| This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Intermontane Islands" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
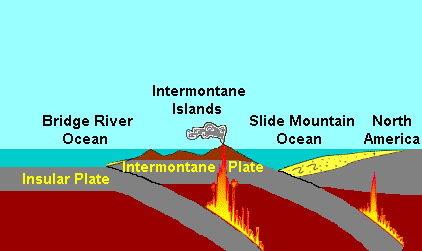
The Intermontane Islands were a giant chain of active volcanic islands somewhere in the Pacific Ocean during the Triassic time beginning around 245 million years ago. They were 600 to 800 miles (1,300 km) long and rode atop a microplate known as the Intermontane Plate. Over early Jurassic time the Intermontane Islands and the Pacific Northwest drew closer together as the continent moved west and the Intermontane Plate subducted. About 180 million years ago in the Mid-Jurassic time the last of the Intermontane Plate subducted and the Intermontane Islands collided with the Pacific Northwest, forming parts of British Columbia, Canada. The Intermontane Islands were too big to sink beneath the continent, and welded onto the continent, forming the Intermontane Belt. Geologists call the ocean that existed between the Intermontane Islands and North America the Slide Mountain Ocean.
See also
External links
- "The Omineca Episode (180-115 million years ago) | Burke Museum". Burke Museum – University of Washington
This article about a specific Canadian geological feature is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This palaeogeography article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This article related to an island or group of islands in Canada is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |