| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Mortar" weapon – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

A mortar today is usually a simple, lightweight, man-portable, muzzle-loaded cannon, consisting of a smooth-bore (although some models use a rifled barrel) metal tube fixed to a base plate (to spread out the recoil) with a lightweight bipod mount and a sight. Mortars are typically used as indirect fire weapons for close fire support with a variety of ammunition. Historically mortars were heavy siege artillery. Mortars launch explosive shells (technically called bombs) in high-arching ballistic trajectories.
History
Mortars have been used for hundreds of years. The earliest reported use of mortars was in Korea in a 1413 naval battle when Korean gunsmiths developed the wan'gu (gourd-shaped mortar) (완구, 碗口). The earliest version of the wan'gu dates back to 1407. Ch'oe Hae-san (1380–1443), the son of Ch'oe Mu-sŏn (1325–1395), is generally credited with inventing the wan'gu. In the Ming dynasty, general Qi Jiguang recorded the use of a mini cannon called the hu dun pao that was similar to the mortar.
The first use in siege warfare was at the 1453 siege of Constantinople by Mehmed the Conqueror. An Italian account of the 1456 siege of Belgrade by Giovanni da Tagliacozzo states that the Ottoman Turks used seven mortars that fired "stone shots one Italian mile high". The time of flight of these was apparently long enough that casualties could be avoided by posting observers to give warning of their trajectories.

Early mortars, such as the Pumhart von Steyr, were large and heavy and could not be easily transported. Simply made, these weapons were no more than iron bowls reminiscent of the kitchen and apothecary mortars whence they drew their name. An early transportable mortar was invented by Baron Menno van Coehoorn in 1701. This mortar fired an exploding shell, which had a fuse that was lit by the hot gases when fired. The Coehorn mortar gained quick popularity, necessitating a new form of naval ship, the bomb vessel. Mortars played a significant role in the Venetian conquest of Morea, and in the course of this campaign an ammunition depot in the Parthenon was blown up. An early use of these more mobile mortars as field artillery (rather than siege artillery) was by British forces in the suppression of the Jacobite rising of 1719 at the Battle of Glen Shiel. High angle trajectory mortars held a great advantage over standard field guns in the rough terrain of the West Highlands of Scotland.

The mortar had fallen out of general use in Europe by the Napoleonic era, although Manby Mortars were widely used on the coast to launch lines to ships in distress, and interest in their use as a weapon was not revived until the beginning of the 20th century. Mortars were heavily used by both sides during the American Civil War. At the Siege of Vicksburg, General Ulysses S. Grant reported making mortars "by taking logs of the toughest wood that could be found, boring them out for 6 or 12 lb (2.7 or 5.4 kg) shells and binding them with strong iron bands. These answered as Coehorns, and shells were successfully thrown from them into the trenches of the enemy".
During the Russo-Japanese War, Lieutenant General Leonid Gobyato of the Imperial Russian Army applied the principles of indirect fire from closed firing positions in the field; and with the collaboration of General Roman Kondratenko, he designed the first mortar that fired navy shells.

The German Army studied the Siege of Port Arthur, where heavy artillery had been unable to destroy defensive structures like barbed wire and bunkers. Consequently they developed a short-barrelled rifled muzzle-loading mortar called the Minenwerfer. Heavily used during World War I, they were made in three sizes: 7.58 cm (2.98 in), 17 cm (6.7 in), and 25 cm (9.8 in).
Types
Stokes mortar

It was not until the Stokes mortar was devised by Sir Wilfred Stokes in 1915 during the First World War that the modern mortar transportable by one person was born. In the conditions of trench warfare, there was a great need for a versatile and easily portable weapon that could be manned by troops under cover in the trenches. Stokes' design was initially rejected in June 1915 because it was unable to use existing stocks of British mortar ammunition, and it took the intervention of David Lloyd George (at that time Minister of Munitions) and Lieutenant Colonel J. C. Matheson of the Trench Warfare Supply Department (who reported to Lloyd George) to expedite manufacture of the Stokes mortar. The weapon proved to be extremely useful in the muddy trenches of the Western Front, as a mortar round could be aimed to fall directly into trenches, where artillery shells, because of their low angle of flight, could not possibly go.
The Stokes mortar was a simple muzzle-loaded weapon, consisting of a smoothbore metal tube fixed to a base plate (to absorb recoil) with a lightweight bipod mount. When a mortar bomb was dropped into the tube, an impact sensitive primer in the base of the bomb would make contact with a firing pin at the base of the tube and detonate, firing the bomb towards the target. The Stokes mortar could fire as many as 25 bombs per minute and had a maximum range of 800 yd (730 m), firing the original cylindrical unstabilised projectile.
A modified version of the mortar, which fired a modern fin-stabilised streamlined projectile and had a booster charge for longer range, was developed after World War I; this was in effect a new weapon. By World War II, it could fire as many as 30 bombs per minute and had a range of over 2,500 yd (2,300 m) with some shell types. The French developed an improved version of the Stokes mortar as the Brandt Mle 27, further refined as the Brandt Mle 31; this design was widely copied with and without license. These weapons were the prototypes for all subsequent light mortar developments around the world.
Mortar carrier


Mortar carriers are vehicles which carry a mortar as a primary weapon. Numerous vehicles have been used to mount mortars, from improvised civilian trucks used by insurgents, to modified infantry fighting vehicles, such as variants of the M3 half-track and M113 armored personnel carrier, to vehicles specifically intended to carry a mortar. Simpler vehicles carry a standard infantry mortar while in more complex vehicles the mortar is fully integrated into the vehicle and cannot be dismounted from the vehicle. Mortar carriers cannot be fired while on the move, and some must be dismounted to fire.
There are numerous armoured fighting vehicles and even main battle tanks that can be equipped with a mortar, either outside or inside of the cabin. The Israeli Merkava tank uses a 60 mm (2.4 in) mortar as a secondary armament. The Russian army uses the 2S4 Tyulpan self-propelled 240 mm (9.4 in) heavy mortar which is one of the largest mortars in current use.
Gun-mortars

Gun-mortars are breech-loaded mortars usually equipped with a hydraulic recoil mechanism, and sometimes equipped with an autoloader. They are usually mounted on an armoured vehicle and are capable of both direct fire and indirect fire. The archetypes are the Brandt Mle CM60A1 and Brandt 60 mm LR, which combine features of modern infantry mortars together with those of modern cannon. Such weapons are most commonly smoothbore, firing fin-stabilised rounds, using relatively small propellant charges in comparison to projectile weight. While some have been fitted with rifled barrels, such as the 2S31 Vena and 2S9 Nona. They have short barrels in comparison to guns and are much more lightly built than guns of a similar calibre – all characteristics of infantry mortars. This produces a hybrid weapon capable of engaging area targets with indirect high-angle fire, and also specific targets such as vehicles and bunkers with direct fire. Such hybrids are much heavier and more complicated than infantry mortars, superior to rocket-propelled grenades in the anti-armour and bunker-busting role, but have a reduced range compared to modern gun-howitzers and inferior anti-tank capability compared to modern anti-tank guided weapons. However, they do have a niche in, for example, providing a multi-role anti-personnel, anti-armour capability in light mobile formations. Such systems, like the Soviet 120 mm 2S9 Nona, are mostly self-propelled (although a towed variant exists). The AMOS (Advanced Mortar System) is an example of an even more advanced gun mortar system. It uses a 120 mm automatic twin-barrelled, breech-loaded mortar turret, which can be mounted on a variety of armoured vehicles and attack boats. A modern example of a gun-mortar is the 2B9 Vasilek.
Spigot mortar

A spigot mortar consists mainly of a solid rod or spigot, onto which a hollow tube in the projectile fits—inverting the normal tube-mortar arrangement. At the top of the tube in the projectile, a cavity contains propellant, such as cordite. There is usually a trigger mechanism built into the base of the spigot, with a long firing pin running up the length of the spigot activating a primer inside the projectile and firing the propellant charge. The advantage of a spigot mortar is that the firing unit (baseplate and spigot) is smaller and lighter than a conventional tube mortar of equivalent payload and range. It is also somewhat simpler to manufacture. Further, most spigot mortars have no barrel in the conventional sense, which means ammunition of almost any weight and diameter can be fired from the same mortar.
The disadvantage is that while most mortar bombs have a streamlined shape towards the back that fits a spigot mortar application well, using that space for the spigot mortar tube takes volume and mass away from the payload of the projectile. If a soldier is carrying only a few projectiles, the projectile weight disadvantage is not significant. However, the weight of a large quantity of the heavier and more complex spigot projectiles offsets the weight saved.
A near-silent mortar can operate using the spigot principle. Each round has a close-fitting sliding plug in the tube that fits over the spigot. When the round is fired, the projectile is pushed off the spigot, but before the plug clears the spigot it is caught by a constriction at the base of the tube. This traps the gases from the propelling charge and hence the sound of the firing. After World War II the Belgium Fly-K silent spigot mortar was accepted into French service as the TN-8111.

Spigot mortars generally fell out of favour after World War II and were replaced by smaller conventional mortars. Military applications of spigot mortars include:
- The 230 mm (9.1 in) petard mortar used on the Churchill AVRE by Britain in World War II.
- The 320 mm (13 in) Type 98 mortar used by Japan in World War II to some psychological effect in the battles of Iwo Jima and Okinawa
- The Blacker Bombard and PIAT anti-tank launchers used by Britain in World War II.
- The Hedgehog launcher, used from the deck of a ship, used 24 spigot mortars which fired a diamond pattern of anti-submarine projectiles into the sea ahead of the ship. A sinking projectile detonated if it struck a submarine, and the pattern was such that any submarine partly in the landing zone of the projectiles would be struck one or more times.
Non-military applications include the use of small-calibre spigot mortars to launch lightweight, low-velocity foam dummy targets used for training retriever dogs for bird hunting. Simple launchers use a separate small primer cap as the sole propellant (similar or identical to the cartridges used in industrial nail guns).
Improvised

Insurgent groups often use improvised, or "homemade" mortars to attack fortified military installations or terrorise civilians. They are usually constructed from heavy steel piping mounted on a steel frame. These weapons may fire standard mortar rounds, purpose-made shells, repurposed gas cylinders filled with explosives and shrapnel, or any other type of improvised explosive, incendiary or chemical munitions. These were called "barrack busters" by the Provisional Irish Republican Army (PIRA).
Syrian civil war
Improvised mortars used by insurgents in the Syrian civil war are known as hell cannons. Observers have noted that they are "wildly inaccurate" and responsible for hundreds of civilian deaths.
Sri Lankan civil war
Improvised mortars used in the Sri Lankan civil war by the rebel Tamil Tigers are known as "Pasilan 2000", also known as a "rocket mortar" or "Arti-mortar" like the 122 mm (4.8 in) cannon, successor to the Baba mortar used by the LTTE for ground operations since the 1980s. As Baba mortar rounds contained tar, they caused a fire when they hit the ground. The Baba, the prototype mortar, was crude. But with time the weapon has improved.
The Pasilan 2000, the improved version, has been developed with characteristics similar to a rocket launcher. The Pasilan 2000 was a heavy mortar fired from a mobile launcher mounted on a tractor. The shell does not emit constant muzzle flares like artillery or MBRL. This is ideal for LTTE's camouflage and conceals attacking style. Once a round is fired, forward observers/spies/civilian spotters can correct the fire. The way the tube is installed is similar to the positioning of rocket pods. The length and calibre of the barrel indicate Pasilan 2000 system has common features to the Chinese made Type 82 130 mm (5.1 in) 30-tube MLRS (introduced by the Palestinian Liberation Army (PLA) in the early 1980s) rather than rail-guided Katyusha variants such as the Qassam Rocket. The warhead weight is 70 kg (150 lb) and it is filled with TNT. It had a range of 15 to 25 km (9.3 to 15.5 mi). The rocket has since then undergone some modifications. The Pasilan 2000 was more lethal than Baba mortar. But it was not heavily used for ground attacks during the Eelam War IV.
Modern
Design


Most modern mortar systems consist of four main components: a barrel, a base plate, a bipod and a sight. Modern mortars normally range in calibre from 60 mm (2.36 in) to 120 mm (4.72 in). However, both larger and smaller mortars have been produced. The modern mortar is a muzzle-loaded weapon and relatively simple to operate. It consists of a barrel into which the gunners drop a mortar round. When the round reaches the base of the barrel it hits a fixed firing pin that fires the round. The barrel is generally set at an angle of between 45 and 85 degrees (800 to 1500 mils), with the higher angle producing a shorter horizontal trajectory. Some mortars have a moving firing pin, operated by a lanyard or trigger mechanism.
Ammunition

Ammunition for mortars generally comes in two main varieties: fin-stabilised and spin-stabilised. Examples of the former have short fins on their posterior portion, which control the path of the bomb in flight. Spin-stabilised mortar bombs rotate as they travel along and leave the mortar tube, which stabilises them in much the same way as a rifle bullet. Both types of rounds can be either illumination (infrared or visible illumination), smoke, high explosive, and training rounds. Mortar bombs are often referred to, incorrectly, as "mortars".
Operators may fire spin-stabilised rounds from either a smoothbore or a rifled barrel. Rifled mortars are more accurate but slower to load. Since mortars are generally muzzle-loaded, mortar bombs for rifled barrels usually have a pre-engraved band, called an obturator, that engages with the rifling of the barrel. Exceptions to this are the U.S. M2 4.2-inch mortar and M30 mortar, whose ammunition has a sub-calibre expandable ring that enlarged when fired. This allows the projectile to slide down the barrel freely but grip the rifling when fired. The system resembles the Minié ball for muzzle-loading rifles. For extra range, propellant rings (augmentation charges) are attached to the bomb's fins. The rings are usually easy to remove, because they have a major influence on the speed and thus the range of the bomb. Some mortar rounds can be fired without any augmentation charges, e.g., the 81 mm L16 mortar.
| Charge | Muzzle velocity m/s (ft/s) |
Range m (yd) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary | 73 (240) | 180–520 (200–570) |
| Charge 1 | 110 (360) | 390–1,120 (430–1,220) |
| Charge 2 | 137 (450) | 580–1,710 (630–1,870) |
| Charge 3 | 162 (530) | 780–2,265 (853–2,477) |
| Charge 4 | 195 (640) | 1,070–3,080 (1,170–3,370) |
| Charge 5 | 224 (730) | 1,340–3,850 (1,470–4,210) |
| Charge 6 | 250 (820) | 1,700–4,680 (1,860–5,120) |
Precision guided

The XM395 Precision Guided Mortar Munition (PGMM) is a 120 mm guided mortar round developed by Alliant Techsystems. Based on Orbital ATK's Precision Guidance Kit for 155 mm artillery projectiles, XM395 combines GPS guidance and directional control surfaces into a package that replaces standard fuses, transforming existing 120 mm mortar bodies into precision-guided munitions. The XM395 munition consists of a GPS-guided kit fitted to standard 120 mm smoothbore mortar rounds that includes the fitting of a nose and tail subsystem containing the maneuvering parts.
The Strix mortar round is a Swedish endphase-guided projectile fired from a 120 mm mortar currently manufactured by Saab Bofors Dynamics. STRIX is fired like a conventional mortar round. The round contains an infrared imaging sensor that it uses to guide itself onto any tank or armoured fighting vehicle in the vicinity where it lands. The seeker is designed to ignore targets that are already burning. Launched from any 120 mm mortar, STRIX has a normal range of up to 4.5 km (2.8 mi). The addition of a special sustainer motor increases the range to 7.5 km (4.7 mi).
The GMM 120 (Guided Mortar Munition 120; known as Patzmi; also referred to as Morty) is a GPS and/or laser-guided mortar munition, which was developed by Israel Military Industries. Another Israeli guided mortar is Iron Sting, developed by Elbit. The Russian KM-8 Gran is also laser-guided.
Compared to long range artillery

Modern mortars and their ammunition are generally much smaller and lighter than long range artillery, such as field guns and howitzers, which allows light (60 mm (2.4 in)) and medium (81 mm (3.2 in)/82 mm (3.2 in)) mortars to be considered light weapons; i.e. capable of transport by personnel without vehicle assistance.
Mortars are short-range weapons and often more effective than long range artillery for many purposes within their shorter range. In particular, because of its high, parabolic trajectory with a near vertical descent, the mortar can land bombs on nearby targets, including those behind obstacles or in fortifications, such as light vehicles behind hills or structures, or infantry in trenches or spider holes. This also makes it possible to launch attacks from positions lower than the target of the attack. (For example, long-range artillery could not shell a target 1 km (0.62 mi) away and 30 m (98 ft) higher, a target easily accessible to a mortar.)
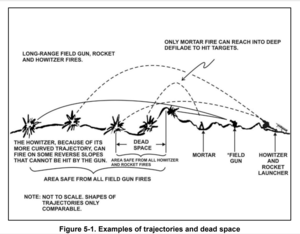
In trench warfare, mortars can use plunging fire directly into the enemy trenches, which is very hard or impossible to accomplish with long range artillery because of its much flatter trajectory. Mortars are also highly effective when used from concealed positions, such as the natural escarpments on hillsides or from woods, especially if forward observers are being employed in strategic positions to direct fire, an arrangement where the mortar is in relatively close proximity both to its forward observer and its target, allowing for fire to be quickly and accurately delivered with lethal effect. Mortars suffer from instability when used on snow or soft ground, because the recoil pushes them into the ground or snow unevenly. A Raschen bag addresses this problem.
Fin-stabilised mortar bombs do not have to withstand the rotational forces placed upon them by rifling or greater pressures, and can therefore carry a higher payload in a thinner skin than rifled artillery ammunition. Because of the difference in available volume, a smooth-bore mortar of a given diameter will have a greater explosive yield than a similarly sized artillery shell of a gun or howitzer. For example, a 120 mm mortar bomb has approximately the same explosive capability as a 152 mm/155 mm artillery shell. Also, fin-stabilised munitions fired from a smooth-bore, which do not rely on the spin imparted by a rifled bore for greater accuracy, do not have the drawback of veering in the direction of the spin.
Largest mortars
For the largest mortars, see list of the largest cannon by caliber.From the 17th to the mid-20th century, very heavy, relatively immobile siege mortars were used, of up to 1 m (3 ft 3 in) calibre, often made of cast iron and with an outside barrel diameter many times that of the bore diameter. An early example was Roaring Meg, with a 15.5 in (390 mm) barrel diameter and firing a 220 lb (100 kg) hollow ball filled with gunpowder and used during the English Civil War in 1646.
The largest mortars ever developed were the Belgian "Monster Mortar" (24 in (610 mm)) developed by Henri-Joseph Paixhans in 1832, Mallet's Mortar (36 in (910 mm)) developed by Robert Mallet in 1857, and the "Little David" ((36 in (910 mm)) developed in the United States for use in World War II. Although the latter two had a calibre of 36 in (910 mm), only the "Monster Mortar" was used in combat (at the Battle of Antwerp in 1832). The World War II German Karl-Gerät was a 60 cm (24 in) mortar and the largest to see combat in modern warfare.
-
 Roaring Meg on display at Goodrich Castle
Roaring Meg on display at Goodrich Castle
- World War II US Army movie footage of the 914 mm "Little David" mortar
See also
- Carcass (projectile), used in mortars before the modern age
- Chemical mortar battalion
- Coehorn a lightweight mortar, sometimes improvised
- Eprouvette, a mortar used to test the strength of gunpowder
- List of heavy mortars
- List of infantry mortars
- Livens Projector
References
- "mortar definition". Oxford Dictionary of English. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on October 9, 2019. Retrieved 10 October 2019.
- Stephen Turnbull (2002). Siege Weapons of the Far East (2): AD 960–1644. Osprey Publishing. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-841-76340-8.
- "Toys". Culturecontent.com. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- "대완구". Data.kdata.kr. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- Needham, Joseph (1987). Science and Civilisation in China. Volume 5. Chemistry and Chemical Technology. Part 7. Military Technology: The Gunpowder Epic. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 313. ISBN 9780521303583.
- Gábor Ágoston (2005). Guns for the Sultan: Military Power and the Weapons Industry in the Ottoman Empire. Cambridge University Press. p. 68. ISBN 978-0-521-84313-3.
- Franz Babinger (1992). Mehmed the Conqueror and His Time. Princeton University Press. p. 140. ISBN 978-0-691-01078-6.
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Coehoorn, Menno, Baron van" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 8 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 40.
- Duffy, Christopher (1985). The Fortress in the Age of Vauban and Frederick the Great 1660–1789 (2017 ed.). Routledge. p. 65. ISBN 1138924644.
- Personal Memoirs of Ulysses S Grant, by Sam Grant, Kindle location 12783,
- naval-military-press.com
- "Stokes Mortar - by WL Ruffell". Archived from the original on 2015-01-15. Retrieved 2014-07-17.
- Ruffell
- War Dept. Technical Manual TM9-2005, Volume 3, Ordnance Materiel – General, Page 17, December 1942
- Chris Bishop (2002). The Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War II. Sterling Publishing Company. p. 202. ISBN 978-1-58663-762-0. Archived from the original on 2015-03-20. Retrieved 2016-03-27.
- "Brandt mle 27 (Mortier Brandt de 81 mm modele 27) Infantry Mortar". Militaryfactory.com. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- John Norris (2002). Infantry Mortars of World War II. Osprey Publishing. pp. 42–43. ISBN 978-1-84176-414-6. Archived from the original on 2015-03-20. Retrieved 2016-03-27.
- "A Second Wind For The Lightweight Infantry Mortar", thinkdefence.co.uk, July 19, 2021
- Fly-K mortar systems – excellent stealth capabilities and tremendous tactical potential, archived from the original on 2023-03-14
- "Tank Hurls Flying Dust Bins and Lays Tracks", Popular Mechanics, Hearst Magazines, p. 7, December 1944
- Oliver Holmes (December 12, 2014). "Syrian rebel "hell cannons" kill 300 civilians: monitoring group". Reuters. Yahoo! News. Archived from the original on December 16, 2014. Retrieved December 13, 2014.
- "Forign1".
- "Pasilan 2000 used by the LTTE".
- "Dossier on LTTE Weapons – PDF document".
- For example: "Suspected Second World War mortar exploded in Windsor today". Slough Observer. 3 October 2014. Archived from the original on 2015-06-18.
- Hogg, Ian V. The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Ammunition, p. 126
- "Alliant Techsystems Takes Army Mortar Contract (Again)". Defense Industry Daily. Dec 7, 2004. Archived from the original on 2006-03-18. Retrieved 2018-06-11.
- "XM395 Precision Mortar (120mm)". Northrop Grumman. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10. Retrieved 2018-06-11.
- Calloway, Audra (29 March 2011). "Picatinny fields first precision-guided mortars to troops in Afghanistan". Army.mil. Archived from the original on 2016-12-30.
- "XM395: 120 mm Precision Mortar" (PDF). ATK Advanced Weapon. ATK. Retrieved 21 February 2012.
- "GMM 120–120 mm Guided Mortar Munition". Israel Military Industries. Archived from the original on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 6 April 2014.
- "Israeli army tests GPS-guided mortar shell". i24news. Archived from the original on 2014-04-07. Retrieved 6 April 2014.
- ""MALAKHIT" AUTOMATED ARTILLERY FIRE CONTROL SYSTEM". KBP Instrument Design Bureau. Archived from the original on 2 November 2019. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- "Largest Mortar". Guinness World Records. Archived from the original on 2006-02-10. Retrieved 2006-04-04.
External links
- A Guide to Modern Mortar Systems
- "Field Manual 3-22.90 – Mortars" (PDF). Department of the Army. December 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 February 2013. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- "Field Manual 3-22.91 – Mortar Fire Direction Procedures" (PDF). Department of the Army. 17 July 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 February 2013. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- "Field Manual 23-91 – Mortar Gunnery" (PDF). Department of the Army. 1 March 2000. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- Mallet's Mortar, the largest British mortar ever made
- Defense Update: Modern mobile 120 mm mortars
- Defense Update: Advanced mortar munitions
- How does a mortar work? – video
- Mortars during World War I
- The Karl Morser, WW II-era German 60 cm self-propelled mortar
- Video (streaming wmv)
