| Ju 60 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | AirlinerType of aircraft |
| National origin | Germany |
| Manufacturer | Junkers Flugzeugwerke |
| Designer | Herman Pohlmann |
| First flight | 8 November 1932 |
| Number built | 2 (plus a one more partially constructed) |
The Junkers Ju 60 was a single engine airliner built in prototype form in Germany in the early 1930s. It was designed to meet a requirement issued by the Reichsverkehrsministerium (Reich Transport Ministry) for a German-built equivalent to the Lockheed Vega with which to equip Deutsche Luft Hansa. The result was a sleek, cantilever monoplane of conventional configuration, with wings skinned in the corrugated duralumin that had been a hallmark of Junkers designs up to this time, although this would be the last Junkers aircraft to have this feature. The main units of the tailwheel undercarriage were retractable.
The Ju 60 was evaluated by Deutsche Luft Hansa against the Heinkel He 70. With the latter able to demonstrate a top speed 75 km/h (47 mph) better than the Ju 60, development of the Junkers design was halted before the third prototype had been completed. The two examples that had already been constructed eventually saw service with the Luftwaffe as liaison aircraft until 1942. The work done on the design would later form the basis of the Ju 160.
Specifications
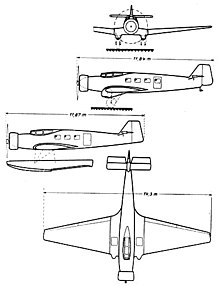
General characteristics
- Crew: Two pilots
- Capacity: Six passengers
- Length: 11.84 m (38 ft 10 in)
- Wingspan: 14.30 m (46 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 34.0 m (366 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 2,040 kg (4,490 lb)
- Gross weight: 3,100 kg (6,820 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Siemens Sh 20 , 470 kW (630 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 285 km/h (178 mph, 155 kn)
- Range: 1,000 km (621 mi, 540 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 5,200 m (17,100 ft)
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Airspeed Envoy
- Heinkel He 70
- Kharkiv KhAI-1
- Lockheed Model 9 Orion
- Manshū Hayabusa
- Polikarpov/Rafaelyants PR-12
- Tairov OKO-1
- Vultee V-1
- Northrop Delta
References
- Zoeller, Horst. "Junkers Facilities". The Hugo Junkers Homepage. Archived from the original on October 27, 2009. Retrieved 2016-06-22.
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 539.
- The Hugo Junkers Homepage
- Уголок неба
| Junkers aircraft | |
|---|---|
| Company designations | |
| Company EF designations (experimental aircraft) | |
| Idflieg designations | |
| RLM designations | |
| Imperial Japanese Navy aircraft designations (short system) | |
|---|---|
| Fighters (A) | |
| Torpedo bombers (B) | |
| Shipboard reconnaissance (C) | |
| Dive bombers (D) | |
| Reconnaissance seaplanes (E) | |
| Observation seaplanes (F) | |
| Land-based bombers (G) | |
| Flying Boats (H) | |
| Land-based Fighters (J) | |
| Trainers (K) | |
| Transports (L) | |
| Special-purpose (M) | |
| Floatplane fighters (N) | |
| Land-based bombers (P) | |
| Patrol (Q) | |
| Land-based reconnaissance (R) | |
| Night fighters (S) | |
| X as second letter is for experimental aircraft or imported technology demonstrators not intended for service, Hyphenated trailing letter (-J, -K, -L, -N or -S) denotes design modified for secondary role, Possibly incorrect designation, but used in many sources | |