Medical condition
| Amoebiasis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Amoebic dysentery, amebiasis, entamoebiasis |
 | |
| The life-cycle of various intestinal Entamoeba species | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain |
| Complications | Severe colitis, colonic perforation, anemia |
| Causes | Entamoeba histolytica |
| Diagnostic method | Stool examination, antibodies in the blood |
| Differential diagnosis | Bacterial colitis |
| Prevention | Improved sanitation |
| Treatment | Tissue disease: metronidazole, tinidazole, nitazoxanide, dehydroemetine, chloroquine, Intestinal infection: diloxanide furoate, iodoquinoline |
| Frequency | ~480 million |
Amoebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection of the intestines caused by a parasitic amoeba Entamoeba histolytica. Amoebiasis can be present with no, mild, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may include lethargy, loss of weight, colonic ulcerations, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or bloody diarrhea. Complications can include inflammation and ulceration of the colon with tissue death or perforation, which may result in peritonitis. Anemia may develop due to prolonged gastric bleeding.
Cysts of Entamoeba can survive for up to a month in soil or for up to 45 minutes under fingernails. Invasion of the intestinal lining results in bloody diarrhea. If the parasite reaches the bloodstream it can spread through the body, most frequently ending up in the liver where it can cause amoebic liver abscesses. Liver abscesses can occur without previous diarrhea. Diagnosis is made by stool examination using microscopy, but it can be difficult to distinguish E. hystolitica from other harmless entamoeba species. An increased white blood cell count may be present in severe cases. The most accurate test is finding specific antibodies in the blood, but it may remain positive following treatment. Bacterial colitis can result in similar symptoms.
Prevention of amoebiasis is by improved sanitation, including separating food and water from faeces. There is no vaccine. There are two treatment options depending on the location of the infection. Amoebiasis in tissues is treated with either metronidazole, tinidazole, nitazoxanide, dehydroemetine or chloroquine. Luminal infection is treated with diloxanide furoate or iodoquinoline. Effective treatment against all stages of the disease may require a combination of medications. Infections without symptoms may be treated with just one antibiotic, and infections with symptoms are treated with two antibiotics.
Amoebiasis is present all over the world, though most cases occur in the developing world. About 480 million people are currently infected with about 40 million new cases per year with significant symptoms. This results in the death of between 40,000–100,000 people a year. The first case of amoebiasis was documented in 1875. In 1891, the disease was described in detail, resulting in the terms amoebic dysentery and amoebic liver abscess. Further evidence from the Philippines in 1913 found that upon swallowing cysts of E. histolytica volunteers developed the disease.
Signs and symptoms
Most infected people, about 90%, are asymptomatic, but this disease has the potential to become serious. It is estimated that about 40,000 to 100,000 people worldwide die annually due to amoebiasis.
Infections can sometimes last for years if there is no treatment. Symptoms take from a few days to a few weeks to develop and manifest themselves, but usually it is about two to four weeks. Symptoms can range from mild diarrhea to dysentery with blood, coupled with intense abdominal pains. Extra-intestinal complications might also arise as a result of invasive infection which includes colitis, liver, lung, or brain abscesses. The blood comes from bleeding lesions created by the amoebae invading the lining of the colon. In about 10% of invasive cases the amoebae enter the bloodstream and may travel to other organs in the body. Most commonly this means the liver, as this is where blood from the intestine reaches first, but they can end up almost anywhere in the body.
Onset time is highly variable and the average asymptomatic infection persists for over a year. It is theorized that the absence of symptoms or their intensity may vary with such factors as strain of amoeba, immune response of the host, and perhaps associated bacteria and viruses.
In asymptomatic infections, the amoeba lives by eating and digesting bacteria and food particles in the gut, a part of the gastrointestinal tract. It does not usually come in contact with the intestine itself due to the protective layer of mucus that lines the gut. Disease occurs when amoeba comes in contact with the cells lining the intestine. It then secretes the same substances it uses to digest bacteria, which include enzymes that destroy cell membranes and proteins. This process can lead to penetration and digestion of human tissues, resulting first in flask-shaped ulcerations in the intestine. Entamoeba histolytica ingests the destroyed cells by phagocytosis and is often seen with red blood cells (a process known as erythrophagocytosis) inside when viewed in stool samples. Especially in Latin America, a granulomatous mass (known as an amoeboma) may form in the wall of the ascending colon or rectum due to long-lasting immunological cellular response, and is sometimes confused with cancer.
The ingestion of one viable cyst may cause an infection.
Steroid therapy can occasionally provoke severe amoebic colitis in people with any E. histolytica infection. This bears high mortality: on average more than 50% with severe colitis die.
Cause
Amoebiasis is an infection caused by the amoeba Entamoeba histolytica.
Transmission
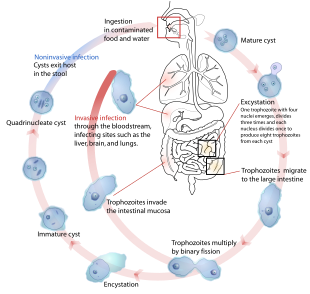
Amoebiasis is usually transmitted by the fecal-oral route, but it can also be transmitted indirectly through contact with dirty hands or objects as well as by anal-oral contact. Infection is spread through ingestion of the cyst form of the parasite, a semi-dormant and hardy structure found in feces. Any non-encysted amoebae, or trophozoites, die quickly after leaving the body but may also be present in stool: these are rarely the source of new infections. Since amoebiasis is transmitted through contaminated food and water, it is often endemic in regions of the world with limited modern sanitation systems, including México, Central America, western South America, South Asia, and western and southern Africa.
Amoebic dysentery is one form of traveler's diarrhea, although most traveler's diarrhea is bacterial or viral in origin.
Pathogenesis

Amoebiasis results from tissue destruction induced by the E. histolytica parasite.
E. histolytica causes tissue damage by three main events: direct host cell killing, inflammation, and parasite invasion. The pathogenesis of amoebiasis involves interplay of various molecules secreted by E. histolytica such as LPPG, lectins, cysteine proteases, and amoebapores. Lectins help in the attachment of the parasite to the mucosal layer of the host during invasion. The amoebapores destroy the ingested bacteria present in the colonic environment. Cysteine proteases lyse the host tissues. Other molecules such as PATMK, myosins, G proteins, C2PK, CaBP3, and EhAK1 play an important role in the process of phagocytosis.
Diagnosis
With colonoscopy it is possible to detect small ulcers of between 3–5mm, but diagnosis may be difficult as the mucous membrane between these areas can look either healthy or inflamed. Trophozoites may be identified at the ulcer edge or within the tissue, using immunohistochemical staining with specific anti-E. histolytica antibodies.
Asymptomatic human infections are usually diagnosed by finding cysts shed in the stool. Various flotation or sedimentation procedures have been developed to recover the cysts from fecal matter and stains help to visualize the isolated cysts for microscopic examination. Since cysts are not shed constantly, a minimum of three stools are examined. In symptomatic infections, the motile form (the trophozoite) is often seen in fresh feces. Serological tests exist, and most infected individuals (with symptoms or not) test positive for the presence of antibodies. The levels of antibody are much higher in individuals with liver abscesses. Serology only becomes positive about two weeks after infection. More recent developments include a kit that detects the presence of amoeba proteins in the feces, and another that detects amoeba DNA in feces. These tests are not in widespread use due to their expense.
Microscopy is still by far the most widespread method of diagnosis around the world. However it is not as sensitive or accurate in diagnosis as the other tests available. It is important to distinguish the E. histolytica cyst from the cysts of nonpathogenic intestinal protozoa such as Entamoeba coli by its appearance. E. histolytica cysts have a maximum of four nuclei, while the commensal Entamoeba coli cyst has up to 8 nuclei. Additionally, in E. histolytica, the endosome is centrally located in the nucleus, while it is usually off-center in Entamoeba coli. Finally, chromatoidal bodies in E. histolytica cysts are rounded, while they are jagged in Entamoeba coli. However, other species, Entamoeba dispar and E. moshkovskii, are also commensals and cannot be distinguished from E. histolytica under the microscope. As E. dispar is much more common than E. histolytica in most parts of the world this means that there is a lot of incorrect diagnosis of E. histolytica infection taking place. The WHO recommends that infections diagnosed by microscopy alone should not be treated if they are asymptomatic and there is no other reason to suspect that the infection is actually E. histolytica. Detection of cysts or trophozoites stools under microscope may require examination of several samples over several days to determine if they are present, because cysts are shed intermittently and may not show up in every sample.
Typically, the organism can no longer be found in the feces once the disease goes extra-intestinal. Serological tests are useful in detecting infection by E. histolytica if the organism goes extra-intestinal and in excluding the organism from the diagnosis of other disorders. An Ova & Parasite (O&P) test or an E. histolytica fecal antigen assay is the proper assay for intestinal infections. Since antibodies may persist for years after clinical cure, a positive serological result may not necessarily indicate an active infection. A negative serological result, however, can be equally important in excluding suspected tissue invasion by E. histolytica.
Stool antigen detection tests have helped to overcome some of the limitations of stool microscopy. Antigen detection tests are easy to use, but they have variable sensitivity and specificity, especially in low-endemic areas.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is considered the gold standard for diagnosis but remains underutilized.
-
 Immature E. histolytica/E. dispar cyst in a concentrated wet mount stained with iodine. This early cyst has only one nucleus and a glycogen mass is visible (brown stain).
Immature E. histolytica/E. dispar cyst in a concentrated wet mount stained with iodine. This early cyst has only one nucleus and a glycogen mass is visible (brown stain).
-
 Amoebae in a colon biopsy from a case of amoebic dysentery.
Amoebae in a colon biopsy from a case of amoebic dysentery.
-
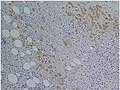 Immunohistochemical staining of trophozoites (brown) using specific anti–Entamoeba histolytica macrophage migration inhibitory factor antibodies in a patient with amoebic colitis.
Immunohistochemical staining of trophozoites (brown) using specific anti–Entamoeba histolytica macrophage migration inhibitory factor antibodies in a patient with amoebic colitis.
Prevention

To help prevent the spread of amoebiasis around the home :
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and hot running water for at least 10 seconds after using the toilet or changing a baby's diaper, and before handling food.
- Clean bathrooms and toilets often; pay particular attention to toilet seats and taps.
- Avoid sharing towels or face washers.
To help prevent infection:
- Avoid raw vegetables when in endemic areas, as they may have been fertilized using human feces.
- Boil water or treat with iodine tablets.
- Avoid eating street foods especially in public places where others are sharing sauces in one container
Good sanitary practice, as well as responsible sewage disposal or treatment, are necessary for the prevention of E. histolytica infection on an endemic level. E.histolytica cysts are usually resistant to chlorination, therefore sedimentation and filtration of water supplies are necessary to reduce the incidence of infection.
E. histolytica cysts may be recovered from contaminated food by methods similar to those used for recovering Giardia lamblia cysts from feces. Filtration is probably the most practical method for recovery from drinking water and liquid foods. E. histolytica cysts must be distinguished from cysts of other parasitic (but nonpathogenic) protozoa and from cysts of free-living protozoa as discussed above. Recovery procedures are not very accurate; cysts are easily lost or damaged beyond recognition, which leads to many falsely negative results in recovery tests.
Treatment
Main article: AmoebicideE. histolytica infections occur in both the intestine and (in people with symptoms) in tissue of the intestine and/or liver. Those with symptoms require treatment with two medications, an amoebicidal tissue-active agent and a luminal cysticidal agent. Individuals that are asymptomatic only need a luminal cysticidal agent.
Prognosis

In the majority of cases, amoebas remain in the gastrointestinal tract of the hosts. Severe ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosal surfaces occurs in less than 16% of cases. In fewer cases, the parasite invades the soft tissues, most commonly the liver. Only rarely are masses formed (amoebomas) that lead to intestinal obstruction.(Mistaken for Ca caecum and appendicular mass) Other local complications include bloody diarrhea, pericolic and pericaecal abscess.
Complications of hepatic amoebiasis includes subdiaphragmatic abscess, perforation of diaphragm to pericardium and pleural cavity, perforation to abdominal cavital (amoebic peritonitis) and perforation of skin (amoebiasis cutis).
Pulmonary amoebiasis can occur from liver lesions by spread through the blood or by perforation of pleural cavity and lung. It can cause lung abscess, pulmono pleural fistula, empyema lung and broncho pleural fistula. It can also reach the brain through blood vessels and cause amoebic brain abscess and amoebic meningoencephalitis. Cutaneous amoebiasis can also occur in skin around sites of colostomy wound, perianal region, region overlying visceral lesion and at the site of drainage of liver abscess.
Urogenital tract amoebiasis derived from intestinal lesion can cause amoebic vulvovaginitis (May's disease), rectovesicle fistula and rectovaginal fistula.
Entamoeba histolytica infection is associated with malnutrition and stunting of growth in children.
Epidemiology
Amoebiasis caused about 55,000 deaths worldwide in 2010, down from 68,000 in 1990. In older textbooks it is often stated that 10% of the world's population is infected with Entamoeba histolytica. Nevertheless, this means that there are up to 50 million true E. histolytica infections and approximately seventy thousand die each year, mostly from liver abscesses or other complications. Although usually considered a tropical parasite, the first case reported (in 1875) was actually in St Petersburg in Russia, near the Arctic Circle. Infection is more common in warmer areas, but this is because of both poorer hygiene and the parasitic cysts surviving longer in warm moist conditions.
History
Amoebiasis was first described by Fedor A. Lösch in 1875, in northern Russia. The most dramatic incident in the US was the Chicago World's Fair outbreak in 1933, caused by contaminated drinking water. There were more than a thousand cases, with 98 deaths. It has been known since 1897 that at least one non-disease-causing species of Entamoeba existed (Entamoeba coli), but it was first formally recognized by the WHO in 1997 that E. histolytica was two species, despite this having first been proposed in 1925. In addition to the now-recognized E. dispar, evidence shows there are at least two other species of Entamoeba that look the same in humans: E. moshkovskii and Entamoeba bangladeshi. The reason these species haven't been differentiated until recently is because of the reliance on appearance.
Joel Connolly of the Chicago Bureau of Sanitary Engineering brought the outbreak to an end when he found that defective plumbing permitted sewage to contaminate drinking water. In 1998 there was an outbreak of amoebiasis in the Republic of Georgia. Between 26 May and 3 September 1998, 177 cases were reported, including 71 cases of intestinal amoebiasis and 106 probable cases of liver abscess.
The Nicobarese people have attested to the medicinal properties found in Glochidion calocarpum, a plant common to India, saying that its bark and seed are most effective in curing abdominal disorders associated with amoebiasis.
Society and culture
An outbreak of amoebic dysentery occurs in Diana Gabaldon's novel A Breath of Snow and Ashes.
References
- "Entamoebiasis". Medical Subject Headings. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 29 December 2024.
- ^ Kelly P (2014). "Intestinal Protozoa". Manson's Tropical Infectious Diseases. pp. 664–682.e2. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-5101-2.00050-9. ISBN 978-0-7020-5101-2.
- ^ "General Information | Amebiasis | Parasites | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 29 December 2021. Retrieved 13 September 2022.
- ^ Carrero JC, Reyes-López M, Serrano-Luna J, Shibayama M, Unzueta J, León-Sicairos N, de la Garza M (January 2020). "Intestinal amoebiasis: 160 years of its first detection and still remains as a health problem in developing countries". Int J Med Microbiol. 310 (1): 151358. doi:10.1016/j.ijmm.2019.151358. PMID 31587966. S2CID 203849436.
- Roy M, Rawat A, Kaushik S, Jyoti A, Srivastava VK (August 2022). "Endogenous cysteine protease inhibitors in upmost pathogenic parasitic protozoa". Microbiological Research. 261: 127061. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2022.127061. PMID 35605309. S2CID 248741177.
- Beeching N, Gill G (17 April 2014). "Amoebiasis". Tropical Medicine. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 177–182. ISBN 978-1-118-73456-8.
- ^ Shirley DT, Farr L, Watanabe K, Moonah S (July 2018). "A Review of the Global Burden, New Diagnostics, and Current Therapeutics for Amebiasis". Open Forum Infectious Diseases. 5 (7): ofy161. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofy161. PMC 6055529. PMID 30046644.
- Beiting DP, John AR (2022). "Parasitic diseases: Protozoa". Yamada's Textbook of Gastroenterology. pp. 3022–3038. doi:10.1002/9781119600206.ch146. ISBN 978-1-119-60016-9.
- ^ Rawat A, Singh P, Jyoti A, Kaushik S, Srivastava VK (August 2020). "Averting transmission: A pivotal target to manage amoebiasis". Chemical Biology & Drug Design. 96 (2): 731–744. doi:10.1111/cbdd.13699. PMID 32356312. S2CID 218475533.
- ^ Nespola B, Betz V, Brunet J, Gagnard JC, Krummel Y, Hansmann Y, et al. (2015). "First case of amebic liver abscess 22 years after the first occurrence". Parasite. 22: 20. doi:10.1051/parasite/2015020. PMC 4472968. PMID 26088504.
- Day DW, Basil C. Morson, Jeremy R. Jass, Geraint Williams, Ashley B. Price (2003). Morson and Dawson's Gastrointestinal Pathology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 978-0-632-04204-3.
- "Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook: Entamoeba histolytica". Bad Bug Book. United States Food and Drug Administration: Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition. 2007-12-28. Archived from the original on 9 July 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ^ Shirley DA, Moonah S (July 2016). "Fulminant Amebic Colitis after Corticosteroid Therapy: A Systematic Review". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 10 (7): e0004879. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0004879. PMC 4965027. PMID 27467600.
- ^ Ryan KJ, Ray CG, eds. (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. pp. 733–8. ISBN 978-0-8385-8529-0.
- "safewateronline.com: Travelers' Diarrhea". Archived from the original on 6 June 2008. Retrieved 2020-06-28.
- Ghosh S, Padalia J, Moonah S (21 January 2019). "Cell Death, Inflammation, Invasion, and the Gut Microbiome". Current Clinical Microbiology Reports. 6 (1): 51–57. doi:10.1007/s40588-019-0113-6. PMC 6449278. PMID 31008019.
- Reeves RE (1985). "Metabolism of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903". Advances in Parasitology. Vol. 23. pp. 105–142. doi:10.1016/S0065-308X(08)60286-9. ISBN 978-0-12-031723-3. PMID 6085216.
- Madden GR, Shirley DA, Townsend G, Moonah S (28 October 2019). "Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding due to Entamoeba histolytica Detected Early by Multiplex PCR: Case Report and Review of the Laboratory Diagnosis of Amebiasis". The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 101 (6): 1380–1383. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.19-0237. PMC 6896859. PMID 31674299.
- "FDA Bacteriological Analytical Manual". Archived from the original on 2008-04-06. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- Mondal D, Petri WA, Sack RB, Kirkpatrick BD, Haque R, et al. (November 2006). "Entamoeba histolytica-associated diarrheal illness is negatively associated with the growth of preschool children: evidence from a prospective study". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 100 (11): 1032–8. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.12.012. PMID 16730764.
- Shirley DT, Watanabe K, Moonah S (November 2019). "Significance of amebiasis: 10 reasons why neglecting amebiasis might come back to bite us in the gut". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 13 (11): e0007744. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0007744. PMC 6855409. PMID 31725715.
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. (December 2012). "Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2095–128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30050819. PMC 10790329. PMID 23245604. S2CID 1541253.
- Lösch F (November 1875). "Massenhafte Entwickelung von Amöben im Dickdarm" [Massive development of amoebas in the large intestine]. Archiv für pathologische Anatomie und Physiologie und für klinische Medicin (in German). 65 (2): 196–211. doi:10.1007/BF02028799.
- Markell EK (June 1986). "The 1933 Chicago outbreak of amebiasis". The Western Journal of Medicine. 144 (6): 750. PMC 1306777. PMID 3524005.
- "Water and Waste Systems". Archived from the original on 2017-01-19. Retrieved 2017-01-19.
- Kreidl P, Imnadze P, Baidoshvili L, Greco D (October 1999). "Investigation of an outbreak of amoebiasis in Georgia". Euro Surveillance. 4 (10): 103–104. doi:10.2807/esm.04.10.00040-en. PMID 12631887.
- See p. 412 in: Hammer K (1990). "Barilla (Salsola soda, Chenopodiaceae)". Economic Botany. 44 (3): 410–412. Bibcode:1990EcBot..44..410H. doi:10.1007/bf03183925. JSTOR 4255259. S2CID 32113455.
- "Outlandish Observations". 17 January 2014. Retrieved 2020-11-24.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Amoebozoal diseases | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lobosea (free-living) |
| ||||
| Conosa/Archamoebae | |||||