In mathematics, Kan complexes and Kan fibrations are part of the theory of simplicial sets. Kan fibrations are the fibrations of the standard model category structure on simplicial sets and are therefore of fundamental importance. Kan complexes are the fibrant objects in this model category. The name is in honor of Daniel Kan.
Definitions
Definition of the standard n-simplex
For each n ≥ 0, recall that the standard -simplex, , is the representable simplicial set
Applying the geometric realization functor to this simplicial set gives a space homeomorphic to the topological standard -simplex: the convex subspace of consisting of all points such that the coordinates are non-negative and sum to 1.
Definition of a horn
Main article: Horn of a simplexFor each k ≤ n, this has a subcomplex , the k-th horn inside , corresponding to the boundary of the n-simplex, with the k-th face removed. This may be formally defined in various ways, as for instance the union of the images of the n maps corresponding to all the other faces of . Horns of the form sitting inside look like the black V at the top of the adjacent image. If is a simplicial set, then maps
correspond to collections of -simplices satisfying a compatibility condition, one for each . Explicitly, this condition can be written as follows. Write the -simplices as a list and require that
- for all with .
These conditions are satisfied for the -simplices of sitting inside .
Definition of a Kan fibration

A map of simplicial sets is a Kan fibration if, for any and , and for any maps and such that (where is the inclusion of in ), there exists a map such that and . Stated this way, the definition is very similar to that of fibrations in topology (see also homotopy lifting property), whence the name "fibration".
Technical remarks
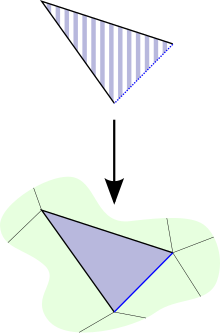
Using the correspondence between -simplices of a simplicial set and morphisms (a consequence of the Yoneda lemma), this definition can be written in terms of simplices. The image of the map can be thought of as a horn as described above. Asking that factors through corresponds to requiring that there is an -simplex in whose faces make up the horn from (together with one other face). Then the required map corresponds to a simplex in whose faces include the horn from . The diagram to the right is an example in two dimensions. Since the black V in the lower diagram is filled in by the blue -simplex, if the black V above maps down to it then the striped blue -simplex has to exist, along with the dotted blue -simplex, mapping down in the obvious way.
Kan complexes defined from Kan fibrations
A simplicial set is called a Kan complex if the map from , the one-point simplicial set, is a Kan fibration. In the model category for simplicial sets, is the terminal object and so a Kan complex is exactly the same as a fibrant object. Equivalently, this could be stated as: if every map from a horn has an extension to , meaning there is a lift such that
for the inclusion map , then is a Kan complex. Conversely, every Kan complex has this property, hence it gives a simple technical condition for a Kan complex.
Examples
Simplicial sets from singular homology
An important example comes from the construction of singular simplices used to define singular homology, called the singular functor
.
Given a space , define a singular -simplex of X to be a continuous map from the standard topological -simplex (as described above) to ,
Taking the set of these maps for all non-negative gives a graded set,
- .
To make this into a simplicial set, define face maps by
and degeneracy maps by
- .
Since the union of any faces of is a strong deformation retract of , any continuous function defined on these faces can be extended to , which shows that is a Kan complex.
Relation with geometric realization
It is worth noting the singular functor is right adjoint to the geometric realization functor
giving the isomorphism
Simplicial sets underlying simplicial groups
It can be shown that the simplicial set underlying a simplicial group is always fibrant. In particular, for a simplicial abelian group, its geometric realization is homotopy equivalent to a product of Eilenberg-Maclane spaces
In particular, this includes classifying spaces. So the spaces , , and the infinite lens spaces are correspond to Kan complexes of some simplicial set. In fact, this set can be constructed explicitly using the Dold–Kan correspondence of a chain complex and taking the underlying simplicial set of the simplicial abelian group.
Geometric realizations of small groupoids
Another important source of examples are the simplicial sets associated to a small groupoid . This is defined as the geometric realization of the simplicial set and is typically denoted . We could have also replaced with an infinity groupoid. It is conjectured that the homotopy category of geometric realizations of infinity groupoids is equivalent to the homotopy category of homotopy types. This is called the homotopy hypothesis.
Non-example: standard n-simplex
It turns out the standard -simplex is not a Kan complex. The construction of a counter example in general can be found by looking at a low dimensional example, say . Taking the map sending
gives a counter example since it cannot be extended to a map because the maps have to be order preserving. If there was a map, it would have to send
but this isn't a map of simplicial sets.
Categorical properties
Simplicial enrichment and function complexes
For simplicial sets there is an associated simplicial set called the function complex , where the simplices are defined as
and for an ordinal map there is an induced map
(since the first factor of Hom is contravariant) defined by sending a map to the composition
Exponential law
This complex has the following exponential law of simplicial sets
which sends a map to the composite map
where for lifted to the n-simplex . ^
Kan fibrations and pull-backs
Given a (Kan) fibration and an inclusion of simplicial sets , there is a fibration
(where is in the function complex in the category of simplicial sets) induced from the commutative diagram
where is the pull-back map given by pre-composition and is the pushforward map given by post-composition. In particular, the previous fibration implies and are fibrations.
Applications
Homotopy groups of Kan complexes
The homotopy groups of a fibrant simplicial set may be defined combinatorially, using horns, in a way that agrees with the homotopy groups of the topological space which realizes it. For a Kan complex and a vertex , as a set is defined as the set of maps of simplicial sets fitting into a certain commutative diagram:
Notice the fact is mapped to a point is equivalent to the definition of the sphere as the quotient for the standard unit ball
Defining the group structure requires a little more work. Essentially, given two maps there is an associated -simplice such that gives their addition. This map is well-defined up to simplicial homotopy classes of maps, giving the group structure. Moreover, the groups are Abelian for . For , it is defined as the homotopy classes of vertex maps .
Homotopy groups of simplicial sets
Using model categories, any simplicial set has a fibrant replacement which is homotopy equivalent to in the homotopy category of simplicial sets. Then, the homotopy groups of can be defined as
where is a lift of to . These fibrant replacements can be thought of a topological analogue of resolutions of a chain complex (such as a projective resolution or a flat resolution).
See also
- Model category
- Simplicial homotopy theory
- Simplicially enriched category
- Weak Kan complex (also called quasi-category, ∞-category)
- ∞-groupoid
- Fibration of simplicial sets
References
- See Goerss and Jardine, page 7
- See May, page 2
- May uses this simplicial definition; see page 25
- ^ Goerss, Paul G.; Jardine, John F. (2009). Simplicial Homotopy Theory. Birkhäuser Basel. ISBN 978-3-0346-0188-7. OCLC 837507571.
- See May, page 3
- Friedman, Greg (2016-10-03). "An elementary illustrated introduction to simplicial sets". arXiv:0809.4221 .
Bibliography
- Goerss, Paul G.; Jardine, John F. (1999). Simplicial Homotopy Theory. Basel: Birkhäuser Basel. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-8707-6. ISBN 978-3-0348-9737-2. MR 1711612.
- May, J. Peter (1992) . Simplicial objects in algebraic topology. Chicago Lectures in Mathematics. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-51180-4. MR 1206474.
 -simplex
-simplex , is the representable simplicial set
, is the representable simplicial set

 consisting of all points
consisting of all points  such that the coordinates are non-negative and sum to 1.
such that the coordinates are non-negative and sum to 1.
 , the k-th horn inside
, the k-th horn inside  corresponding to all the other faces of
corresponding to all the other faces of  sitting inside
sitting inside  look like the black V at the top of the adjacent image. If
look like the black V at the top of the adjacent image. If  is a simplicial set, then maps
is a simplicial set, then maps

 -simplices satisfying a compatibility condition, one for each
-simplices satisfying a compatibility condition, one for each  . Explicitly, this condition can be written as follows. Write the
. Explicitly, this condition can be written as follows. Write the  and require that
and require that
 for all
for all  with
with  .
. is a Kan fibration if, for any
is a Kan fibration if, for any  and
and  , and for any maps
, and for any maps  and
and  such that
such that  (where
(where  is the inclusion of
is the inclusion of  such that
such that  and
and
 . Stated this way, the definition is very similar to that of
. Stated this way, the definition is very similar to that of  (a consequence of the
(a consequence of the  can be thought of as a horn as described above. Asking that
can be thought of as a horn as described above. Asking that  factors through
factors through  corresponds to requiring that there is an
corresponds to requiring that there is an  whose faces make up the horn from
whose faces make up the horn from  corresponds to a simplex in
corresponds to a simplex in  . The diagram to the right is an example in two dimensions. Since the black V in the lower diagram is filled in by the blue
. The diagram to the right is an example in two dimensions. Since the black V in the lower diagram is filled in by the blue  -simplex, if the black V above maps down to it then the striped blue
-simplex, if the black V above maps down to it then the striped blue  -simplex, mapping down in the obvious way.
-simplex, mapping down in the obvious way.
 , the one-point simplicial set, is a Kan fibration. In the
, the one-point simplicial set, is a Kan fibration. In the  is the terminal object and so a Kan complex is exactly the same as a
is the terminal object and so a Kan complex is exactly the same as a  from a horn has an extension to
from a horn has an extension to  such that
such that
 , then
, then  .
.
 .
. by
by

 by
by
 .
. faces of
faces of  is a strong
is a strong  is a Kan complex.
is a Kan complex.



 ,
,  , and the infinite lens spaces
, and the infinite lens spaces  are correspond to Kan complexes of some simplicial set. In fact, this set can be constructed explicitly using the
are correspond to Kan complexes of some simplicial set. In fact, this set can be constructed explicitly using the  . This is defined as the geometric realization of the simplicial set
. This is defined as the geometric realization of the simplicial set  and is typically denoted
and is typically denoted  . We could have also replaced
. We could have also replaced  . Taking the map
. Taking the map  sending
sending
 because the maps have to be order preserving. If there was a map, it would have to send
because the maps have to be order preserving. If there was a map, it would have to send
 there is an associated simplicial set called the function complex
there is an associated simplicial set called the function complex  , where the simplices are defined as
, where the simplices are defined as
 there is an induced map
there is an induced map
 to the composition
to the composition

 to the composite map
to the composite map
 for
for  lifted to the n-simplex
lifted to the n-simplex  and an inclusion of simplicial sets
and an inclusion of simplicial sets  , there is a fibration
, there is a fibration 
 is in the function complex in the category of simplicial sets) induced from the commutative diagram
is in the function complex in the category of simplicial sets) induced from the commutative diagram
 is the pull-back map given by pre-composition and
is the pull-back map given by pre-composition and  is the pushforward map given by post-composition. In particular, the previous fibration implies
is the pushforward map given by post-composition. In particular, the previous fibration implies  and
and  are fibrations.
are fibrations.
 , as a set
, as a set  is defined as the set of maps
is defined as the set of maps  of simplicial sets fitting into a certain commutative diagram:
of simplicial sets fitting into a certain commutative diagram: 
 is mapped to a point is equivalent to the definition of the sphere
is mapped to a point is equivalent to the definition of the sphere  as the quotient
as the quotient  for the standard unit ball
for the standard unit ball
 there is an associated
there is an associated  -simplice
-simplice  such that
such that  gives their addition. This map is well-defined up to simplicial homotopy classes of maps, giving the group structure. Moreover, the groups
gives their addition. This map is well-defined up to simplicial homotopy classes of maps, giving the group structure. Moreover, the groups  . For
. For  , it is defined as the homotopy classes
, it is defined as the homotopy classes  of vertex maps
of vertex maps  which is homotopy equivalent to
which is homotopy equivalent to 
 is a lift of
is a lift of