| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
 |
Languages
|
| Philology |
Origins
|
|
Archaeology
Pontic Steppe Caucasus East Asia Eastern Europe Northern Europe Pontic Steppe Northern/Eastern Steppe Europe
South Asia Steppe Europe Caucasus India |
|
Peoples and societies
Indo-Aryans Iranians East Asia Europe East Asia Europe Indo-Aryan Iranian |
Religion and mythology
Others
|
Indo-European studies
|
The Illyrians (Ancient Greek: Ἰλλυριοί, Illyrioi; Latin: Illyrii) were a conglomeration of Indo-European peoples and tribes in the Balkan Peninsula, Southeastern Europe.
Illyrian tribes
Main article: List of ancient tribes in Illyria| Tribe | Description |
|---|---|
| Abroi | |
| Albanoi | The Albanoi populated the region between the Mat and Shkumbin. Their chief settlement was Albanopolis located in Zgërdhesh, near Krujë. |
| Amantes | Also referred to as the Amantieis or Amantini, the Amantes lived in the inland region of the Bay of Vlorë. |
| Ardiaei | The Ardiaei lived in a region between Konjic on the north, the Neretva on the west, Lake Shkodër to the southeast and the Adriatic Sea on the south. The chief settlements of the Ardiaean State were Rhizon and Scodra. |
| Armistae | |
| Arthitae | |
| Autariatae | The Autariatae, alternatively known as Autariatai or Autariates, inhabited the valleys of Lim, Tara and West Morava within the Accursed Mountains. |
| Balaites | |
| Baridustae | |
| Bathiatae | The Bathiatae were located among today's modern Bosna River which was once known as Bathinus flumen and they took their name from this river. |
| Bylliones | |
| Cavii | The Cavii lived close to Lake Shkodër. Their main settlement was Epicaria, which is thought to be probably located around modern-day Pukë. |
| Dalmatae | The Dalmatae lived in the region of Dalmatia. |
| Daorsi | The Daorsi lived in the valley of Neretva. |
| Dardani | The Dardani lived in the Kosovo and areas around it. |
| Dassareti | |
| Daunians | |
| Deraemestae | |
| Deretini | |
| Deuri | |
| Dindari | The Dindari were of Celtic influence and lived on the western bank of the Drina Valley, close to Skelani and Srebrenica. |
| Docleatae | |
| Dyestes | |
| Enchele | |
| Endirudini | |
| Grabaei | |
| Iapydes | |
| Kinambroi | |
| Labeatae | |
| Mazaei | |
| Melcumani | |
| Messapians | |
| Narensi | |
| Ozuaei | |
| Parthini | |
| Penestae | |
| Peucetians | |
| Pleraei | |
| Sardiatae | |
| Sasaei | |
| Selepitani | |
| Tariotes | |
| Taulantii | The Taulantii or Taulantians were are among the most archaic attested Illyrian peoples. They inhabited the region across the hinterland of Dyrrhachion-Epidamnos between the valleys of Mat and Shkumbin. |
Possibly related peoples

- Antitani / Atintanes / Atintani? (Illyrian Atintani)
- Dassaretae (Dassareti)?
- Turboletae
- Molossians
Pannonians
Eastern group
Western group
Paeonians
Main article: Paeonians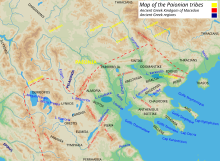
There are different views and still no agreement among scholars about the Paeonians/Paeones ethnic and linguistic kinship. Some such as Wilhelm Tomaschek and Paul Kretschmer claim that the language spoken by the Paeonians belonged to the Illyrian family, while Dimitar Dechev claims affinities with Thracian. Irwin L. Merker considers that the language spoken by the Paeonians was closely related to Greek (and ancient Macedonian if it was a distinct language from ancient Greek), a Hellenic language with "a great deal of Illyrian and Thracian influence as a result of this proximity".
- Agrianes (also, Agriani and Agrii) (it is also claimed that this tribe was Thracian)
- Almopians (also Almopioi)
- Derrones (also Derroni) (it is also claimed that this tribe was Thracian)
- Doberes
- Laeaeans (also Laeaei and Laiai)
- Odomantes (also Odomanti) (it is also claimed that this tribe was Thracian)
- Paeoplae
- Siropaiones
See also
References
- Nicolò Marchetti (2005). Epirus and the Molossians: A Historical Review.
- Emily M. S. Laszlo (2013). The Molossian Kingdom: Origins and Development.
- The "Histories" by Herodotus (Book 7): Herodotus provides some descriptions of the Molossians and other peoples of the region, but he primarily associates the Molossians with Greek-speaking culture. There is no direct claim of Illyrian ethnicity in his account, but the proximity of the Molossians to the Illyrians is noted. The "Geography" of Strabo (Book 7): Strabo, a geographer and historian from the early Roman period, mentions the Molossians in relation to their territory, which bordered Illyrian lands. While he emphasizes the Greek cultural and linguistic elements of the Molossians, Strabo also notes that the region of Epirus was ethnically complex, with Illyrians living nearby. Some modern scholars interpret Strabo’s mention of these neighboring groups as indicative of some shared ethnic or cultural characteristics between the Molossians and Illyrians. Modern Scholarship: "The Illyrians" by John Wilkes (1992): Wilkes examines the relationship between Greek and Illyrian tribes in the region and mentions that while the Molossians are generally considered Greek, the fluid nature of ethnic identities in antiquity, especially in border regions, might have led to some overlap or mutual influences. "The Epirus: From the Earliest Times to the Roman Conquest" by W. A. McGillivray (1996): This work provides a detailed history of the Epirus region, noting that the Molossians were a part of the Greek-speaking world, but they lived in close proximity to Illyrian-speaking peoples. McGillivray suggests that there might have been a degree of ethnic or cultural mixing in the area, which could have led some historians to consider Illyrian elements in Molossian identity.
- "The Ancient Kingdom of Paionia". Balkan Studies 6. 1965.
- ^ Early symbolic systems for communication in Southeast Europe, Part 2 by Lolita Nikolova, ISBN 1-84171-334-1, 2003, page 529, "eastern Paionians (Agrianians and Laeaeans)"
- The Landmark Thucydides: A Comprehensive Guide to the Peloponnesian War by Thucydides, Robert B. Strassler, Richard Crawley, and Victor Davis Hanson, 1998, ISBN 0-684-82790-5, page 153,"... of them still live round Physcasb- and the Almopians from Almopia.
- The Cambridge Ancient History, Martin Percival Charlesworth, ISBN 0-521-85073-8, ISBN 978-0-521-85073-5 Volume 4, Persia, Greece and the Western Mediterranean, C. 525 to 479 B.C, John Boardman, page 252, "The Paeonians were the earlier owners of some of these mines, but after their defeat in the coastal sector they maintained their independence in the mainland and coined large denominations in the upper Strymon and the Upper Axius area in the names of the Laeaei and the Derrones"
- The Histories (Penguin Classics) by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, ISBN 0-14-044908-6, 2003, page 452, "... Then he passed through the country of the Doberes and Paeoplae (Paeonian tribes living north of Pangaeum), and continued in a ..."
- An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen and Thomas Heine Nielsen, 2005, ISBN 0-19-814099-1, page 854, ... Various tribes have occupied this part of Thrace: Bisaltians (lower Strymon valley), Odomantes (the plain to the north of the Strymon) ...
- Thrace in the Graeco-Roman world, p. 112 but others claim that together with the Agrianes and Odomanti, at least the latter of which were with certainty Thracian, not Paeonian.
- The Histories (Penguin Classics) by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, ISBN 0-14-044908-6, 2003, page 315, ... "was that a number of Paeonian tribes – the Siriopaeones, Paeoplae, ..."
- The Histories (Penguin Classics) by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, ISBN 0-14-044908-6, 2003, page 315, "... was that a number of Paeonian tribes – the Siriopaeones, Paeoplae, ..."
Sources
- Mallory, James P.; Adams, D. Q. (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. Routledge. ISBN 1884964982 ISBN 978-1884964985
- Wilkes, John. (1996). The Illyrians. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 0631198075 ISBN 978-0631198079