| Stroma of iris | |
|---|---|
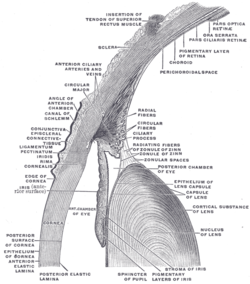 The upper half of a sagittal section through the front of the eyeball. ("Stroma of iris" labeled at bottom right.) The upper half of a sagittal section through the front of the eyeball. ("Stroma of iris" labeled at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | stroma iridis |
| TA98 | A15.2.03.031 |
| FMA | 58526 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The stroma of the iris is a fibrovascular layer of tissue located at the front of the iris.
Structure
The stroma is a delicate interlacement of fibres. Some circle the circumference of the iris and the majority radiate toward the pupil. Blood vessels and nerves intersperse this mesh.
In dark eyes, the stroma often contains pigment granules. Blue eyes and the eyes of albinos, however, lack pigment.

The stroma connects to a sphincter muscle (sphincter pupillae), which contracts the pupil in a circular motion, and a set of dilator muscles (dilator pupillae) which pull the iris radially to enlarge the pupil, pulling it in folds. The back surface is covered by a commonly, heavily pigmented epithelial layer that is two cells thick (the iris pigment epithelium), but the front surface has no epithelium. This anterior surface projects as the muscles dilate.
References
 This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1013 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1013 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
| Anatomy of the globe of the human eye | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrous tunic (outer) |
|  | |||||
| Uvea / vascular tunic (middle) |
| ||||||
| Retina (inner) |
| ||||||
| Anatomical regions of the eye |
| ||||||
| Other | |||||||
This article about the eye is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |