases rapidly at first and then approaches an asymptote called magnetic saturation. If the magnetic field is now reduced monotonically, M follows a different curve. At zero field strength, the magnetization is offset from the origin by an amount called the remanence. If the H-M relationship is plotted for all strengths of applied magnetic field the result is a hysteresis loop called the main loop. The width of the middle section is twice the coercivity of the material.
A closer look at a magnetization curve generally reveals a series of small, random jumps in magnetization called Barkhausen jumps. This effect is due to crystallographic defects such as dislocations.
Magnetic hysteresis loops are not exclusive to materials with ferromagnetic ordering. Other magnetic orderings, such as spin glass ordering, also exhibit this phenomenon.
Physical origin
Main article: FerromagnetismThe phenomenon of hysteresis in ferromagnetic materials is the result of two effects: rotation of magnetization and changes in size or number of magnetic domains. In general, the magnetization varies (in direction but not magnitude) across a magnet, but in sufficiently small magnets, it does not. In these single-domain magnets, the magnetization responds to a magnetic field by rotating. Single-domain magnets are used wherever a strong, stable magnetization is needed (for example, magnetic recording).
Larger magnets are divided into regions called domains. Across each domain, the magnetization does not vary; but between domains are relatively thin domain walls in which the direction of magnetization rotates from the direction of one domain to another. If the magnetic field changes, the walls move, changing the relative sizes of the domains. Because the domains are not magnetized in the same direction, the magnetic moment per unit volume is smaller than it would be in a single-domain magnet; but domain walls involve rotation of only a small part of the magnetization, so it is much easier to change the magnetic moment. The magnetization can also change by addition or subtraction of domains (called nucleation and denucleation).
Magnetic hysteresis models
The most known empirical models in hysteresis are Preisach and Jiles-Atherton models. These models allow an accurate modeling of the hysteresis loop and are widely used in the industry. However, these models lose the connection with thermodynamics and the energy consistency is not ensured. A more recent model, with a more consistent thermodynamical foundation, is the vectorial incremental nonconservative consistent hysteresis (VINCH) model of Lavet et al. (2011)
Applications
Main article: Magnet § Common usesThere are a great variety of applications of the hysteresis in ferromagnets. Many of these make use of their ability to retain a memory, for example magnetic tape, hard disks, and credit cards. In these applications, hard magnets (high coercivity) like iron are desirable, such that as much energy is absorbed as possible during the write operation and the resultant magnetized information is not easily erased.
On the other hand, magnetically soft (low coercivity) iron is used for the cores in electromagnets. The low coercivity minimizes the energy loss associated with hysteresis, as the magnetic field periodically reverses in the presence of an alternating current. The low energy loss during a hysteresis loop is the reason why soft iron is used for transformer cores and electric motors.
Electrical hysteresis
Electrical hysteresis typically occurs in ferroelectric material, where domains of polarization contribute to the total polarization. Polarization is the electrical dipole moment (either C·m or C·m). The mechanism, an organization of the polarization into domains, is similar to that of magnetic hysteresis.
Liquid–solid-phase transitions
Hysteresis manifests itself in state transitions when melting temperature and freezing temperature do not agree. For example, agar melts at 85 °C (185 °F) and solidifies from 32 to 40 °C (90 to 104 °F). This is to say that once agar is melted at 85 °C, it retains a liquid state until cooled to 40 °C. Therefore, from the temperatures of 40 to 85 °C, agar can be either solid or liquid, depending on which state it was before.
In biology
Cell biology and genetics
Main article: Cell biologyHysteresis in cell biology often follows bistable systems where the same input state can lead to two different, stable outputs. Where bistability can lead to digital, switch-like outputs from the continuous inputs of chemical concentrations and activities, hysteresis makes these systems more resistant to noise. These systems are often characterized by higher values of the input required to switch into a particular state as compared to the input required to stay in the state, allowing for a transition that is not continuously reversible, and thus less susceptible to noise.
Irreversible Hysteresis

In the case of mitosis, irreversibility is essential to maintain the overall integrity of the system such that we have three designated checkpoints to account for this: G1/S, G2/M, and the spindle checkpoint. Irreversible hysteresis in this context ensures that once a cell commits to a specific phase (e.g., entering mitosis or DNA replication), it does not revert to a previous phase, even if conditions or regulatory signals change. Based on the irreversible hysteresis curve, there does exit a at which the cell jumps to the next bistable region, but there isn’t a that allows the cell to revert to its previous bistable region. The cell has no way of reverting back down to its previous bistable region even when is 0, demonstrating irreversibility. Positive feedback is critical for generating hysteresis in the cell cycle. For example: In the G2/M transition, active CDK1 promotes the activation of more CDK1 molecules by inhibiting Wee1 (an inhibitor) and activating Cdc25 (a phosphatase that activates CDK1). These loops lock the cell into its current state and amplifying the activation of CDK1. Positive feedback also serves to create a bistable system where CDK1 is either fully inactivated or fully activated. Hysteresis prevents the cell from oscillating between these two states from small perturbations in signal (input).
Reversible Hysteresis

A biochemical system that is under the control of reversible hysteresis has both forward and reverse trajectories. The system generally requires a higher to proceed forward into the next bistable state then to exit from that stage. For example, cells undergoing cell division exhibit reversible hysteresis in that it takes a higher concentration of cyclins to switch them from G2 phase into mitosis than to stay in mitosis once begun . Additionally, because the required to reverse the cell back to the G2 phase is much lower than the to enter mitosis, this improved the bistability of mitosis because it is more resistance to weak or transient signals. Small perturbations the won’t be able to push the cell out of mitosis so easily.
History and Memory
In systems with bistability, the same input level can correspond to two distinct stable states (e.g., "low output" and "high output"). The actual state of the system depends on its history — whether the input level was increasing (forward trajectory) or decreasing (backward trajectory). Thus, it is difficult to determine which state a cell is in if given only a bistability curve. The cell’s ability to "remember" its prior state ensures stability and prevents it from switching states unnecessarily due to minor fluctuations in input. This memory is often maintained through molecular feedback loops, such as positive feedback in signaling pathways, or the persistence of regulatory molecules like proteins or phosphorylated components. For example, the refractory period in action potentials is primarily controlled by history. Absolute refraction period prevents a volted-gated sodium channel from activating or refiring after it has just fired. This is because following the absolute refractory period, the neuron is less excitable due to hyperpolarization caused by potassium efflux. This molecular inhibitory feedback creates a memory for the neuron or cell, so that the neuron doesn’t fire too soon. As time passes, the neuron or cell will slowly lose the memory of having fired and will begin to fire again. Thus, memory is time-dependent, which is important in maintaining homeostasis and regulating many different biological processes.
Biochemical Systems: Regulating the Cell Cycle in Xenopus Laevis Egg Extracts
Cells advancing through the cell cycle must make an irreversible commitment to mitosis, ensuring they do not revert to interphase before successfully segregating their chromosomes. A mathematical model of cell-cycle progression in cell-free egg extracts from frogs suggests that hysteresis in the molecular control system drives these irreversible transitions into and out of mitosis. Here, Cdc2 (Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 or CDK1) is responsible for mitotic entry and exit such that binding of cyclin B forms a complex called Maturation-Promoting Factor (MPF). The activation threshold for mitotic entry was found to be between 32 and 40 nM cyclin B in the frog extracts while the inactivation threshold for exiting mitosis was lower, between 16 and 24 nM cyclin B. The higher threshold for mitotic entry compared to the lower threshold for mitotic exit indicates hysteresis, a hallmark of history-dependent behavior in the system. Concentrations between 24 and 32 nM cyclin B demonstrated bistability, where the system could exist in either interphase or mitosis, depending on its prior state (history). Though, the cell cycle isn’t completely irreversible, the difference in thresholds is enough for growth and survival of the cells.
Hysteric thresholds in biological systems are not definite and can be recalibrated. For example, unreplicated DNA or chromosomes inhibits Cdc25 phosphatase and maintains Wee1 kinase activity. This prevents the activation of Cyclin B-Cdc2, effectively raising the threshold for mitotic entry. As a result, the cell delays the transition to mitosis until replication is complete, ensuring genomic integrity. Other instances may be DNA damage and unattached chromosomes during the spindle assembly checkpoint.
Biochemical Systems: Regulating the Cell Cycle in Yeast
Biochemical systems can also show hysteresis-like output when slowly varying states that are not directly monitored are involved, as in the case of the cell cycle arrest in yeast exposed to mating pheromone. The proposed model is that α-factor, a yeast mating pheromone binds to its analog receptor on another yeast cell promoting transcription of Fus3 and promoting mating. Fus3 further promotes Far1 which inhibits Cln1/2, activators of the cell cycle. This is representative of a coherent feedforward loop that can modeled as a hysteresis curve.
Far1 transcription is the primary mechanism responsible for the hysteresis observed in cell-cycle reentry. The history of pheromone exposure influences the accumulation of Far1, which, in turn, determines the delay in cell-cycle reentry. Previous pulse experiments demonstrated that after exposure to high pheromone concentrations, cells enter a stabilized arrested state where reentry thresholds are elevated due to increased Far1-dependent inhibition of CDK activity. Even when pheromone levels drop to concentrations that would allow naive cells to reenter the cell cycle, pre-exposed cells take longer to resume proliferation. This delay reflects the history-dependent nature of hysteresis, where past exposure to high pheromone concentrations influences the current state. Hysteresis ensures that cells make robust and irreversible decisions about mating and proliferation in response to pheromone signals. It allows cells to "remember" high pheromone exposure, and this helps yeast cells adapt and stability their responses to environmental conditions, avoiding fast premature reentry into the cell cycle, the moment that pheromone signal dies down.
Additionally, the duration of cell cycle arrest depends not only on the final level of input Fus3, but also on the previously achieved Fus3 levels. This effect is achieved due to the slower time scales involved in the transcription of intermediate Far1, such that the total Far1 activity reaches its equilibrium value slowly, and for transient changes in Fus3 concentration, the response of the system depends on the Far1 concentration achieved with the transient value. Experiments in this type of hysteresis benefit from the ability to change the concentration of the inputs with time. The mechanisms are often elucidated by allowing independent control of the concentration of the key intermediate, for instance, by using an inducible promoter.
Biochemical systems can also show hysteresis-like output when slowly varying states that are not directly monitored are involved, as in the case of the cell cycle arrest in yeast exposed to mating pheromone. Here, the duration of cell cycle arrest depends not only on the final level of input Fus3, but also on the previously achieved Fus3 levels. This effect is achieved due to the slower time scales involved in the transcription of intermediate Far1, such that the total Far1 activity reaches its equilibrium value slowly, and for transient changes in Fus3 concentration, the response of the system depends on the Far1 concentration achieved with the transient value. Experiments in this type of hysteresis benefit from the ability to change the concentration of the inputs with time. The mechanisms are often elucidated by allowing independent control of the concentration of the key intermediate, for instance, by using an inducible promoter.
Main article: ChromatinDarlington in his classic works on genetics discussed hysteresis of the chromosomes, by which he meant "failure of the external form of the chromosomes to respond immediately to the internal stresses due to changes in their molecular spiral", as they lie in a somewhat rigid medium in the limited space of the cell nucleus.
Main article: MorphogenIn developmental biology, cell type diversity is regulated by long range-acting signaling molecules called morphogens that pattern uniform pools of cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. The morphogen sonic hedgehog (Shh), for example, acts on limb bud and neural progenitors to induce expression of a set of homeodomain-containing transcription factors to subdivide these tissues into distinct domains. It has been shown that these tissues have a 'memory' of previous exposure to Shh. In neural tissue, this hysteresis is regulated by a homeodomain (HD) feedback circuit that amplifies Shh signaling. In this circuit, expression of Gli transcription factors, the executors of the Shh pathway, is suppressed. Glis are processed to repressor forms (GliR) in the absence of Shh, but in the presence of Shh, a proportion of Glis are maintained as full-length proteins allowed to translocate to the nucleus, where they act as activators (GliA) of transcription. By reducing Gli expression then, the HD transcription factors reduce the total amount of Gli (GliT), so a higher proportion of GliT can be stabilized as GliA for the same concentration of Shh.
Immunology
There is some evidence that T cells exhibit hysteresis in that it takes a lower signal threshold to activate T cells that have been previously activated. Ras GTPase activation is required for downstream effector functions of activated T cells. Triggering of the T cell receptor induces high levels of Ras activation, which results in higher levels of GTP-bound (active) Ras at the cell surface. Since higher levels of active Ras have accumulated at the cell surface in T cells that have been previously stimulated by strong engagement of the T cell receptor, weaker subsequent T cell receptor signals received shortly afterwards will deliver the same level of activation due to the presence of higher levels of already activated Ras as compared to a naïve cell.
Neuroscience
See also: Refractory period (physiology)The property by which some neurons do not return to their basal conditions from a stimulated condition immediately after removal of the stimulus is an example of hysteresis.
Neuropsychology
Main articles: Context-dependent memory and State-dependent memoryNeuropsychology, in exploring the neural correlates of consciousness, interfaces with neuroscience, although the complexity of the central nervous system is a challenge to its study (that is, its operation resists easy reduction). Context-dependent memory and state-dependent memory show hysteretic aspects of neurocognition.
Respiratory physiology
Lung hysteresis is evident when observing the compliance of a lung on inspiration versus expiration. The difference in compliance (Δvolume/Δpressure) is due to the additional energy required to overcome surface tension forces during inspiration to recruit and inflate additional alveoli.
The transpulmonary pressure vs Volume curve of inhalation is different from the Pressure vs Volume curve of exhalation, the difference being described as hysteresis. Lung volume at any given pressure during inhalation is less than the lung volume at any given pressure during exhalation.
Voice and speech physiology
A hysteresis effect may be observed in voicing onset versus offset. The threshold value of the subglottal pressure required to start the vocal fold vibration is lower than the threshold value at which the vibration stops, when other parameters are kept constant. In utterances of vowel-voiceless consonant-vowel sequences during speech, the intraoral pressure is lower at the voice onset of the second vowel compared to the voice offset of the first vowel, the oral airflow is lower, the transglottal pressure is larger and the glottal width is smaller.
Ecology and epidemiology
Hysteresis is a commonly encountered phenomenon in ecology and epidemiology, where the observed equilibrium of a system can not be predicted solely based on environmental variables, but also requires knowledge of the system's past history. Notable examples include the theory of spruce budworm outbreaks and behavioral-effects on disease transmission.
It is commonly examined in relation to critical transitions between ecosystem or community types in which dominant competitors or entire landscapes can change in a largely irreversible fashion.
In ocean and climate science
Complex ocean and climate models rely on the principle.
In economics
Main article: Hysteresis (economics)Economic systems can exhibit hysteresis. For example, export performance is subject to strong hysteresis effects: because of the fixed transportation costs it may take a big push to start a country's exports, but once the transition is made, not much may be required to keep them going.
When some negative shock reduces employment in a company or industry, fewer employed workers then remain. As usually the employed workers have the power to set wages, their reduced number incentivizes them to bargain for higher wages when the economy again gets better instead of letting the wage be at the equilibrium wage level, where the supply and demand of workers would match. This causes hysteresis: the unemployment becomes permanently higher after negative shocks.
Permanently higher unemployment
The idea of hysteresis is used extensively in the area of labor economics, specifically with reference to the unemployment rate. According to theories based on hysteresis, severe economic downturns (recession) and/or persistent stagnation (slow demand growth, usually after a recession) cause unemployed individuals to lose their job skills (commonly developed on the job) or to find that their skills have become obsolete, or become demotivated, disillusioned or depressed or lose job-seeking skills. In addition, employers may use time spent in unemployment as a screening tool, i.e., to weed out less desired employees in hiring decisions. Then, in times of an economic upturn, recovery, or "boom", the affected workers will not share in the prosperity, remaining unemployed for long periods (e.g., over 52 weeks). This makes unemployment "structural", i.e., extremely difficult to reduce simply by increasing the aggregate demand for products and labor without causing increased inflation. That is, it is possible that a ratchet effect in unemployment rates exists, so a short-term rise in unemployment rates tends to persist. For example, traditional anti-inflationary policy (the use of recession to fight inflation) leads to a permanently higher "natural" rate of unemployment (more scientifically known as the NAIRU). This occurs first because inflationary expectations are "sticky" downward due to wage and price rigidities (and so adapt slowly over time rather than being approximately correct as in theories of rational expectations) and second because labor markets do not clear instantly in response to unemployment.
The existence of hysteresis has been put forward as a possible explanation for the persistently high unemployment of many economies in the 1990s. Hysteresis has been invoked by Olivier Blanchard among others to explain the differences in long run unemployment rates between Europe and the United States. Labor market reform (usually meaning institutional change promoting more flexible wages, firing, and hiring) or strong demand-side economic growth may not therefore reduce this pool of long-term unemployed. Thus, specific targeted training programs are presented as a possible policy solution. However, the hysteresis hypothesis suggests such training programs are aided by persistently high demand for products (perhaps with incomes policies to avoid increased inflation), which reduces the transition costs out of unemployment and into paid employment easier.
Models
Hysteretic models are mathematical models capable of simulating complex nonlinear behavior (hysteresis) characterizing mechanical systems and materials used in different fields of engineering, such as aerospace, civil, and mechanical engineering. Some examples of mechanical systems and materials having hysteretic behavior are:
- materials, such as steel, reinforced concrete, wood;
- structural elements, such as steel, reinforced concrete, or wood joints;
- devices, such as seismic isolators and dampers.
Each subject that involves hysteresis has models that are specific to the subject. In addition, there are hysteretic models that capture general features of many systems with hysteresis. An example is the Preisach model of hysteresis, which represents a hysteresis nonlinearity as a linear superposition of square loops called non-ideal relays. Many complex models of hysteresis arise from the simple parallel connection, or superposition, of elementary carriers of hysteresis termed hysterons.
A simple and intuitive parametric description of various hysteresis loops may be found in the Lapshin model. Along with the smooth loops, substitution of trapezoidal, triangular or rectangular pulses instead of the harmonic functions allows piecewise-linear hysteresis loops frequently used in discrete automatics to be built in the model. There are implementations of the hysteresis loop model in Mathcad and in R programming language.
The Bouc–Wen model of hysteresis is often used to describe non-linear hysteretic systems. It was introduced by Bouc and extended by Wen, who demonstrated its versatility by producing a variety of hysteretic patterns. This model is able to capture in analytical form, a range of shapes of hysteretic cycles which match the behaviour of a wide class of hysteretical systems; therefore, given its versability and mathematical tractability, the Bouc–Wen model has quickly gained popularity and has been extended and applied to a wide variety of engineering problems, including multi-degree-of-freedom (MDOF) systems, buildings, frames, bidirectional and torsional response of hysteretic systems two- and three-dimensional continua, and soil liquefaction among others. The Bouc–Wen model and its variants/extensions have been used in applications of structural control, in particular in the modeling of the behaviour of magnetorheological dampers, base isolation devices for buildings and other kinds of damping devices; it has also been used in the modelling and analysis of structures built of reinforced concrete, steel, masonry and timber.. The most important extension of Bouc-Wen Model was carried out by Baber and Noori and later by Noori and co-workers. That extended model, named, BWBN, can reproduce the complex shear pinching or slip-lock phenomenon that earlier model could not reproduce. The BWBN model has been widely used in a wide spectrum of applications and implementations are available in software such as OpenSees.
Hysteretic models may have a generalized displacement as input variable and a generalized force as output variable, or vice versa. In particular, in rate-independent hysteretic models, the output variable does not depend on the rate of variation of the input one.
Rate-independent hysteretic models can be classified into four different categories depending on the type of equation that needs to be solved to compute the output variable:
- algebraic models
- transcendental models
- differential models
- integral models
List of models
Some notable hysteretic models are listed below, along with their associated fields.
- Bean's critical state model (magnetism)
- Bouc–Wen model (structural engineering)
- Ising model (magnetism)
- Jiles–Atherton model (magnetism)
- Novak–Tyson model (cell-cycle control)
- Preisach model (magnetism)
- Stoner–Wohlfarth model (magnetism)
Energy
When hysteresis occurs with extensive and intensive variables, the work done on the system is the area under the hysteresis graph.
See also
- Backlash (engineering)
- Bean's critical state model
- Black box
- Deadband
- Fuzzy control system
- Hysteresivity
- Markov property
- Memristor
- Path dependence
- Path dependence (physics)
- Remanence
References
- Mayergoyz, I. D. (2003). Mathematical models of hysteresis and their applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier. p. xiv. ISBN 978-0-12-480873-7. OCLC 162129543.
- "VII. On the production of transient electric currents in iron and steel conductors by twisting them when magnetised or by magnetising them when twisted". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. 33 (216–219): 21–23. 1882. doi:10.1098/rspl.1881.0067. S2CID 110895565.
- ^ Bertotti, Giorgio (1998). "Ch. 2". Hysteresis in magnetism: For physicists, materials scientists, and engineers. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-093270-2.
- The term is attributed to Truesdell & Noll 1965 by Visintin 1994, page 13.
- Visintin 1994, page 13
- Mohammad Al Janaideh, Subhash Rakheja, Chun-Yi Su An analytical generalized Prandtl–Ishlinskii model inversion for hysteresis compensation in micropositioning control, IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, Volume:16 Issue:4, pp 734−744, 15 July 2010
- Johnson, R. Colin. "'Missing link' memristor created: Rewrite the textbooks?". EE Times April 30, 2008. Archived from the original on 30 September 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- Zifeng Yang; Hirofumi Igarashi; Mathew Martin; Hui Hu (Jan 7–10, 2008). An Experimental Investigation on Aerodynamic Hysteresis of a Low-Reynolds Number Airfoil (PDF). 46th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reno, Nevada: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. AIAA-2008-0315. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-08-10. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- Holmes, Robert R. Jr. (February 2018). River rating complexity (PDF). Proceedings of the International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics (River flow 2016).
- Warnecke, Martin; Jouaneh, Musa (1 September 2003). "Backlash Compensation in Gear Trains by Means of Open-Loop Modification of the Input Trajectory". Journal of Mechanical Design. 125 (3): 620–624. doi:10.1115/1.1596241.
- Love, Augustus E. (1927). Treatise on the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity (Dover Books on Physics & Chemistry). New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-60174-8.
- Ewing, J. A. (1889). "On hysteresis in the relation of strain to stress". British Association Reports: 502.
- Hopkinson, B.; Williams, G. T. (1912). "The Elastic Hysteresis of Steel". Proceedings of the Royal Society. 87 (598): 502. Bibcode:1912RSPSA..87..502H. doi:10.1098/rspa.1912.0104.
- ^ Chandran Suja, V.; Frostad, J. M.; Fuller, G. G. (2016-10-31). "Impact of Compressibility on the Control of Bubble-Pressure Tensiometers". Langmuir. 32 (46): 12031–12038. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03258. ISSN 0743-7463. PMID 27798833.
- Alvarez, Nicolas J.; Walker, Lynn M.; Anna, Shelley L. (2010-08-17). "A Microtensiometer To Probe the Effect of Radius of Curvature on Surfactant Transport to a Spherical Interface". Langmuir. 26 (16): 13310–13319. doi:10.1021/la101870m. ISSN 0743-7463. PMID 20695573.
- Gregg, S. J.; Sing, Kenneth S. W. (1982). Adsorption, Surface Area, and Porosity (Second ed.). London: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-300956-2.
- Sing, K. S. W.; Everett, D. H.; Haul, R. A. W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R. A.; J. Roquérol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. (1985). "Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 57 (4): 603–619. doi:10.1351/pac198557040603. S2CID 14894781.
- Tompsett, G. A.; Krogh, L.; Griffin, D. W.; Conner, W. C. (2005). "Hysteresis and Scanning Behavior of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves". Langmuir. 21 (8): 8214–8225. doi:10.1021/la050068y. PMID 16114924.
- Parkes, Martin (8 April 1999). "Subject: Accuracy of capacitance soil moisture ..." SOWACS (Mailing list). Archived from the original on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 28 September 2011.
- Scanlon, Bridget R.; Andraski, Brian J.; Bilskie, Jim (2002). "3.2.4 Miscellaneous methods for measuring matric or water potential" (PDF). Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4 Physical Methods. SSSA Book Series. Soil Science Society of America. pp. 643–670. doi:10.2136/sssabookser5.4.c23. ISBN 978-0-89118-893-3. S2CID 102411388. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-03-13. Retrieved 2006-05-26.
- Chikazumi 1997, Chapter 1
- Chikazumi 1997, Chapter 15
- Monod, P.; PréJean, J. J.; Tissier, B. (1979). "Magnetic hysteresis of CuMn in the spin glass state". J. Appl. Phys. 50 (B11): 7324. Bibcode:1979JAP....50.7324M. doi:10.1063/1.326943.
- Vincent Francois-Lavet et al (2011-11-14). Vectorial Incremental Nonconservative Consistent Hysteresis model.
- Makar, A. B.; McMartin, K. E.; Palese, M.; Tephly, T. R. (June 1975). "Formate assay in body fluids: application in methanol poisoning". Biochemical Medicine. 13 (2): 117–126. doi:10.1016/0006-2944(75)90147-7. ISSN 0006-2944. PMID 1.
- Schmidt, Matthias; Rohe, Alexander; Platzer, Charlott; Najjar, Abdulkarim; Erdmann, Frank; Sippl, Wolfgang (2017-11-23). "Regulation of G2/M Transition by Inhibition of WEE1 and PKMYT1 Kinases". Molecules. 22 (12): 2045. doi:10.3390/molecules22122045. PMC 6149964. PMID 29168755.
- Pomerening, Joseph R.; Sontag, Eduardo D.; Ferrell, James E. (2003). "Building a cell cycle oscillator: hysteresis and bistability in the activation of Cdc2". Nature Cell Biology. 5 (4): 346–251. doi:10.1038/ncb954. PMID 12629549. S2CID 11047458.
- Ferrell JE Jr.; Machleder EM (1998). "The biochemical basis of an all-or-none cell fate switch in Xenopus oocytes". Science. 280 (5365): 895–8. Bibcode:1998Sci...280..895F. doi:10.1126/science.280.5365.895. PMID 9572732.
- Smith, R. J.; Bryant, R. G. (1975-10-27). "Metal substitutions incarbonic anhydrase: a halide ion probe study". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 66 (4): 1281–1286. doi:10.1016/0006-291x(75)90498-2. ISSN 0006-291X. PMID 3.
- Jiang, Yanfei; Hao, Nan (2021-04-01). "Memorizing environmental signals through feedback and feedforward loops". Current Opinion in Cell Biology. Cell Signalling. 69: 96–102. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2020.11.008. ISSN 0955-0674. PMC 8058236. PMID 33549848.
- Schmidt, Robert F.; Thews, Gerhard, eds. (1983). Human physiology. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-11669-1.
- Chow, Y. W.; Pietranico, R.; Mukerji, A. (1975-10-27). "Studies of oxygen binding energy to hemoglobin molecule". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 66 (4): 1424–1431. doi:10.1016/0006-291x(75)90518-5. ISSN 0006-291X. PMID 6.
- Hoffmann, I.; Clarke, P. R.; Marcote, M. J.; Karsenti, E.; Draetta, G. (January 1993). "Phosphorylation and activation of human cdc25-C by cdc2--cyclin B and its involvement in the self-amplification of MPF at mitosis". The EMBO Journal. 12 (1): 53–63. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05631.x. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 413175. PMID 8428594.
- Perry, Jennifer A.; Kornbluth, Sally (2007-05-04). "Cdc25 and Wee1: analogous opposites?". Cell Division. 2: 12. doi:10.1186/1747-1028-2-12. PMC 1868713. PMID 17480229.
- Marniemi, J.; Parkki, M. G. (1975-09-01). "Radiochemical assay of glutathione S-epoxide transferase and its enhancement by phenobarbital in rat liver in vivo". Biochemical Pharmacology. 24 (17): 1569–1572. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(75)90080-5. ISSN 0006-2952. PMID 9.
- Doncic, Andreas; Skotheim, Jan M (2013). "Feedforward regulation ensures stability and rapid reversibility of a cellular state". Molecular Cell. 50 (6): 856–68. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.04.014. PMC 3696412. PMID 23685071.
- Doncic, Andreas; Skotheim, Jan M. (2013-06-27). "Feedforward Regulation Ensures Stability and Rapid Reversibility of a Cellular State". Molecular Cell. 50 (6): 856–868. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.04.014. ISSN 1097-2765. PMC 3696412. PMID 23685071.
- Darlington, C. D. (1937). Recent Advances in Cytology (Genes, Cells, & Organisms) (Second ed.). P. Blakiston's Son & Co. ISBN 978-0-8240-1376-9.
- Rieger, R.; Michaelis, A.; M. M. (1968). A Glossary of Genetics and Cytogenetics: Classical and Molecular (Third ed.). Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-04316-4.
- Harfe, B. D.; Scherz, P. J.; Nissim, S.; Tian, H.; McMahon, A. P.; Tabin, C. J. (2004). "Evidence for an expansion-based temporal Shh gradient in specifying vertebrate digit identities". Cell. 118 (4): 517–28. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.024. PMID 15315763. S2CID 16280983.
- Lek, M.; Dias, J. M.; Marklund, U.; Uhde, C. W.; Kurdija, S.; Lei, Q.; Sussel, L.; Rubenstein, J. L.; Matise, M. P.; Arnold, H. -H.; Jessell, T. M.; Ericson, J. (2010). "A homeodomain feedback circuit underlies step-function interpretation of a Shh morphogen gradient during ventral neural patterning". Development. 137 (23): 4051–4060. doi:10.1242/dev.054288. PMID 21062862.
- Das, J.; Ho, M.; Zikherman, J.; Govern, C.; Yang, M.; Weiss, A.; Chakraborty, A. K.; Roose, J. P. (2009). "Digital Signaling and Hysteresis Characterize Ras Activation in Lymphoid Cells". Cell. 136 (2): 337–351. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.051. PMC 2662698. PMID 19167334.
- Escolar, J. D.; Escolar, A. (2004). "Lung histeresis: a morphological view" (PDF). Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology. 19 (1): 159–166. PMID 14702184. Retrieved 1 March 2011.
- West, John B. (2005). Respiratory physiology: the essentials. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-5152-0.
- Lucero, Jorge C. (1999). "A theoretical study of the hysteresis phenomenon at vocal fold oscillation onset–offset". The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 105 (1): 423–431. Bibcode:1999ASAJ..105..423L. doi:10.1121/1.424572. ISSN 0001-4966. PMID 9921668.
- Strogatz, Stephen H. (1994). Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos. Perseus Books Publishing. pp. 73–79. ISBN 0-7382-0453-6.
- Sternberg, Leonel Da Silveira Lobo (21 December 2001). "Savanna–forest hysteresis in the tropics". Global Ecology and Biogeography. 10 (4): 369–378. Bibcode:2001GloEB..10..369D. doi:10.1046/j.1466-822X.2001.00243.x.
- Beisner, BE; Haydon, DT; Cuddington, K (1 September 2003). "Alternative stable states in ecology". Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. 1 (7): 376–382. doi:10.2307/3868190. JSTOR 3868190.
- Hofmann, Matthias; Rahmstorf, Stefan (2009-12-08). "On the stability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (49): 20584–20589. doi:10.1073/pnas.0909146106. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 2791639. PMID 19897722.
- Das, Moupriya; Kantz, Holger (2020-06-29). "Stochastic resonance and hysteresis in climate with state-dependent fluctuations". Physical Review E. 101 (6): 062145. Bibcode:2020PhRvE.101f2145D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.101.062145. ISSN 2470-0045. PMID 32688620.
- ^ Ball, Laurence M. (March 2009). "Hysteresis in Unemployment: Old and New Evidence". NBER Working Paper No. 14818. doi:10.3386/w14818.
- Blanchard, Olivier J.; Summers, Lawrence H. (1986). "Hysteresis and the European Unemployment Problem". NBER Macroeconomics Annual. 1: 15–78. doi:10.2307/3585159. JSTOR 3585159.
- S.P. Hargreaves Heap (1980). "Choosing the Wrong `Natural' Rate: Accelerating Inflation or Decelerating Employment and Growth?" The Economic Journal Vol. 90, No. 359 (Sep., 1980), pp. 611-620. JSTOR 2231931
- Vaiana, Nicolò; Spizzuoco, Mariacristina; Serino, Giorgio (June 2017). "Wire rope isolators for seismically base-isolated lightweight structures: Experimental characterization and mathematical modeling". Engineering Structures. 140: 498–514. Bibcode:2017EngSt.140..498V. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.02.057.
- ^ Mayergoyz, Isaak D. (2003). Mathematical Models of Hysteresis and their Applications: Second Edition (Electromagnetism). Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-480873-7.
- ^ R. V. Lapshin (1995). "Analytical model for the approximation of hysteresis loop and its application to the scanning tunneling microscope" (PDF). Review of Scientific Instruments. 66 (9). USA: AIP: 4718–4730. arXiv:2006.02784. Bibcode:1995RScI...66.4718L. doi:10.1063/1.1145314. ISSN 0034-6748. S2CID 121671951. (Russian translation is available).
- ^ R. V. Lapshin (2020). "An improved parametric model for hysteresis loop approximation". Review of Scientific Instruments. 91 (6). USA: AIP: 065106. arXiv:1701.08070. Bibcode:2020RScI...91f5106L. doi:10.1063/5.0012931. ISSN 0034-6748. PMID 32611047. S2CID 13489477.
- S. Maynes; F. Yang; A. Parkhurst (November 20, 2013). "Package Hysteresis (Tools for Modeling Rate-Dependent Hysteretic Processes and Ellipses)". R-project. Retrieved June 11, 2020.
- Bouc, R. (1967). "Forced vibration of mechanical systems with hysteresis". Proceedings of the Fourth Conference on Nonlinear Oscillation. Prague, Czechoslovakia. p. 315.
- Bouc, R. (1971). "Modèle mathématique d'hystérésis: application aux systèmes à un degré de liberté". Acustica (in French). 24: 16–25.
- Wen, Y. K. (1976). "Method for random vibration of hysteretic systems". Journal of Engineering Mechanics. 102 (2): 249–263.
- Dimian, Mihai; Andrei, Petru (4 November 2013). Noise-driven phenomena in hysteretic systems. Springer. ISBN 9781461413745.
- Vaiana, Nicolò; Sessa, Salvatore; Rosati, Luciano (January 2021). "A generalized class of uniaxial rate-independent models for simulating asymmetric mechanical hysteresis phenomena". Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. 146: 106984. Bibcode:2021MSSP..14606984V. doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106984. S2CID 224951872.
Further reading
- Chikazumi, Sōshin (1997). Physics of Ferromagnetism. Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-851776-4.
- Jiles, D. C.; Atherton, D. L. (1986). "Theory of ferromagnetic hysteresis". Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials. 61 (1–2): 48–60. Bibcode:1986JMMM...61...48J. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(86)90066-1.
- Krasnosel'skii, Mark; Pokrovskii, Alexei (1989). Systems with Hysteresis. New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-15543-2.
- Mayergoyz, Isaak D.; Bertotti, Giorgio, eds. (2005). The Science of Hysteresis (3-volume set). Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-480874-4.
- Mielke, A.; Roubíček, T. (2015). Rate-Independent Systems: Theory and Application. New York: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4939-2705-0.
- Truesdell, C.; Noll, Walter (2004). Antman, Stuart (ed.). The Non-Linear Field Theories of Mechanics (Third ed.). Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-02779-9. Originally published as Volume III/3 of Handbuch der Physik in 1965.
- Visintin, Augusto (1994). Differential Models of Hysteresis. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-54793-8.
- Noori, Hamid R. (2014). Hysteresis Phenomena in Biology. Springer. ISBN 978-3-642-38217-8.
External links
- Overview of contact angle Hysteresis
- Preisach model of hysteresis – Matlab codes developed by Zs. Szabó
- Hysteresis
- What's hysteresis? Archived 2009-09-04 at the Wayback Machine
- Dynamical systems with hysteresis (interactive web page)
- Magnetization reversal app (coherent rotation)
- Elastic hysteresis and rubber bands


 is the instantaneous response and
is the instantaneous response and  is the
is the  time units in the past. In the
time units in the past. In the  ; it is mathematically equivalent to a
; it is mathematically equivalent to a  as input variable and a generalized force
as input variable and a generalized force  as output variable, or vice versa. In particular, in rate-independent hysteretic models, the output variable does not depend on the rate of variation of the input one.
as output variable, or vice versa. In particular, in rate-independent hysteretic models, the output variable does not depend on the rate of variation of the input one.