| Kingdom of Morocco | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Motto: ٱللَّٰه، ٱلْوَطَن، ٱلْمَلِك "Allāh, al-Waṭan, al-Malik" "God, Country, King" | |
| Anthem: ٱلنَّشِيْد ٱلْوَطَنِي "an-Našīd al-Waṭanīy" "Cherifian Anthem" | |
 Location of Morocco in northwest Africa
Undisputed territory of Morocco
Western Sahara, a territory claimed and occupied mostly by Morocco as its Southern Provinces Location of Morocco in northwest Africa
Undisputed territory of Morocco
Western Sahara, a territory claimed and occupied mostly by Morocco as its Southern Provinces | |
| Capital | Rabat 34°02′N 6°51′W / 34.033°N 6.850°W / 34.033; -6.850 |
| Largest city | Casablanca 33°32′N 7°35′W / 33.533°N 7.583°W / 33.533; -7.583 |
| Official languages | |
| Spoken languages (2024) |
|
| Foreign languages | |
| Ethnic groups | See Ethnic groups |
| Religion (2020) | |
| Demonym(s) | Moroccan |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary semi-constitutional monarchy |
| • King | Mohammed VI |
| • Prime Minister | Aziz Akhannouch |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| • Upper house | House of Councillors |
| • Lower house | House of Representatives |
| Establishment | |
| • Idrisid dynasty | 788 |
| • 'Alawi dynasty (current dynasty) | 1631 |
| • Protectorate established | 30 March 1912 |
| • Independence | 7 April 1956 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 446,550 km (172,410 sq mi) (57th) |
| • Water (%) | 0.056 (250 km) |
| Population | |
| • 2024 estimate | 37,493,183 (38th) |
| • 2024 census | 36,828,330 |
| • Density | 79.0/km (204.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| Gini (2015) | 40.3 medium inequality |
| HDI (2022) | medium (120th) |
| Currency | Moroccan dirham (MAD) |
| Time zone | UTC
|
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +212 |
| ISO 3166 code | MA |
| Internet TLD | |
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It has a population of approximately 37 million. Islam is both the official and predominant religion, while Arabic and Berber are the official languages. Additionally, French and the Moroccan dialect of Arabic are widely spoken. The culture of Morocco is a mix of Arab, Berber, African and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca.
The region constituting Morocco has been inhabited since the Paleolithic era over 300,000 years ago. The Idrisid dynasty was established by Idris I in 788 and Morocco was subsequently ruled by a series of other independent dynasties, reaching its zenith as a regional power in the 11th and 12th centuries, under the Almoravid and Almohad dynasties, when it controlled most of the Iberian peninsula and the Maghreb. Centuries of Arab migration to the Maghreb since the 7th century shifted the demographic scope of the region. In the 15th and 16th centuries, Morocco faced external threats to its sovereignty, with Portugal seizing some territory and the Ottoman Empire encroaching from the east. The Marinid and Saadi dynasties otherwise resisted foreign domination, and Morocco was the only North African nation to escape Ottoman dominion. The 'Alawi dynasty, which rules the country to this day, seized power in 1631, and over the next two centuries expanded diplomatic and commercial relations with the Western world. Morocco's strategic location near the mouth of the Mediterranean drew renewed European interest; in 1912, France and Spain divided the country into respective protectorates, reserving an international zone in Tangier. Following intermittent riots and revolts against colonial rule, in 1956, Morocco regained its independence and reunified.
Since independence, Morocco has remained relatively stable. It has the fifth-largest economy in Africa and wields significant influence in both Africa and the Arab world; it is considered a middle power in global affairs and holds membership in the Arab League, the Arab Maghreb Union, the Union for the Mediterranean, and the African Union. Morocco is a unitary semi-constitutional monarchy with an elected parliament. The executive branch is led by the King of Morocco and the prime minister, while legislative power is vested in the two chambers of parliament: the House of Representatives and the House of Councillors. Judicial power rests with the Constitutional Court, which may review the validity of laws, elections, and referendums. The king holds vast executive and legislative powers, especially over the military, foreign policy and religious affairs; he can issue decrees called dahirs, which have the force of law, and can also dissolve the parliament after consulting the prime minister and the president of the constitutional court.
Morocco claims ownership of the non-self-governing territory of Western Sahara, which it has designated its Southern Provinces. In 1975, after Spain agreed to decolonise the territory and cede its control to Morocco and Mauritania, a guerrilla war broke out between those powers and some of the local inhabitants. In 1979, Mauritania relinquished its claim to the area, but the war continued to rage. In 1991, a ceasefire agreement was reached, but the issue of sovereignty remained unresolved. Today, Morocco occupies two-thirds of the territory, and efforts to resolve the dispute have thus far failed to break the political deadlock.
Etymology and name
The English Morocco is an anglicisation of the Spanish name for the country, Marruecos, derived from the name of the city of Marrakesh, which was the capital of the Almoravid dynasty, the Almohad Caliphate, and the Saadian dynasty. During the Almoravid dynasty, the city of Marrakesh was established under the name of Tāmurākušt, derived from the city's ancient Berber name of amūr n Yakuš (lit. 'land/country of God'). In English, the first vowel has been changed, likely influenced by the word "Moor".
Historically, the territory has been part of what Muslim geographers referred to as al-Maghrib al-Aqṣā [ar] (المغرب الأقصى, 'the Farthest West ' designating roughly the area from Tiaret to the Atlantic) in contrast with neighbouring regions of al-Maghrib al-Awsaṭ [ar] (المغرب الأوسط, 'the Middle West': Tripoli to Béjaïa) and al-Maghrib al-Adnā [ar] (المغرب الأدنى, 'the Nearest West': Alexandria to Tripoli).
Morocco's modern Arabic name is al-Maghrib (المغرب, transl. the land of the sunset; the west), with the Kingdom's official Arabic name being al-Mamlakah al-Maghribīyah (المملكة المغربية; transl. the kingdom of sunset/the west). In Turkish, Morocco is known as Fas, a name derived from its medieval capital of Fes which is derived from the Arabic word Faʾs (فأس; transl. pickaxe), as the city's founder Idris I ibn Abd Allah reputedly used a silver and gold pickaxe to trace the outlines of the city. In other parts of the Islamic world, for example in Egyptian and Middle Eastern Arabic literature before the mid-20th century, Morocco was commonly referred to as Murrakush (مراكش). The term is still used to refer to Morocco today in several Indo-Iranian languages, including Persian, Urdu, and Punjabi.
Morocco has also been referred to politically by a variety of terms denoting the Sharifi heritage of the 'Alawi dynasty, such as al-Mamlakah ash-Sharīfah (المملكة الشريفة), al-Iyālah ash-Sharīfah (الإيالة الشريفة) and al-Imbarāṭūriyyah ash-Sharīfah (الإمبراطورية الشريفة), rendered in French as l'Empire chérifien and in English as the 'Sharifian Empire'.
History
Main article: History of MoroccoPrehistory and antiquity
The area of present-day Morocco has been inhabited since at least Paleolithic times, beginning sometime between 190,000 and 90,000 BC. A recent publication has suggested that there is evidence for even earlier human habitation of the area: Homo sapiens fossils that had been discovered in the late 2000s near the Atlantic coast in Jebel Irhoud were recently dated to roughly 315,000 years ago. During the Upper Paleolithic, the Maghreb was more fertile than it is today, resembling a savanna, in contrast to its modern arid landscape.
DNA studies of Iberomaurusian peoples at Taforalt, Morocco dating to around 15,000 years ago have found them to have a distinctive Maghrebi ancestry formed from a mixture of Near Eastern and African ancestry, which is still found as a part of the genome of modern Northwest Africans. Later during the Neolithic, from around 7,500 years ago onwards, there was a migration into Northwest Africa of European Neolithic Farmers from the Iberian Peninsula (who had originated in Anatolia several thousand years prior), as well as pastoralists from the Levant, both of whom also significantly contributed to the ancestry of modern Northwest Africans. The proto-Berber tribes evolved from these prehistoric communities during the late Bronze- and early Iron ages.
In the early part of Classical Antiquity, Northwest Africa and Morocco were slowly drawn into the wider emerging Mediterranean world by the Phoenicians, who established trading colonies and settlements there, the most substantial of which were Chellah, Lixus, and Mogador. Mogador was established as a Phoenician colony as early as the 6th century BC.

Morocco later became a realm of the Northwest African civilisation of ancient Carthage, and part of the Carthaginian empire. The earliest known independent Moroccan state was the Berber kingdom of Mauretania, under King Baga. This ancient kingdom (not to be confused with the modern state of Mauritania) flourished around 225 BC or earlier. Mauretania became a client kingdom of the Roman Empire in 33 BC. Emperor Claudius annexed Mauretania directly in 44 AD, making it a Roman province ruled by an imperial governor (either a procurator Augusti, or a legatus Augusti pro praetore).
Christianity in Morocco appeared during the Roman times, when it was practiced by Berber Christians in Roman Mauretania Tingitana. During the Crisis of the Third Century, parts of Mauretania were reconquered by Berbers. By the late 3rd century, direct Roman rule had become confined to a few coastal cities, such as Septum (Ceuta) in Mauretania Tingitana and Cherchell in Mauretania Caesariensis. When, in 429 AD, the area was devastated by the Vandals, the Roman Empire lost its remaining possessions in Mauretania, and local Mauro-Roman kings assumed control of them. In the 530s, the Eastern Roman Empire, under Byzantine control, re-established direct imperial rule of Septum and Tingi, fortified Tingis and erected a church.
Foundation and dynasties

The Muslim conquest of the Maghreb that had begun during the mid-7th century was completed under the Umayyad Caliphate by 709. The caliphate introduced both Islam and the Arabic language to the area; this period also saw the beginning of a trend of Arab migration to the Maghreb which would last for centuries and effect a demographic shift in the region. While constituting part of the larger empire, Morocco was initially organised as a subsidiary province of Ifriqiya, with the local governors appointed by the Muslim governor in Kairouan.
The indigenous Berber tribes adopted Islam, but retained their customary laws. They also paid taxes and tribute to the new Muslim administration. The first independent Muslim state in the area of modern Morocco was the Kingdom of Nekor, an emirate in the Rif Mountains. It was founded by Salih I ibn Mansur in 710, as a client state to the Umayyad Caliphate. After the outbreak of the Berber Revolt in 739, the Berbers formed other independent states such as the Miknasa of Sijilmasa and the Barghawata.

The founder of the Idrisid dynasty and the great-grandson of Hasan ibn Ali, Idris ibn Abdallah, had fled to Morocco after the massacre of his family by the Abbasids in the Hejaz. He convinced the Awraba Berber tribes to break their allegiance to the distant Abbasid caliphs and he founded the Idrisid dynasty in 788. The Idrisids established Fes as their capital and Morocco became a centre of Muslim learning and a major regional power. The Idrisids were ousted in 927 by the Fatimid Caliphate and their Miknasa allies. After Miknasa broke off relations with the Fatimids in 932, they were removed from power by the Maghrawa of Sijilmasa in 980.
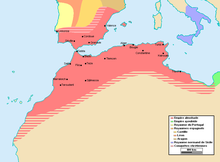
From the 11th century onward, a series of Berber dynasties arose. Under the Sanhaja Almoravid dynasty and the Masmuda Almohad dynasty, Morocco dominated the Maghreb, al-Andalus in Iberia, and the western Mediterranean region. From the 13th century onward the country saw a massive migration of the Banu Hilal Arab tribes. In the 13th and 14th centuries the Zenata Berber Marinids held power in Morocco and strove to replicate the successes of the Almohads through military campaigns in Algeria and Spain. They were followed by the Wattasids. In the 15th century, the Reconquista ended Muslim rule in Iberia and many Muslims and Jews fled to Morocco.
Portuguese efforts to control the Atlantic sea trade in the 15th century did not greatly affect the interior of Morocco even though they managed to control some possessions on the Moroccan coast but not venturing further afield inland.

In 1549, the region fell to successive Arab dynasties claiming descent from the Islamic prophet Muhammad: first the Saadi dynasty who ruled from 1549 to 1659, and then the 'Alawi dynasty, who have remained in power since the 17th century. Morocco faced aggression from Spain in the north, and the Ottoman Empire's allies pressing westward.

Under the Saadis, the sultanate ended the Portuguese Aviz dynasty in 1578 at the Battle of Alcácer Quibir. The reign of Ahmad al-Mansur brought new wealth and prestige to the Sultanate, and a large expedition to West Africa inflicted a crushing defeat on the Songhay Empire in 1591. However, managing the territories across the Sahara proved too difficult. Upon the death of al-Mansur, the country was divided among his sons.
After a period of political fragmentation and conflict during the decline of the Saadi dynasty, Morocco was finally reunited by the Alawi sultan al-Rashid in the late 1660s, who took Fez in 1666 and Marrakesh in 1668. The 'Alawis succeeded in stabilising their position, and while the kingdom was smaller than previous ones in the region, it remained quite wealthy. Against the opposition of local tribes Ismail Ibn Sharif (1672–1727) began to create a unified state. With his Riffian army, he re-occupied Tangier from the English who had abandoned it in 1684 and drove the Spanish from Larache in 1689. The Portuguese abandoned Mazagão, their last territory in Morocco, in 1769. However, the siege of Melilla against the Spanish ended in defeat in 1775.
Morocco was the first nation to recognise the fledgling United States as an independent nation in 1777. In the beginning of the American Revolution, American merchant ships in the Atlantic Ocean were subject to attacks by other fleets. On 20 December 1777, Morocco's Sultan Mohammed III declared that American merchant ships would be under the protection of the sultanate and could thus enjoy safe passage. The 1786 Moroccan–American Treaty of Friendship stands as the United States' oldest unbroken friendship treaty.
French and Spanish protectorates
Main articles: French protectorate in Morocco and Spanish protectorate in Morocco
As Europe industrialised, Northwest Africa was increasingly prized for its potential for colonisation. France showed a strong interest in Morocco as early as 1830, not only to protect the border of its Algerian territory, but also because of the strategic position of Morocco with coasts on the Mediterranean and the open Atlantic. In 1860, a dispute over Spain's Ceuta enclave led Spain to declare war. Victorious Spain won a further enclave and an enlarged Ceuta in the settlement. In 1884, Spain created a protectorate in the coastal areas of Morocco.

In 1904, France and Spain carved out zones of influence in Morocco. Recognition by the United Kingdom of France's sphere of influence provoked a strong reaction from the German Empire; and a crisis loomed in 1905. The matter was resolved at the Algeciras Conference in 1906. The Agadir Crisis of 1911 increased tensions between European powers. The 1912 Treaty of Fez made Morocco a protectorate of France, and triggered the 1912 Fez riots. Spain continued to operate its coastal protectorate. By the same treaty, Spain assumed the role of protecting power over the northern coastal and southern Saharan zones.

Tens of thousands of colonists entered Morocco. Some bought up large amounts of rich agricultural land, while others organised the exploitation and modernisation of mines and harbours. Interest groups that formed among these elements continually pressured France to increase its control over Morocco – with some Moroccan tribes allying with the French against other competing tribes from early on in its conquest. The French colonial administrator, Governor general Marshal Hubert Lyautey, sincerely admired Moroccan culture and succeeded in imposing a joint Moroccan-French administration, while creating a modern school system. Several divisions of Moroccan soldiers (Goumiers or regular troops and officers) served in the French army in both World War I and World War II, and in the Spanish Nationalist Army in the Spanish Civil War and after (Regulares). The institution of slavery was abolished in 1925.
Between 1921 and 1926, an uprising in the Rif Mountains, led by Abd el-Krim, led to the establishment of the Republic of the Rif. The Spanish used anti-civilian bombing raids and mustard gas to prevent the Rif republic from gaining independence. They lost more than 13,000 soldiers at Annual in July–August 1921 alone. The Riffi were eventually suppressed by 1927 by the Franco-Spanish military. The casualties on the Spanish-French side were 52,000 and from the Riffi 10,000 died.

In 1943, the Istiqlal Party (Independence Party) was founded to press for independence, with discreet US support. Moroccan nationalists drew heavily on transnational activist networks for lobbying to end colonial rule, primarily at the United Nations. The Istiqlal Party subsequently provided most of the leadership for the nationalist movement.

France's exile of Sultan Mohammed V in 1953 to Madagascar and his replacement by the unpopular Mohammed Ben Aarafa sparked active opposition to the French and Spanish protectorates. The most notable violence occurred in Oujda where Moroccans attacked French and other European residents in the streets. France allowed Mohammed V to return in 1955, and the negotiations that led to Moroccan independence began the following year. In March 1956 Morocco regained its independence from France as the Kingdom of Morocco. A month later Spain forsook its protectorate in Northern Morocco to the new state but kept its two coastal enclaves (Ceuta and Melilla) on the Mediterranean coast which dated from earlier conquests, but over which Morocco still claims sovereignty to this day.
Post-independence
| This section needs expansion. You can help by making an edit requestadding to it . (July 2023) |
Sultan Mohammed became King in 1957. Upon the death of Mohammed V, Hassan II became King of Morocco on 3 March 1961. Morocco held its first general elections in 1963. However, Hassan declared a state of emergency and suspended parliament in 1965. In 1971 and 1972, there were two failed attempts to depose the king and establish a republic. A truth commission set up in 2005 to investigate human rights abuses during his reign confirmed nearly 10,000 cases, ranging from death in detention to forced exile. Some 592 people were recorded killed during Hassan's rule according to the truth commission.
In 1963, the Sand War was fought between Algerian and Moroccan troops over Moroccan claims to parts of Algerian territory. A formal peace agreement was signed in February 1964; however, relations remained strained between the two countries following the conflict. The Spanish enclave of Ifni in the south was returned to Morocco in 1969.
The Polisario movement was formed in 1973, with the aim of establishing an independent state in the Spanish Sahara. On 6 November 1975, King Hassan asked for volunteers to cross into the Spanish Sahara. Some 350,000 civilians were reported as being involved in the "Green March". A month later, Spain agreed to leave the Spanish Sahara, soon to become Western Sahara, and to transfer it to joint Moroccan-Mauritanian control, despite the objections and threats of military intervention by Algeria. Moroccan forces occupied the territory.
Moroccan and Algerian troops soon clashed in Western Sahara. Morocco and Mauritania divided up Western Sahara. Fighting between the Moroccan military and Polisario forces continued for many years. The prolonged war was a considerable financial drain on Morocco. In 1983, Hassan cancelled planned elections amid political unrest and economic crisis. In 1984, Morocco left the Organisation of African Unity in protest at the SADR's admission to the body. Polisario claimed to have killed more than 5,000 Moroccan soldiers between 1982 and 1985. Algerian authorities have estimated the number of Sahrawi refugees in Algeria to be 165,000. Diplomatic relations with Algeria were restored in 1988. In 1991, a UN-monitored ceasefire began in Western Sahara, but the territory's status remains undecided and ceasefire violations are reported. The following decade saw much wrangling over a proposed referendum on the future of the territory but the deadlock was not broken.

Political reforms in the 1990s resulted in the establishment of a bicameral legislature with Morocco's first opposition-led government coming to power. King Hassan II died in 1999 and was succeeded by his son, Mohammed VI. He is a cautious moderniser who has introduced some economic and social liberalisation. Mohammed VI paid a controversial visit to the Western Sahara in 2002. Morocco unveiled an autonomy blueprint for Western Sahara to the United Nations in 2007. The Polisario rejected the plan and put forward its own proposal. Morocco and the Polisario Front held UN-sponsored talks in New York City but failed to come to any agreement. In 2010, security forces stormed a protest camp in the Western Sahara, triggering violent demonstrations in the regional capital El Aaiún.

In 2002, Morocco and Spain agreed to a US-brokered resolution over the disputed island of Perejil. Spanish troops had taken the normally uninhabited island after Moroccan soldiers landed on it and set up tents and a flag. There were renewed tensions in 2005, as dozens of African migrants stormed the borders of the Spanish enclaves of Melilla and Ceuta. In response, Spain deported dozens of the illegal migrants to Morocco from Melilla. In 2006, the Spanish Premier Zapatero visited Spanish enclaves. He was the first Spanish leader in 25 years to make an official visit to the territories. The following year, Spanish King Juan Carlos I visited Ceuta and Melilla, further angering Morocco which demanded control of the enclaves.
During the 2011–2012 Moroccan protests, thousands of people rallied in Rabat and other cities calling for political reform and a new constitution curbing the powers of the king. In July 2011, the King won a landslide victory in a referendum on a reformed constitution he had proposed to placate the Arab Spring protests. In the first general elections that followed, the moderate Islamist Justice and Development Party won a plurality of seats, with Abdelilah Benkirane being designated as head of government per the new constitution. Despite the reforms made by Mohammed VI, demonstrators continued to call for deeper reforms. Hundreds took part in a trade union rally in Casablanca in May 2012. Participants accused the government of failing to deliver on reforms.
On 10 December 2020, Israel–Morocco normalisation agreement was announced and Morocco announced its intention to resume diplomatic relations with Israel. Joint Declaration of the Kingdom of Morocco, the United States of America and the State of Israel was signed on 22 December 2020.
On 24 August 2021, neighbouring Algeria cut diplomatic relations with Morocco, accusing Morocco of supporting a separatist group and hostile actions against Algeria. Morocco called the decision unjustified.
On 8 September 2023, a 6.8 magnitude earthquake hit Morocco killing more than 2,800 people and injuring thousands. The epicentre of the quake was around 70 km southwest of city of Marrakech.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Morocco


Morocco has a coast by the Atlantic Ocean that reaches past the Strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Spain to the north (a water border through the Strait and land borders with three small Spanish-controlled exclaves, Ceuta, Melilla, and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera), Algeria to the east, and Western Sahara to the south. Since Morocco controls most of Western Sahara, its de facto southern boundary is with Mauritania.
The internationally recognised borders of the country lie between latitudes 27° and 36°N, and longitudes 1° and 14°W.
The geography of Morocco spans from the Atlantic Ocean, to mountainous areas, to the Sahara desert. Morocco is a Northern African country, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, between Algeria and the annexed Western Sahara. It is one of only three nations (along with Spain and France) to have both Atlantic and Mediterranean coastlines.
A large part of Morocco is mountainous. The Atlas Mountains are located mainly in the centre and the south of the country. The Rif Mountains are located in the north of the country. Both ranges are mainly inhabited by the Berber people. Its total area is about 446,300 km (172,317 sq mi). Algeria borders Morocco to the east and southeast, though the border between the two countries has been closed since 1994.
Spanish territory in Northwest Africa neighbouring Morocco comprises five enclaves on the Mediterranean coast: Ceuta, Melilla, Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, Peñón de Alhucemas, the Chafarinas islands, and the disputed islet Perejil. Off the Atlantic coast the Canary Islands belong to Spain, whereas Madeira to the north is Portuguese. To the north, Morocco is bordered by the Strait of Gibraltar, where international shipping has unimpeded transit passage between the Atlantic and Mediterranean.
The Rif mountains stretch over the region bordering the Mediterranean from the north-west to the north-east. The Atlas Mountains run down the backbone of the country, from the northeast to the southwest. Most of the southeast portion of the country is in the Sahara Desert and as such is generally sparsely populated and unproductive economically. Most of the population lives to the north of these mountains, while to the south lies the Western Sahara, a former Spanish colony that was annexed by Morocco in 1975 (see Green March). Morocco claims that the Western Sahara is part of its territory and refers to that as its Southern Provinces.
Morocco's capital city is Rabat; its largest city is its main port, Casablanca. Other cities recording a population over 500,000 in the 2014 Moroccan census are Fes, Marrakesh, Meknes, Salé and Tangier.
Morocco is represented in the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 geographical encoding standard by the symbol MA. This code was used as the basis for Morocco's internet domain, .ma.
Climate

In area, Morocco's climate is mainly "hot summer Mediterranean" (Csa) and "hot desert" (BWh) zones.
Central mountain ranges and the effects of the cold Canary Current, off the Atlantic coast, are significant factors in Morocco's relatively large variety of vegetation zones, ranging from lush forests in the northern and central mountains, giving way to steppe, semi-arid and desert areas in the eastern and southern regions. The Moroccan coastal plains experience moderate temperatures even in summer.
In the Rif, Middle and High Atlas Mountains, there exist several different types of climates: Mediterranean along the coastal lowlands, giving way to a humid temperate climate at higher elevations with sufficient moisture to allow for the growth of different species of oaks, moss carpets, junipers, and Atlantic fir which is a royal conifer tree endemic to Morocco. In the valleys, fertile soils and high precipitation allow for the growth of thick and lush forests. Cloud forests can be found in the west of the Rif Mountains and Middle Atlas Mountains. At higher elevations, the climate becomes alpine in character, and can sustain ski resorts.
Southeast of the Atlas mountains, near the Algerian borders, the climate becomes very dry, with long and hot summers. Extreme heat and low moisture levels are especially pronounced in the lowland regions east of the Atlas range due to the rain shadow effect of the mountain system. The southeasternmost portions of Morocco are very hot, and include portions of the Sahara desert, where vast swathes of sand dunes and rocky plains are dotted with lush oases.
In contrast to the Sahara region in the south, coastal plains are fertile in the central and northern regions of the country, and comprise the backbone of the country's agriculture, in which 95% of the population live. The direct exposure to the North Atlantic Ocean, the proximity to mainland Europe and the long stretched Rif and Atlas mountains are the factors of the rather European-like climate in the northern half of the country. That makes Morocco a country of contrasts. Forested areas cover about 12% of the country while arable land accounts for 18%. Approximately 5% of Moroccan land is irrigated for agricultural use.


In general, apart from the southeast regions (pre-Saharan and desert areas), Morocco's climate and geography are very similar to the Iberian peninsula. Thus Morocco has the following climate zones:
- Mediterranean: Dominates the coastal Mediterranean regions of the country, along the (500 km strip), and some parts of the Atlantic coast. Summers are hot to moderately hot and dry, average highs are between 29 °C (84.2 °F) and 32 °C (89.6 °F). Winters are generally mild and wet, daily average temperatures hover around 9 °C (48.2 °F) to 11 °C (51.8 °F), and average low are around 5 °C (41.0 °F) to 8 °C (46.4 °F), typical to the coastal areas of the west Mediterranean. Annual Precipitation in this area vary from 600 to 800 mm in the west to 350–500 mm in the east. Notable cities that fall into this zone are Tangier, Tetouan, Al Hoceima, Nador and Safi.
- Sub-Mediterranean: It influences cities that show Mediterranean characteristics, but remain fairly influenced by other climates owing to their either relative elevation, or direct exposure to the North Atlantic Ocean. We thus have two main influencing climates:
- Oceanic: Determined by the cooler summers, where highs are around 27 °C (80.6 °F) and in terms of the Essaouira region, are almost always around 21 °C (69.8 °F). The medium daily temperatures can get as low as 19 °C (66.2 °F), while winters are chilly to mild and wet. Annual precipitation varies from 400 to 700 mm. Notable cities that fall into this zone are Rabat, Casablanca, Kénitra, Salé and Essaouira.
- Continental: Determined by the bigger gap between highs and lows, that results in hotter summers and colder winters, than found in typical Mediterranean zones. In summer, daily highs can get as high as 40 °C (104.0 °F) during heat waves, but usually are between 32 °C (89.6 °F) and 36 °C (96.8 °F). However, temperatures drop as the sun sets. Night temperatures usually fall below 20 °C (68.0 °F), and sometimes as low as 10 °C (50.0 °F) in mid-summer. Winters are cooler, and can get below the freezing point multiple times between December and February. Also, snow can fall occasionally. Fès for example registered −8 °C (17.6 °F) in winter 2005. Annual precipitation varies between 500 and 900 mm. Notable cities are Fès, Meknès, Chefchaouen, Beni-Mellal and Taza.
- Continental: Dominates the mountainous regions of the north and central parts of the country, where summers are hot to very hot, with highs between 32 °C (89.6 °F) and 36 °C (96.8 °F). Winters on the other hand are cold, and lows usually go beyond the freezing point. And when cold damp air comes to Morocco from the northwest, for a few days, temperatures sometimes get below −5 °C (23.0 °F). It often snows abundantly in this part of the country. Precipitation varies between 400 and 800 mm. Notable cities are Khenifra, Imilchil, Midelt and Azilal.
- Alpine: Found in some parts of the Middle Atlas Mountain range and the eastern part of the High Atlas Mountain range. Summers are very warm to moderately hot, and winters are longer, cold and snowy. Precipitation varies between 400 and 1200 mm. In summer highs barely go above 30 °C (86.0 °F), and lows are cool and average below 15 °C (59.0 °F). In winters, highs average around 8 °C (46.4 °F), and lows go well below the freezing point. In this part of country, there are many ski resorts, such as Oukaimeden and Mischliefen. Notable cities are Ifrane, Azrou and Boulmane.
- Semi-arid: This type of climate is found in the south of the country and some parts of the east of the country, where rainfall is lower and annual precipitations are between 200 and 350 mm. However, one usually finds Mediterranean characteristics in those regions, such as the precipitation pattern and thermal attributes. Notable cities are Agadir, Marrakesh and Oujda.
South of Agadir and east of Jerada near the Algerian borders, arid and desert climate starts to prevail.
Due to Morocco's proximity to the Sahara desert and the North Sea of the Atlantic Ocean, two phenomena occur to influence the regional seasonal temperatures, either by raising temperatures by 7–8 degrees Celsius when sirocco blows from the east creating heatwaves, or by lowering temperatures by 7–8 degrees Celsius when cold damp air blows from the northwest, creating a coldwave or cold spell. However, these phenomena do not last for more than two to five days on average.
Climate change is expected to significantly impact Morocco on multiple dimensions. As a coastal country with hot and arid climates, environmental impacts are likely to be wide and varied. As of the 2019 Climate Change Performance Index, Morocco was ranked second in preparedness behind Sweden.
Biodiversity
Main article: Wildlife of Morocco

Morocco has a wide range of biodiversity. It is part of the Mediterranean basin, an area with exceptional concentrations of endemic species undergoing rapid rates of habitat loss, and is therefore considered to be a hotspot for conservation priority. Avifauna are notably variant. The avifauna of Morocco includes a total of 454 species, five of which have been introduced by humans, and 156 are rarely or accidentally seen.
The Barbary lion, hunted to extinction in the wild, was a subspecies native to Morocco and is a national emblem. The last Barbary lion in the wild was shot in the Atlas Mountains in 1922. The other two primary predators of northern Africa, the Atlas bear and Barbary leopard, are now extinct and critically endangered, respectively. Relic populations of the West African crocodile persisted in the Draa river until the 20th century.
The Barbary macaque, a primate endemic to Morocco and Algeria, is also facing extinction due to offtake for trade human interruption, urbanisation, wood and real estate expansion that diminish forested area – the macaque's habitat.
Trade of animals and plants for food, pets, medicinal purposes, souvenirs and photo props is common across Morocco, despite laws making much of it illegal. This trade is unregulated and causing unknown reductions of wild populations of native Moroccan wildlife. Because of the proximity of northern Morocco to Europe, species such as cacti, tortoises, mammal skins, and high-value birds (falcons and bustards) are harvested in various parts of the country and exported in appreciable quantities, with especially large volumes of eel harvested – 60 tons exported to the Far East in the period 2009‒2011.
Morocco is home to six terrestrial ecoregions: Mediterranean conifer and mixed forests, Mediterranean High Atlas juniper steppe, Mediterranean acacia-argania dry woodlands and succulent thickets, Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe, Mediterranean woodlands and forests, and North Saharan steppe and woodlands.
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of Morocco
According to the 2022 Economist Democracy Index, Morocco is ruled under a hybrid regime, scoring #3 in the Middle East and North Africa, and #95 in the world. Morocco has a "difficult" ranking on the 2023 World Press Freedom Index.
Following the March 1998 elections, a coalition government headed by opposition socialist leader Abderrahmane Youssoufi and composed largely of ministers drawn from opposition parties, was formed. Prime Minister Youssoufi's government was the first ever government drawn primarily from opposition parties, and also represents the first opportunity for a coalition of socialists, left-of-centre, and nationalist parties to be included in the government until October 2002. It was also the first time in the modern political history of the Arab world that the opposition assumed power following an election. The current government is headed by Aziz Akhannouch.
The Constitution of Morocco provides for a monarchy with a Parliament and an independent judiciary. With the 2011 constitutional reforms, the King of Morocco retains less executive powers whereas those of the prime minister have been enlarged.
The constitution grants the king honorific powers (among other powers); he is both the secular political leader and the "Commander of the Faithful" as a direct descendant of the Prophet Mohammed. He presides over the Council of Ministers; appoints the Prime Minister from the political party that has won the most seats in the parliamentary elections, and on recommendations from the latter, appoints the members of the government.
The constitution of 1996 theoretically allowed the king to terminate the tenure of any minister, and after consultation with the heads of the higher and lower Assemblies, to dissolve the Parliament, suspend the constitution, call for new elections, or rule by decree. The only time this happened was in 1965. The King is formally the commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
Legislative branch

Since the constitutional reform of 1996, the bicameral legislature consists of two chambers. The Assembly of Representatives of Morocco (Majlis an-Nuwwâb/Assemblée des Répresentants) has 395 members elected for a five-year term, 305 elected in multi-seat constituencies and 90 in national lists consisting of women and youth.
The Assembly of Councillors (Majlis al-Mustasharin) has 120 members, elected for a six-year term. 72 members are elected at the regional level, 20 members are elected from trade unions, 8 seats from professional organisations and 20 from wage-earners.
The Parliament's powers, though still relatively limited, were expanded under the 1992 and 1996 and even further in the 2011 constitutional revisions and include budgetary matters, approving bills, questioning ministers, and establishing ad hoc commissions of inquiry to investigate the government's actions. The lower chamber of Parliament may dissolve the government through a vote of no confidence.
The latest parliamentary elections were held on 8 September 2021. Voter turnout in these elections was estimated to be 50.35% of registered voters.
Administrative divisions

Morocco is officially divided into 12 regions, which, in turn, are subdivided into 62 provinces and 13 prefectures.
Regions
- Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima
- Oriental
- Fès-Meknès
- Rabat-Salé-Kénitra
- Béni Mellal-Khénifra
- Casablanca-Settat
- Marrakesh-Safi
- Drâa-Tafilalet
- Souss-Massa
- Guelmim-Oued Noun
- Laâyoune-Sakia El Hamra
- Dakhla-Oued Ed-Dahab
Foreign relations
Main article: Foreign relations of MoroccoMorocco is a member of the United Nations and belongs to the African Union (AU), Arab League, Arab Maghreb Union (UMA), Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), the Non-Aligned Movement and the Community of Sahel–Saharan States (CEN_SAD). Morocco's relationships vary greatly between African, Arab, and Western states. Morocco has had strong ties to the West in order to gain economic and political benefits. France and Spain remain the primary trade partners, as well as the primary creditors and foreign investors in Morocco. From the total foreign investments in Morocco, the European Union invests approximately 73.5%, whereas, the Arab world invests only 19.3%. Many countries from the Persian Gulf and Maghreb regions are getting more involved in large-scale development projects in Morocco.

Morocco's membership in the African Union has been marked by significant events. In 1984, Morocco withdrew from the organisation after it admitted the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic in 1982 without conducting a referendum of self-determination in the disputed territory of Western Sahara. This decision was made unilaterally by Morocco. However, in 2017, Morocco rejoined the AU, signaling a shift in its diplomatic stance. In August 2021, Algeria severed diplomatic relations with Morocco.
In 2002, a dispute with Spain in 2002 over the small island of Perejil arose, which brought attention to the issue of the sovereignty of Melilla and Ceuta. These small enclaves on the Mediterranean coast are surrounded by Morocco and have been under Spanish administration for centuries.
In 2004, the George W. Bush administration granted Morocco the status of major non-NATO ally. Morocco was the first country in the world to recognise US sovereignty, in 1777.
After gaining independence, Morocco established strong ties with the United States, receiving significant economic and military aid. This partnership flourished during the Cold War, with Morocco becoming a key ally against communist expansion in North Africa. In return, the US supported Morocco's territorial ambitions and efforts to modernise its economy. Morocco received more than $400 million in American aid between 1957 and 1963, which elevated it to the fifth-largest recipient of US agricultural assistance by 1966. The long-lasting relationship between the two nations has endured, with the US remaining one of Morocco's top allies.
Additionally, Morocco is included in the European Union's European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP), which aims at bringing the EU and its neighbours closer.
Western Sahara status
Main article: Legal status of Western Sahara
The status of the Saguia el-Hamra and Río de Oro regions is disputed. The Western Sahara War saw the Polisario Front, the Sahrawi rebel national liberation movement, battling both Morocco and Mauritania between 1976 and a ceasefire in 1991 that is still in effect. A United Nations mission, MINURSO, is tasked with organising a referendum on whether the territory should become independent or recognised as a part of Morocco.
Part of the territory, the Free Zone, is a mostly uninhabited area that the Polisario Front controls as the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. Its administrative headquarters are located in Tindouf, Algeria. As of 2006, no UN member state had recognised Moroccan sovereignty over Western Sahara. In 2020, the United States under the Trump administration became the first Western country to back Morocco's contested sovereignty over the disputed Western Sahara region, on the agreement that Morocco would simultaneously normalise relations with Israel.
In 2006, the government of Morocco suggested autonomous status for the region, through the Moroccan Royal Advisory Council for Saharan Affairs (CORCAS). The project was presented to the United Nations Security Council in mid-April 2007. The proposal was encouraged by Moroccan allies such as the United States, France and Spain. The Security Council has called upon the parties to enter into direct and unconditional negotiations to reach a mutually accepted political solution.
Military
Main article: Royal Moroccan Armed Forces
Morocco's military consists of the Royal Armed Forces—this includes the Army (the largest branch), the Navy, the Air Force, the Royal Guard, the Royal Gendarmerie and the Auxiliary Forces. Internal security is generally effective, and acts of political violence are rare (with one exception, the 2003 Casablanca bombings which killed 45 people).
The UN maintains a small observer force in Western Sahara, where a large number of Moroccan troops are stationed. The Sahrawi Polisario Front maintains an active militia of an estimated 5,000 fighters in Western Sahara and has engaged in intermittent warfare with Moroccan forces since the 1970s.
Human rights
See also: Human rights in Morocco and LGBT rights in MoroccoDuring the early 1960s to the late 1980s, under the leadership of Hassan II, Morocco had one of the worst human rights records in both Africa and the world. Government repression of political dissent was widespread during Hassan II's leadership, until it dropped sharply in the mid-1990s. The decades during which abuses were committed are referred to as the Years of Lead (les années de plomb), and included forced disappearances, assassinations of government opponents and protesters, and secret internment camps such as Tazmamart. To examine abuses committed during the reign of King Hassan II (1961–1999), the government under King Mohammed set up an Equity and Reconciliation Commission (IER).
According to a Human Rights Watch annual report in 2016, Moroccan authorities restricted the rights to peaceful expression, association and assembly through several laws. The authorities continue to prosecute both printed and online media which criticises the government or the king (or the royal family). There are also persistent allegations of violence against both Sahrawi pro-independence and pro-Polisario demonstrators in Western Sahara; a disputed territory which is occupied by and considered by Morocco as part of its Southern Provinces. Morocco has been accused of detaining Sahrawi pro-independence activists as prisoners of conscience.
Homosexual acts as well as pre-marital sex are illegal in Morocco, and can be punishable by six months to three years of imprisonment. It is illegal to proselytise for any religion other than Islam (article 220 of the Moroccan Penal Code), and that crime is punishable by a maximum of 15 years of imprisonment. Violence against women and sexual harassment have been criminalised. The penalty can be from one month to five years, with fines ranging from $200 to $1,000.
It is a criminal offence in Morocco to undermine the monarchy; in August 2023, a Moroccan resident of Qatar was sentenced to five years' imprisonment for criticising the King's policy decisions on Facebook.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Morocco
Morocco's economy is considered a relatively liberal economy governed by the law of supply and demand. Since 1993, the country has followed a policy of privatisation of certain economic sectors which used to be in the hands of the government. Morocco has become a major player in African economic affairs, and is the sixth largest economy in Africa by GDP (PPP). Morocco was ranked as the first African country by the Economist Intelligence Unit's quality-of-life index, ahead of South Africa. However, in the years since that first-place ranking was given, Morocco has slipped into fourth place behind Egypt.
Government reforms and steady yearly growth in the region of 4–5% from 2000 to 2007, including 4.9% year-on-year growth in 2003–2007 helped the Moroccan economy to become much more robust compared to a few years earlier. For 2012 the World Bank forecast a rate of 4% growth for Morocco and 4.2% for following year, 2013.
The services sector accounts for just over half of GDP and industry, made up of mining, construction and manufacturing, is an additional quarter. The industries that recorded the highest growth are tourism, telecoms, information technology, and textile.
Tourism
Main article: Tourism in Morocco
Tourism is one of the most important sectors in Moroccan economy. It is well developed with a strong tourist industry focused on the country's coast, culture, and history. Morocco attracted more than 13 million tourists in 2019. Tourism is the second largest foreign exchange earner in Morocco after the phosphate industry. The Moroccan government is heavily investing in tourism development, in 2010 the government launched its Vision 2020 which plans to make Morocco one of the top 20 tourist destinations in the world and to double the annual number of international arrivals to 20 million by 2020, with the hope that tourism will then have risen to 20% of GDP.
Large government sponsored marketing campaigns to attract tourists advertised Morocco as an inexpensive and exotic, yet safe, place for tourists. Most of the visitors to Morocco continue to be European, with French nationals making up almost 20% of all visitors. Most Europeans visit between April and August. Morocco's relatively high number of tourists has been aided by its location—Morocco is close to Europe and attracts visitors to its beaches. Because of its proximity to Spain, tourists in southern Spain's coastal areas take one- to three-day trips to Morocco.
Since air services between Morocco and Algeria have been established, many Algerians have gone to Morocco to shop and visit family and friends. Morocco is relatively inexpensive because of the devaluation of the dirham and the increase of hotel prices in Spain. Morocco has an excellent road and rail infrastructure that links the major cities and tourist destinations with ports and cities with international airports. Low-cost airlines offer reduced-price flights to the country.

Tourism is increasingly focused on Morocco's culture, such as its ancient cities. The modern tourist industry capitalises on Morocco's ancient and Islamic sites, and on its landscape and cultural history. 60% of Morocco's tourists visit for its culture and heritage. Agadir is a major coastal resort and has a third of all Moroccan bed nights. It is a base for tours to the Atlas Mountains. Other resorts in north Morocco are also very popular.
Casablanca is the major cruise port in Morocco, and has the best developed market for tourists in Morocco, Marrakech in central Morocco is a popular tourist destination, but is more popular among tourists for one- and two-day excursions that provide a taste of Morocco's history and culture. The Majorelle botanical garden in Marrakech is a popular tourist attraction. It was bought by the fashion designer Yves Saint-Laurent and Pierre Bergé in 1980. Their presence in the city helped to boost the city's profile as a tourist destination.
As of 2006, activity and adventure tourism in the Atlas and Rif Mountains are the fastest growth area in Moroccan tourism. These locations have excellent walking and trekking opportunities from late March to mid-November. The government is investing in trekking circuits. They are also developing desert tourism in competition with Tunisia.
Agriculture
Main article: Agriculture in Morocco This section is an excerpt from Agriculture in Morocco.
Agriculture in Morocco employs about 40% of the nation's workforce. Thus, it is the largest employer in the country. In the rainy sections of the northwest, barley, wheat, and other cereals can be raised without irrigation. On the Atlantic coast, where there are extensive plains, olives, citrus fruits, and wine grapes are grown, largely with water supplied by artesian wells. Livestock are raised and forests yield cork, cabinet wood, and building materials. Part of the maritime population fishes for its livelihood. Agadir, Essaouira, El Jadida, and Larache are among the important fishing harbors. Both the agriculture and fishing industries are expected to be severely impacted by climate change.
Moroccan agricultural production also consists of oranges, tomatoes, potatoes, olives, and olive oil. High quality agricultural products are usually exported to Europe. Morocco produces enough food for domestic consumption except for grains, sugar, coffee and tea. More than 40% of Morocco's consumption of grains and flour is imported from the United States and France.
Agriculture industry in Morocco enjoyed a complete tax exemption until 2013. Many Moroccan critics said that rich farmers and large agricultural companies were taking too much benefit of not paying the taxes and that poor farmers were struggling with high costs and are getting very poor support from the state. In 2014, as part of the Finance Law, it was decided that agricultural companies with a turnover of greater than MAD 5 million would pay progressive corporate income taxes.Infrastructure

According to the Global Competitiveness Report of 2019, Morocco Ranked 32nd in the world in terms of Roads, 16th in Sea, 45th in Air and 64th in Railways. This gives Morocco the best infrastructure rankings in the African continent.
Modern infrastructure development, such as ports, airports, and rail links, is a top government priority. To meet the growing domestic demand, the Moroccan government invested more than $15 billion from 2010 to 2015 in upgrading its basic infrastructure.
Morocco has one of the best road systems on the continent. Over the past 20 years, the government has built approximately 1770 kilometers of modern roads, connecting most major cities via toll expressways. The Moroccan Ministry of Equipment, Transport, Logistics, and Water aims to build an additional 3380 kilometers of expressway and 2100 kilometers of highway by 2030, at an expected cost of $9.6 billion. It focuses on linking the southern provinces, notably the cities of Laayoune and Dakhla to the rest of Morocco.
In 2014, Morocco began the construction of the first high-speed railway system in Africa linking the cities of Tangier and Casablanca. It was inaugurated in 2018 by the King following over a decade of planning and construction by Moroccan national railway company ONCF. It is the first phase of what is planned to eventually be a 1,500 kilometeres (930 mi) high-speed rail network in Morocco. An extension of the line to Marrakesh is already being planned.
Morocco also has the largest port in Africa and the Mediterranean, Tanger-Med, which is ranked the 18th in the world with a handling capacity of over 9 million containers. It is situated in the Tangier free economic zone and serves as a logistics hub for Africa and the world.
Energy
Main article: Energy in Morocco
In 2008, about 56% of Morocco's electricity supply was provided by coal. However, as forecasts indicate that energy requirements in Morocco will rise 6% per year between 2012 and 2050, a new law passed encouraging Moroccans to look for ways to diversify the energy supply, including more renewable resources. The Moroccan government has launched a project to build a solar thermal energy power plant and is also looking into the use of natural gas as a potential source of revenue for Morocco's government.
Morocco has embarked upon the construction of large solar energy farms to lessen dependence on fossil fuels, and to eventually export electricity to Europe.
On 17 April 2022, Rabat-Moroccan agency for solar energy (Masen) and the ministry of energy transition and sustainable development announced the launch of phase one of the mega project Nor II solar energy plant which is a multi-site solar energy project with a total capacity set at 400 megawatts (MN).
Narcotics

Since the 7th century, cannabis has been cultivated in the Rif region. In 2004, according to the UN World Drugs Report, cultivation and transformation of cannabis represents 0.57% of the national GDP of Morocco in 2002. According to a French Ministry of the Interior 2006 report, 80% of the cannabis resin (hashish) consumed in Europe comes from the Rif region in Morocco, which is mostly mountainous terrain in the north of Morocco, also hosting plains that are very fertile and expanding from Melwiyya River and Ras Kebdana in the East to Tangier and Cape Spartel in the West. Also, the region extends from the Mediterranean in the south, home of the Wergha River, to the north. In addition to that, Morocco is a transit point for cocaine from South America destined for Western Europe.
Water supply and sanitation
Main article: Water supply and sanitation in MoroccoWater supply and sanitation in Morocco is provided by a wide array of utilities. They range from private companies in the largest city, Casablanca, the capital, Rabat, and two other cities, to public municipal utilities in 13 other cities, as well as a national electricity and water company (ONEE). The latter is in charge of bulk water supply to the aforementioned utilities, water distribution in about 500 small towns, as well as sewerage and wastewater treatment in 60 of these towns.
There have been substantial improvements in access to water supply, and to a lesser extent to sanitation, over the past fifteen years. Remaining challenges include a low level of wastewater treatment (only 13% of collected wastewater is being treated), lack of house connections in the poorest urban neighbourhoods, and limited sustainability of rural systems (20 percent of rural systems are estimated not to function). In 2005 a National Sanitation Programme was approved that aims at treating 60% of collected wastewater and connecting 80% of urban households to sewers by 2020. The issue of lack of water connections for some of the urban poor is being addressed as part of the National Human Development Initiative, under which residents of informal settlements have received land titles and have fees waived that are normally paid to utilities in order to connect to the water and sewer network.
Science and technology
Main article: Science and technology in Morocco
The Moroccan government has been implementing reforms to improve the quality of education and make research more responsive to socio-economic needs. In May 2009, Morocco's prime minister, Abbas El Fassi, announced greater support for science during a meeting at the National Centre for Scientific and Technical Research. The aim was to give universities greater financial autonomy from the government to make them more responsive to research needs and better able to forge links with the private sector, in the hope that this would nurture a culture of entrepreneurship in academia. He announced that investment in science and technology would rise from US$620,000 in 2008 to US$8.5 million (69 million Moroccan dirhams) in 2009, in order to finance the refurbishment and construction of laboratories, training courses for researchers in financial management, a scholarship programme for postgraduate research and incentive measures for companies prepared to finance research, such as giving them access to scientific results that they could then use to develop new products. Morocco was ranked 66th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.
The Moroccan Innovation Strategy was launched at the country's first National Innovation Summit in June 2009 by the Ministry of Industry, Commerce, Investment and the Digital Economy. The Moroccan Innovation Strategy fixed the target of producing 1,000 Moroccan patents and creating 200 innovative start-ups by 2014. In 2012, Moroccan inventors applied for 197 patents, up from 152 two years earlier. In 2011, the Ministry of Industry, Commerce and New Technologies created a Moroccan Club of Innovation, in partnership with the Moroccan Office of Industrial and Commercial Property. The idea is to create a network of players in innovation, including researchers, entrepreneurs, students and academics, to help them develop innovative projects.
The Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research is supporting research in advanced technologies and the development of innovative cities in Fez, Rabat and Marrakesh. The government is encouraging public institutions to engage with citizens in innovation. One example is the Moroccan Phosphate Office (Office chérifien des phosphates), which has invested in a project to develop a smart city, King Mohammed VI Green City, around Mohammed VI University located between Casablanca and Marrakesh, at a cost of DH 4.7 billion (circa US$479 million).
As of 2015, Morocco had three technoparks. Since the first technopark was established in Rabat in 2005, a second has been set up in Casablanca, followed, in 2015, by a third in Tangers. The technoparks host start-ups and small and medium-sized enterprises specialising in information and communication technologies (ICTs), 'green' technologies (namely, environmentally friendly technologies) and cultural industries.
In 2012, the Hassan II Academy of Science and Technology identified a number of sectors where Morocco has a comparative advantage and skilled human capital, including mining, fisheries, food chemistry and new technologies. It also identified a number of strategic sectors, such as energy, with an emphasis on renewable energies such as photovoltaic, thermal solar energy, wind and biomass; as well as the water, nutrition and health sectors, the environment and geosciences.
On 20 May 2015, less than a year after its inception, the Higher Council for Education, Training and Scientific Research presented a report to the king offering a Vision for Education in Morocco 2015–2030. The report advocated making education egalitarian and, thus, accessible to the greatest number. Since improving the quality of education goes hand in hand with promoting research and development, the report also recommended developing an integrated national innovation system which would be financed by gradually increasing the share of GDP devoted to research and development (R&D) from 0.73% of GDP in 2010 'to 1% in the short term, 1.5% by 2025 and 2% by 2030'.
Demographics
Main articles: Demographics of Morocco and MoroccansPopulation
Morocco has a population of around 37,076,584 inhabitants (2021 est.). Morocco's population was 11.6 million in 1960. According to the 2014 Morocco population census, there were around 84,000 immigrants in the country. Of these foreign-born residents, most were of French origin, followed by individuals mainly from various nations in West Africa and Algeria. There are also a number of foreign residents of Spanish origin. Some of them are descendants of colonial settlers, who primarily work for European multinational companies, while others are married to Moroccans or are retirees. Prior to independence, Morocco was home to half a million Europeans; who were mostly Christians. Also, prior to independence, Morocco was home to 250,000 Spaniards. Morocco's once prominent Jewish minority has decreased significantly since its peak of 265,000 in 1948, declining to around 3,500 in 2022.
Morocco has a large diaspora, most of which is located in France, which has reportedly over one million Moroccans of up to the third generation. There are also large Moroccan communities in Spain (about 700,000 Moroccans), the Netherlands (360,000), and Belgium (300,000). Other large communities can be found in Italy, Canada, the United States, and Israel, where Moroccan Jews are thought to constitute the second biggest Jewish ethnic subgroup.
Ethnic groups
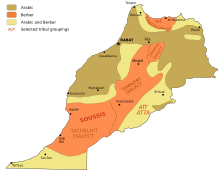
In Morocco, ethnic identity is deeply intertwined with language and culture, with the population primarily comprising two major groups: Arabs and Berbers. However, the Higher Planning Commission, the country’s state statistics bureau, does not collect data on ethnic demographics, citing the historical difficulty of distinguishing between Arabs and Berbers, even among Berber speakers.
Arabs form the largest and majority ethnic group, making up between 65% and 80% of the Moroccan population. It is estimated that the indigenous Berbers constitute between 30% and 35% of the population. Berbers, who are also known as Amazigh, are typically divided into three main groups with varying dialects who live spread out in rural mountain areas, namely the Rifians in the Rif, the Zayanes in the Middle Atlas, and the Shilha people in the Anti-Atlas. Since the 7th century, the influx of Arab migrants from the Arabian Peninsula has contributed to shaping Morocco’s demographic, cultural, and genetic landscape. Additionally, a considerable portion of the population includes Haratin, Sahrawis, and Gnawa, descendants of West African or mixed-race enslaved peoples, as well as Moriscos, European Muslims expelled from Spain and Portugal in the 17th century.
According to Encyclopædia Britannica, 44% of Moroccans are Arab, 24% are Arabized Berbers, 21% are Berbers, and 10% are Mauritanian Moors. Additionally, Minority Rights Group International estimates that around 90,000 Sahrawis reside in internationally recognized Morocco, compared to approximately 190,000 in the disputed Western Sahara.
Religion
Main article: Religion in Morocco The interior of a mosque in Fes, Islam is the predominant religion in Morocco
The interior of a mosque in Fes, Islam is the predominant religion in Morocco The Hassan II Mosque in Casablanca
The Hassan II Mosque in Casablanca The Beth-El Synagogue in Casablanca, Judaism was the main minority religion in Morocco
The Beth-El Synagogue in Casablanca, Judaism was the main minority religion in Morocco The St Andrew's Church in Tangier, an Anglican church built in 1894
The St Andrew's Church in Tangier, an Anglican church built in 1894
The religious affiliation in the country was estimated by the Pew Forum in 2010 as 99% Muslim, with all remaining groups accounting for less than 1% of the population. Of those affiliated with Islam, virtually all are Sunni Muslims, with Shia Muslims accounting for less than 0.1%. However, nearly 15% of Moroccans nonetheless describe themselves as non religious according to a 2018 survey conducted by the research network Arab Barometer; the same survey saw nearly 100 percent of respondents identify as Muslims. Another 2021 Arab Barometer survey found that 67.8% of Moroccans identified as religious, 29.1% as somewhat religious, and 3.1% as non religious. The 2015 Gallup International poll reported that 93% of Moroccans considered themselves to be religious.
Prior to Morocco's independence in 1956, the country was home to a significant Christian community, numbering over 500,000 Christians, predominantly of Spanish and French ancestry. These Catholic settlers had a historic legacy and a powerful presence. However, following Morocco's independence, many of these Christian settlers left to Spain or France. The predominantly Catholic and Protestant foreign-resident Christian community consists of approximately 40,000 practising members. Most foreign resident Christians reside in the Casablanca, Tangier, Marrakesh and Rabat urban areas. Various local Christian leaders estimate that between 2005 and 2010 there are 5,000 citizen converted Christians (mostly ethnically Berber) who regularly attend "house" churches and live predominantly in the south. Some local Christian leaders estimate that there may be as many as 8,000 Christian citizens throughout the country, but many reportedly do not meet regularly due to fear of government surveillance and social persecution. Meanwhile, the Moroccan Association of Human Rights estimates there are 25,000 Christian citizens. The number of the Moroccans who converted to Christianity (most of them secret worshippers) are estimated between 8,000 and 50,000.
Before the founding of the State of Israel in 1948, there were about 265,000 Jews in the country, which gave Morocco the largest Jewish community in the Muslim world. The most recent estimates put the size of the historic Casablanca Jewish community at about 2,500, and the Rabat and Marrakesh Jewish communities at about 100 members each. The remainder of the Jewish population is dispersed throughout the country. This population is mostly elderly, with a decreasing number of young people. The Baháʼí Faith community, located in urban areas, numbers 350 to 400 persons.
Languages
Main article: Languages of Morocco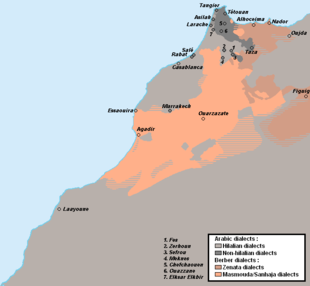
Morocco's official languages are Arabic and Berber. The country's distinctive group of Moroccan Arabic dialects is referred to as Darija. Approximately 92.7% of the whole population can speak Arabic. Berber languages are spoken by 24.8% of the population in three dialects (Tarifit spoken by 3.2%, Tashelhit spoken by 14.2%, and Central Atlas Tamazight spoken by 7.4%). According to the 2024 census, 99.2%, or almost the entire literate population of Morocco, could read and write in Arabic, whereas 1.5% of the population could read and write in Berber. The census also revealed that 80.6% of Moroccans consider Arabic to be their native language, while 18.9% regard any of the various Berber languages as their mother tongue.
French is widely used in governmental institutions, media, mid-size and large companies, international commerce with French-speaking countries, and often in international diplomacy. French is taught as an obligatory language in all schools. In 2010, there were 10,366,000 French-speakers in Morocco, or about 32% of the population.
According to the 2004 census, 2.19 million Moroccans spoke a foreign language other than French. English, while far behind French in terms of number of speakers, is the first foreign language of choice, since French is obligatory, among educated youth and professionals.
According to Ethnologue, as of 2016, there are 1,536,590 individuals (or approximately 4.5% of the population) in Morocco who speak Spanish. Spanish is mostly spoken in northern Morocco and the former Spanish Sahara because Spain had previously occupied those areas. Meanwhile, a 2018 study by the Instituto Cervantes found 1.7 million Moroccans who were at least proficient in Spanish, placing Morocco as the country with the most Spanish speakers outside the Hispanophone world (unless the United States is also excluded from Spanish-speaking countries). A significant portion of northern Morocco receives Spanish media, television signal and radio airwaves, which reportedly facilitate competence in the language in the region.
After Morocco declared independence in 1956, French and Arabic became the main languages of administration and education, causing the role of Spanish to decline.
Education
Main article: Education in Morocco| Literate population of Morocco (2024) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| percent | ||||
| Can read and write in Arabic | 99.2% | |||
| Can read and write in French | 57.7% | |||
| Can read and write in English | 20.5% | |||
| Can read and write in Berber languages | 1.5% | |||
Education in Morocco is free and compulsory through primary school. The estimated literacy rate for the country in 2012 was 72%. In September 2006, UNESCO awarded Morocco amongst other countries such as Cuba, Pakistan, India and Turkey the "UNESCO 2006 Literacy Prize".
Morocco has more than four dozen universities, institutes of higher learning, and polytechnics dispersed at urban centres throughout the country. Its leading institutions include Mohammed V University in Rabat, the country's largest university, with branches in Casablanca and Fès; the Hassan II Agriculture and Veterinary Institute in Rabat, which conducts leading social science research in addition to its agricultural specialties; and Al-Akhawayn University in Ifrane, the first English-language university in Northwest Africa, inaugurated in 1995 with contributions from Saudi Arabia and the United States.

The al-Qarawiyin University, founded by Fatima al-Fihri in the city of Fez in 859 as a madrasa, is considered by some sources, including UNESCO, to be the "oldest university of the world". Morocco has also some of prestigious postgraduate schools, including: Mohammed VI Polytechnic University, l'Institut national des postes et télécommunications [fr; ar], École Nationale Supérieure d'Électricité et de Mecanique (ENSEM), EMI, ISCAE, INSEA, National School of Mineral Industry, École Hassania des Travaux Publics, Les Écoles nationales de commerce et de gestion, École supérieure de technologie de Casablanca.
Health
Main article: Health in Morocco
Many efforts are made by countries around the world to address health issues and eradicate disease, Morocco included. Child health, maternal health, and diseases are all components of health and well-being. Morocco is a developing country that has made many strides to improve these categories. However, Morocco still has many health issues to improve on. According to research published, in 2005 only 16% of citizens in Morocco had health insurance or coverage. In data from the World Bank, Morocco experiences high infant mortality rates at 20 deaths per 1,000 births (2017) and high maternal mortality rates at 121 deaths per 100,000 births (2015).
The government of Morocco sets up surveillance systems within the already existing healthcare system to monitor and collect data. Mass education in hygiene is implemented in primary education schools which are free for residents of Morocco. In 2005, The government of Morocco approved two reforms to expand health insurance coverage. The first reform was a mandatory health insurance plan for public and private sector employees to expand coverage from 16 percent of the population to 30 percent. The second reform created a fund to cover services for the poor. Both reforms improved access to high-quality care. Infant mortality has improved significantly since 1960 when there were 144 deaths per 1,000 live births, in 2000, 42 per 1,000 live births, and now it is 20 per 1,000 live births. The country's under-five mortality rate dropped by 60% between 1990 and 2011.
According to data from the World Bank, the present mortality rate is still very high, over seven times higher than in neighbouring country Spain. In 2014, Morocco adopted a national plan to increase progress on maternal and child health. The Moroccan Plan was started by the Moroccan Minister of Health, El Houssaine Louardi, and Ala Alwan, WHO Regional Director for the Eastern Mediterranean Region, on 13 November 2013 in Rabat. Morocco has made significant progress in reducing deaths among both children and mothers. Based on World Bank data, the nation's maternal mortality ratio fell by 67% between 1990 and 2010. In 2014, spending on healthcare accounted for 5.9% of the country's GDP. Since 2014, spending on healthcare as part of the GDP has decreased. However, health expenditure per capita (PPP) has steadily increased since 2000. In 2015, the Moroccan health expenditure was $435.29 per capita. In 2016 the life expectancy at birth was 74.3, or 73.3 for men and 75.4 for women, and there were 6.3 physicians and 8.9 nurses and midwives per 10,000 inhabitants.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Morocco
Morocco is a country with a rich culture and civilisation. Through Moroccan history, it has hosted many people. All of whom have affected the social structure of Morocco.
Since independence, a veritable blossoming has taken place in painting and sculpture, popular music, amateur theatre, and filmmaking. The Moroccan National Theatre (founded 1956) offers regular productions of Moroccan and French dramatic works. Art and music festivals take place throughout the country during the summer months, among them the World Sacred Music Festival at Fès.
Each region possesses its own specificities, thus contributing to the national culture and to the legacy of civilisation. Morocco has set among its top priorities the protection of its diverse legacy and the preservation of its cultural heritage.
Culturally speaking, Morocco has always been successful in combining its Arabic, Berber and Jewish cultural heritage with external influences such as the French and the Spanish and, during the last decades, the Anglo-American lifestyles.
Architecture
Main article: Moroccan architecture This section is an excerpt from Moroccan architecture. The Hassan II Mosque in Casablanca
The Hassan II Mosque in Casablanca The ksar of Ait Benhaddou in the southern High Atlas mountains
The ksar of Ait Benhaddou in the southern High Atlas mountains Colonial architecture in Casablanca (20th century)
Colonial architecture in Casablanca (20th century)
Moroccan architecture reflects Morocco's diverse geography and long history, marked by successive waves of settlers through both migration and military conquest. This architectural heritage includes ancient Roman sites, historic Islamic architecture, local vernacular architecture, 20th-century French colonial architecture, and modern architecture.
Much of Morocco's traditional architecture is marked by the style that developed during the Islamic period, from the 7th century onward. This architecture was part of a wider tradition of "Moorish" or western Islamic architecture, which characterized both the Maghreb (Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia) and al-Andalus (Muslim Spain and Portugal). It blended influences from Amazigh (Berber) culture in North Africa, pre-Islamic Spain (Roman, Byzantine, and Visigothic), and contemporary artistic currents in the Islamic Middle East to elaborate a unique style over centuries with recognizable features such as the horseshoe arch, riad gardens, and elaborate geometric and arabesque motifs in wood, carved stucco, and zellij tilework.
Although Moroccan Amazigh architecture is not strictly separate from the rest of Moroccan architecture, many structures and architectural styles are distinctively associated with traditionally Amazigh or Amazigh-dominated regions such as the Atlas Mountains and the Sahara and pre-Sahara regions. These mostly rural regions are marked by numerous kasbahs (fortresses) and ksour (fortified villages) shaped by local geography and social structures, of which one of the most famous is Ait Benhaddou. They are typically made of rammed earth and decorated with local geometric motifs. Far from being isolated from other historical artistic currents around them, the Amazigh peoples of Morocco (and across North Africa) adapted the forms and ideas of Islamic architecture to their own conditions and in turn contributed to the formation of Western Islamic art, particularly during their political domination of the region over the centuries of Almoravid, Almohad, and Marinid rule.
Modern architecture in Morocco includes many examples of early 20th-century Art Deco and local neo-Moorish architecture constructed during the French and Spanish colonial occupation of the country between 1912 and 1956 (or until 1958 for Spain). In the later 20th century, after Morocco regained its independence, some new buildings continued to pay tribute to traditional Moroccan architecture and motifs (even when designed by foreign architects), as exemplified by the Mausoleum of King Mohammed V (completed in 1971) and the massive Hassan II Mosque in Casablanca (completed in 1993). Modernist architecture is also evident in contemporary constructions, not only for regular everyday structures but also in major prestige projects.Literature
Main article: Moroccan literature
Moroccan literature is written mostly in Arabic, Berber, Hebrew, and French. Particularly under the Almoravid and Almohad empires, Moroccan literature was closely related to the literature of al-Andalus, and shared important poetic and literary forms such as zajal, the muwashshah, and the maqama. Islamic literature, such as Quranic exegeses and other religious works such as Qadi Ayyad's Al-Shifa were influential. The University of al-Qarawiyyin in Fes was an important literary centre attracting scholars from abroad, including Maimonides, Ibn al-Khatib, and Ibn Khaldun.
Under the Almohad dynasty Morocco experienced a period of prosperity and brilliance of learning. The Almohad built the Kutubiyya Mosque in Marrakesh, which accommodated no fewer than 25,000 people, but was also famed for its books, manuscripts, libraries and book shops, which gave it its name; the first book bazaar in history. The Almohad Caliph Abu Yakub had a great love for collecting books. He founded a great library, which was eventually carried to the Casbah and turned into a public library.
Modern Moroccan literature began in the 1930s. Two main factors gave Morocco a pulse toward witnessing the birth of a modern literature. Morocco, as a French and Spanish protectorate left Moroccan intellectuals the opportunity to exchange and to produce literary works freely enjoying the contact of other Arabic literature and Europe. Three generations of writers especially shaped 20th century Moroccan literature. The first was the generation that lived and wrote during the Protectorate (1912–56), its most important representative being Mohammed Ben Brahim (1897–1955).
The second generation was the one that played an important role in the transition to independence with writers like Abdelkrim Ghallab (1919–2006), Allal al-Fassi (1910–1974) and Mohammed al-Mokhtar Soussi (1900–1963). The third generation is that of writers of the sixties. Moroccan literature then flourished with writers such as Mohamed Choukri, Driss Chraïbi, Mohamed Zafzaf and Driss El Khouri. Those writers were an important influence to the many Moroccan novelists, poets and playwrights that were still to come.
During the 1950s and 1960s, Morocco was a refuge and artistic centre and attracted writers as Paul Bowles, Tennessee Williams and William S. Burroughs. Moroccan literature flourished with novelists such as Mohamed Zafzaf and Mohamed Choukri, who wrote in Arabic, and Driss Chraïbi and Tahar Ben Jelloun who wrote in French. Other important Moroccan authors include: Abdellatif Laabi, Abdelkrim Ghallab, Fouad Laroui, Mohammed Berrada and Leila Abouzeid. Orature (oral literature) is an integral part of Moroccan culture, be it in Moroccan Arabic or Berber.
Music
Main article: Music of MoroccoMoroccan music is of Arabic, Berber and sub-Saharan origins. Rock-influenced chaabi bands are widespread, as is trance music with historical origins in Islamic music.
Morocco is home to Andalusian classical music that is found throughout Northwest Africa. It probably evolved under the Moors in Cordoba, and the Persian-born musician Ziryab is usually credited with its invention. A genre known as Contemporary Andalusian Music and art is the brainchild of Morisco visual artist/composer/oudist Tarik Banzi, founder of the Al-Andalus Ensemble.

Aita is a Bedouin musical style sung in the countryside.
Chaabi ("popular") is a music consisting of numerous varieties which are descended from the multifarious forms of Moroccan folk music. Chaabi was originally performed in markets, but is now found at any celebration or meeting.
Popular Western forms of music are becoming increasingly popular in Morocco, such as fusion, rock, country, metal and, in particular, hip hop.
Morocco participated in the 1980 Eurovision Song Contest, where it finished in the penultimate position.
Media
Main articles: Media of Morocco and Cinema of MoroccoCinema in Morocco has a long history, stretching back over a century to the filming of Le chevrier Marocain ("The Moroccan Goatherd") by Louis Lumière in 1897. Between that time and 1944, many foreign movies were shot in the country, especially in the Ouarzazate area. In 1944, the Moroccan Cinematographic Centre [fr] (CCM), the nation's film regulatory agency, was established. Studios were also opened in Rabat.
In 1952, Orson Welles' Othello won the Palme d'Or at the Cannes Film Festival under the Moroccan flag. However, the Festival's musicians did not play the Moroccan national anthem, as no one in attendance knew what it was. Six years later, Mohammed Ousfour would create the first Moroccan movie, Le fils maudit ("The Damned Son").
In 1968, the first Mediterranean Film Festival was held in Tangier. In its current incarnation, the event is held in Tetouan. This was followed in 1982 with the first national festival of cinema, which was held in Rabat. In 2001, the first International Film Festival of Marrakech (FIFM) was also held in Marrakech.
Cuisine
Main article: Moroccan cuisine
Moroccan cuisine is considered one of the most diversified cuisines in the world. This is a result of the centuries-long interaction of Morocco with the outside world. The cuisine of Morocco is mainly a fusion of Moorish, European and Mediterranean cuisines.
Spices are used extensively in Moroccan cuisine. While spices have been imported to Morocco for thousands of years, many ingredients such as saffron from Tiliouine, mint and olives from Meknes, and oranges and lemons from Fez, are home-grown. Chicken is the most widely eaten meat in Morocco. The most commonly eaten red meat in Morocco is beef; lamb is preferred but is relatively expensive. The main Moroccan dish most people are familiar with is couscous, the old national delicacy.
Beef is the most commonly eaten red meat in Morocco, usually eaten in a Tagine with vegetables or legumes. Chicken is also very commonly used in Tagines, knowing that one of the most famous tagine is the Tagine of Chicken, potatoes and olives. Lamb is also consumed, but as Northwest African sheep breeds store most of their fat in their tails, Moroccan lamb does not have the pungent flavour that Western lamb and mutton have. Poultry is also very common, and the use of seafood is increasing in Moroccan food. In addition, there are dried salted meats and salted preserved meats such as kliia/khlia and "g'did" which are used to flavor tagines or used in "el ghraif" a folded savory Moroccan pancake.
Among the most famous Moroccan dishes are Couscous, Pastilla (also spelled Bsteeya or Bestilla), Tajine, Tanjia and Harira. Although the latter is a soup, it is considered a dish in itself and is served as such or with dates especially during the month of Ramadan. Pork consumption is forbidden in accordance with Sharia, religious laws of Islam.
A big part of the daily meal is bread. Bread in Morocco is principally from durum wheat semolina known as khobz. Bakeries are very common throughout Morocco and fresh bread is a staple in every city, town and village. The most common is whole grain coarse ground or white flour bread. There are also a number of flat breads and pulled unleavened pan-fried breads.
The most popular drink is "atai", green tea with mint leaves and other ingredients. Tea occupies a very important place in the culture of Morocco and is considered an art form. It is served not only at mealtimes but all through the day, and it is especially a drink of hospitality, commonly served whenever there are guests. It is served to guests, and it is impolite to refuse it.
Sport
Main article: Sport in Morocco
Football is the country's most popular sport, popular among the urban youth in particular. In 1986, Morocco became the first Arab and African country to qualify for the second round of the FIFA World Cup. Morocco hosted the Africa Cup of Nations in 1988 and will host it again in 2025 after original host Guinea was stripped from hosting rights due to inadequacy of hosting preparations. Morocco was originally scheduled to host the 2015 Africa Cup of Nations, but refused to host the tournament on the scheduled dates because of fears over the Ebola outbreak on the continent. Morocco made six attempts to host the FIFA World Cup but lost five times to the United States, France, Germany, South Africa and a Canada–Mexico–United States joint bid, however Morocco will co-host it in 2030 along with Portugal and Spain having finally won the bid in their sixth attempt. In 2022, Morocco became the first African and Arab team to reach the semifinals and finished 4th in the tournament.
At the 1984 Olympic Games, two Moroccans won gold medals in track and field. Nawal El Moutawakel won in the 400 metres hurdles; she was the first woman from an Arab or Islamic country to win an Olympic gold medal. Saïd Aouita won the 5000 metres at the same games. Hicham El Guerrouj won gold medals for Morocco at the 2004 Summer Olympics in the 1500 metres and 5000 metres and holds several world records in the mile run.
Spectator sports in Morocco traditionally centred on the art of horsemanship until European sports—football, polo, swimming, and tennis—were introduced at the end of the 19th century. Tennis and golf have become popular. Several Moroccan professional players have competed in international competition, and the country fielded its first Davis Cup team in 1999. Morocco was one of the continent's pioneers in basketball as it established one of Africa's first competitive leagues. Rugby came to Morocco in the early 20th century, mainly by the French who occupied the country. As a result, Moroccan rugby was tied to the fortunes of France, during the first and second World War, with many Moroccan players going away to fight. Like many other Maghreb nations, Moroccan rugby tended to look to Europe for inspiration, rather than to the rest of Africa.
Kickboxing is also popular in Morocco. The Moroccan-Dutch Badr Hari, heavyweight kickboxer and martial artist, is a former K-1 heavyweight champion and K-1 World Grand Prix 2008 and 2009 finalist.
See also
Notes
- See Political status of Western Sahara
- The French language in Morocco is also used in official government documents and by the business community, although it has no official status: "French (often the language of business, government, and diplomacy)..."
- The area 446,300 km (172,300 sq mi) excludes all disputed territories, while 716,550 km (276,660 sq mi) includes the Moroccan-claimed and partially-controlled parts of Western Sahara (claimed as the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic by the Polisario Front). Morocco also claims Ceuta and Melilla, making up about 22.8 km (8.8 sq mi) more claimed territory.
- /məˈrɒkoʊ/
-
- Arabic: المملكة المغربية, romanized: al-Mamlakah al-Maghribiyah, lit. 'the Western kingdom'
- Standard Moroccan Tamazight: ⵜⴰⴳⵍⴷⵉⵜ ⵏ ⵍⵎⵖⵔⵉⴱ, romanized: Tageldit n Lmeɣrib
- French: Royaume du Maroc
- Pending resolution of the Western Sahara conflict
References
Citations
- "Constitution of Morocco". Constitute. Archived from the original on 6 October 2022. Retrieved 11 March 2024.
- ^ Gauthier, Christophe. "كلمة افتتاحية للسيد المندوب السامي للتخطيط بمناسبة الندوة الصحفية الخاصة بتقديم معطيات الإحصاء العام للسكان والسكنى 2024". Site institutionnel du Haut-Commissariat au Plan du Royaume du Maroc (in French). Retrieved 23 December 2024.
- ^ "Morocco". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 12 January 2022. Archived from the original on 2 December 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2021.
- ^ "Présentation du Maroc" (in French). Ministère de l'Europe et des Affaires étrangères. Archived from the original on 7 February 2023. Retrieved 20 December 2020.
- Hyde, Martin (October 1994). "The teaching of English in Morocco: the place of culture". ELT Journal. 48 (4): 295–305. doi:10.1093/elt/48.4.295. ISSN 0951-0893.
- "Regional Profiles: Morocco". The Association of Religion Data Archives. World Religion Database. Archived from the original on 5 September 2022. Retrieved 5 September 2022.
- ^ Constitution of the Kingdom of Morocco. Translated by Ruchti, Jefri J. Getzville: William S. Hein & Co. 2012. Archived from the original on 6 October 2022. Retrieved 6 October 2022. First published in the Official Bulletin on 30 July 2011.
- Trinidad, Jamie (2012). "An Evaluation of Morocco's Claims to Spain's Remaining Territories in Africa". The International and Comparative Law Quarterly. 61 (4): 961–975. doi:10.1017/S0020589312000371. ISSN 0020-5893. JSTOR 23279813. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 8 March 2024.
- Gauthier, Christophe (2022). "Horloge de la population". Site Institutionnel du Haut-Commissariat Au Plan du Royaume du Maroc (in French). HCP. Archived from the original on 20 May 2023. Retrieved 18 December 2022.
- "Recensement général de la population et de l'habitat (RGPH 2024)". www.hcp.ma (in French). Haut Commissariat au Plan (Morocco) (HCP). 22 November 2024. Retrieved 11 December 2024.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Morocco)". International Monetary Fund. 22 October 2024. Retrieved 11 December 2024.
- Africa's Development Dynamics 2018: Growth, Jobs and Inequalities. AUC/OECD. 2018. p. 179. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2020.
- "Human Development Report 2023/2024" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- "Décret royal n° 455-67 du 23 safar 1387 (2 juin 1967) portant loi relatif à l'heure légale". Bulletin Officiel du Royaume du Maroc (in French) (2854). Archived from the original on 13 January 2023. Retrieved 13 January 2023 – via Banque de Données Juridiques.
- "Changements d'heure pour ramadan, quels impacts ?". TelQuel (in French). Archived from the original on 13 January 2023. Retrieved 13 January 2023.
- ⴰⴷⵓⵙⵜⵓⵔ ⵏ ⵜⴳⵍⴷⵉⵜ ⵏ ⵍⵎⵖⵔⵉⴱ [Constitution of the Kingdom of Morocco] (PDF). Translated by Ladimat, Mohammed. Royal Institute of Amazigh Culture. 2021. ISBN 978-9920-739-39-9.
- "Ceuta, Melilla profile". BBC News. 2018. Archived from the original on 19 May 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2018.
- ^ Abun-Nasr, Jamil M. (20 August 1987). A History of the Maghrib in the Islamic Period. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33767-0. Archived from the original on 9 May 2024. Retrieved 20 March 2018.
- Hall, John G. (2002). North Africa. Chelsea House. ISBN 978-0-7910-5746-9.
- Balfour, Rosa (March 2009). "The Transformation of the Union for the Mediterranean". Mediterranean Politics. 14 (1): 99–105. doi:10.1080/13629390902747491. ISSN 1362-9395.
- "Morocco: Remove Obstacles to Access to the Constitutional Court". Archived 21 July 2021 at the Wayback Machine. International Commission of Jurists.
- "Country names". The CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 7 December 2023. Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- Ghouirgate, Mehdi (27 February 2020), "Chapitre VIII. Le calife en son palais : maintenir son rang", L’Ordre almohade (1120-1269) : Une nouvelle lecture anthropologique, Tempus (in French), Toulouse: Presses universitaires du Midi, pp. 357–402, ISBN 978-2-8107-0867-3, archived from the original on 2 October 2023, retrieved 9 December 2023
- "morocco | Etymology of morocco by etymonline". www.etymonline.com. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 29 April 2024.
- Hareir, Idris El; Mbaye, Ravane (1 January 2011). The Spread of Islam Throughout the World. UNESCO. ISBN 978-92-3-104153-2.
- "Maghreb, en arabe Maghrib ou Marhrib (" le Couchant ")". Encyclopédie Larousse (in French). Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- Abun-Nasr, Jamil M., ed. (1987), "Introduction", A History of the Maghrib in the Islamic Period, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–25, doi:10.1017/cbo9780511608100.003, ISBN 978-0-521-33767-0, archived from the original on 16 June 2018, retrieved 9 December 2023
- "Maghreb". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 13 September 2023. Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- Dumper, Michael R. T.; Stanley, Bruce E., eds. (2007). Cities of the Middle East and North Africa: A Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 151. ISBN 978-1-57607-919-5. Archived from the original on 16 March 2023. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- Bressolette, Henri (2016). "Fondation de Fès El Bali par Idriss Ier et Idriss II". A la découverte de Fès. L'Harmattan. ISBN 978-2-343-09022-1. Archived from the original on 20 July 2023. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- Gershovich, Moshe (12 October 2012). French Military Rule in Morocco. doi:10.4324/9780203044988. ISBN 9780203044988.
- "مراکش - معنی در دیکشنری آبادیس" [Morocco]. abadis.ir (in Persian). Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- ملين, نبيل (2017). فكرة الدستور في المغرب : وثائق ونصوص (19012011) (in Arabic). Tīl Kīl Mīdiyā. ISBN 978-9954-28-764-4. OCLC 994641823.
- Laskier, Michael M. (1 September 2019). "Prelude to Colonialism: Moroccan Muslims and Jews through Western Lenses, 1860–1912". European Judaism. 52 (2): 111–128. doi:10.3167/ej.2019.520209. ISSN 0014-3006. S2CID 203553804. Archived from the original on 5 November 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2022.
- Field Projects – Jebel Irhoud Archived 12 January 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Department of Human Evolution. Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
- Oldest Homo sapiens fossil claim rewrites our species' history Archived 16 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine News. Nature Magazine, International Weekly Journal of Science
- Rubella, D. (1984). "Environmentalism and Pi Paleolithic economies in the Maghreb (c. 20,000 to 5000 B.P.)". In J.D. Clark & S.A. Brandt (ed.). From hunters to farmers the causes and consequences of food production in Africa. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 41–56. ISBN 978-0520045743.
- van de Loosdrecht, Marieke; Bouzouggar, Abdeljalil; Humphrey, Louise; Posth, Cosimo; Barton, Nick; Aximu-Petri, Ayinuer; Nickel, Birgit; Nagel, Sarah; Talbi, El Hassan; El Hajraoui, Mohammed Abdeljalil; Amzazi, Saaïd; Hublin, Jean-Jacques; Pääbo, Svante; Schiffels, Stephan; Meyer, Matthias (4 May 2018). "Pleistocene North African genomes link Near Eastern and sub-Saharan African human populations". Science. 360 (6388): 548–552. Bibcode:2018Sci...360..548V. doi:10.1126/science.aar8380. ISSN 0036-8075.
- Simões, Luciana G.; Günther, Torsten; Martínez-Sánchez, Rafael M.; Vera-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos; Iriarte, Eneko; Rodríguez-Varela, Ricardo; Bokbot, Youssef; Valdiosera, Cristina; Jakobsson, Mattias (15 June 2023). "Northwest African Neolithic initiated by migrants from Iberia and Levant". Nature. 618 (7965): 550–556. Bibcode:2023Natur.618..550S. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06166-6. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 10266975. PMID 37286608.
- Mário Curtis Giordani, História da África. Anterior aos descobrimentos. Editora Vozes, Petrópolis (Brasil) 1985, pp. 42f., 77f. Giordani references Bousquet, Les Berbères (Paris 1961).
- The Megalithic Portal and Megalith Map. "C. Michael Hogan, Mogador: Promontory Fort, The Megalithic Portal, ed. Andy Burnham". Megalithic.co.uk. Archived from the original on 5 August 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- Moscati, Sabatino (2001) The Phoenicians, Tauris, ISBN 1-85043-533-2
- Livy Ab Urbe Condita Libri 29.30
- Asiwaju, A.I. (January 1985). Partitioned Africans: Ethnic Relations Across Africa's International Boundaries. C. Hurst & Co. p. 237. ISBN 0-905838-91-2.
- Abun-Nasr 1987, p.33
- Abun-Nasr 1987, pp. 33–34
- Ramirez-Faria, Carlos (2007). Concise Encyclopaedia of World History. Atlantic Publishers & Dist. ISBN 978-81-269-0775-5. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- "Almoravides". Universalis Encyclopedia. 19 January 1999. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 25 July 2011.
- "Marīnid dynasty". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 2 June 2015. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- "The Maghrib under the Almoravids and the Almohads". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 14 March 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- ^ "Morocco – History". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 31 July 2011. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- Kaba, Lansiné (1981), "Archers, musketeers, and mosquitoes: The Moroccan invasion of the Sudan and the Songhay resistance (1591–1612)", Journal of African History, 22 (4): 457–475, doi:10.1017/S0021853700019861, JSTOR 181298, PMID 11632225, S2CID 41500711.
- Rivet, Daniel (2012). Histoire du Maroc: de Moulay Idrîs à Mohammed VI. Fayard.
- "Morocco (Page 8 of 9)". Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2009. 1 November 2009.
- "Joint Statement by the United States of America and the Kingdom of Morocco". whitehouse.gov. 22 November 2013. Archived from the original on 10 November 2016. Retrieved 1 March 2021 – via National Archives.
- USA (NA) International Business Publications (2004). Morocco Foreign Policy And Government Guide. Int'l Business Publications. pp. 114–. ISBN 978-0-7397-6000-0.
- Kozaryn, Linda D. "Cohen Renews U.S.-Morocco Ties". U.S. Department of Defense. Archived from the original on 28 February 2010. Retrieved 12 March 2009.
- Roberts, Priscilla H. and Richard S. Roberts, Thomas Barclay (1728–1793): Consul in France, Diplomat in Barbary, Lehigh University Press, 2008, pp. 206–223 ISBN 093422398X.
- "Milestones of American Diplomacy, Interesting Historical Notes, and Department of State History". U.S. Department of State. Archived from the original on 10 December 2019. Retrieved 17 December 2007.
- Miller, Susan Gilson. (2013). A history of modern Morocco. New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-1-139-62469-5. OCLC 855022840.
- Pennell, C. R. (2000). Morocco since 1830: A History. New York: New York University Press. p. 40. ISBN 978-0814766774.
- "Tangier(s)". Jewish Virtual Library. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- Hirschberg, H. Z (1981). A history of the Jews in North Africa: From the Ottoman conquests to the present time / edited by Eliezer Bashan and Robert Attal. BRILL. p. 318. ISBN 978-90-04-06295-5. Archived from the original on 14 January 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Furlong, Charles Wellington (1911). "The French Conquest Of Morocco: The Real Meaning Of The International Trouble". The World's Work: A History of Our Time. XXII: 14988–14999. Archived from the original on 14 January 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Abdennebi, Zakia (14 January 2009). "Morocco tackles painful role in Spain's past". Reuters. Archived from the original on 17 August 2021.
- "Morocco: Date of the abolishment of slavery in Morocco; whether descendants of ex-slaves are singled out in any way; and fate of the Palace household and grounds staff when King Mohamed V was in exile". MAR32476.E. Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada. 13 August 1999. Archived from the original on 3 February 2014 – via Refworld.
- Wyrtzen, Jonathan (2022). Worldmaking in the Long Great War: How Local and Colonial Struggles Shaped the Modern Middle East. New York: Columbia University Press. p. 195. ISBN 978-0-231-54657-7. OCLC 1336403490. Archived from the original on 16 February 2024. Retrieved 24 January 2024.
- Porch, Douglas; Spain's African Nightmare; MHQ: Quarterly Journal of Military History; (2006); 18#2; pp. 28–37.
- Wyrtzen, Jonathan (2022). Worldmaking in the Long Great War: How Local and Colonial Struggles Shaped the Modern Middle East. New York: Columbia University Press. p. 198. ISBN 978-0-231-54657-7. OCLC 1336403490. Archived from the original on 16 February 2024. Retrieved 24 January 2024.
- ^ Stenner, David (2019). Globalizing Morocco: Transnational Activism and the Postcolonial State. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. p. 198. ISBN 978-1-5036-0900-6. OCLC 1082294927. Archived from the original on 16 February 2024. Retrieved 24 January 2024.
- Babas, Latifa (19 July 2019). "Mohammed Ben Arafa, Morocco's unpopular sultan and the story of his unmarked grave". Yabiladi. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- "Quatre-vingt-seize Marocains poursuivis pour participation à la « tuerie d'Oujda », qui fit trente morts le 16 août 1953, passent en jugement". Le Monde (in French). 30 November 1954. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- "Morocco (Page 9 of 9)". Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2009.
- Farsoun, Karen; Paul, Jim (1976). "War in the Sahara: 1963". MERIP Reports (45): 13–16. doi:10.2307/3011767. ISSN 0047-7265. JSTOR 3011767. Archived from the original on 4 February 2022. Retrieved 13 August 2023.
- "Spanish Return Ifni to Morocco". The New York Times. 5 January 1969. Archived from the original on 13 August 2023. Retrieved 13 August 2023.
- "Morocco profile – Timeline". BBC News. 19 September 2012. Archived from the original on 23 December 2012. Retrieved 9 January 2013.
- "Western Sahara Short Mission Brief" (PDF). sites.tufts.edu/. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 October 2023. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- "Yahoo! Groups". groups.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on 18 April 2001.
- Walter, Christian; Ungern-Sternberg, Antje von; Abushov, Kavus, eds. (2014). Self-Determination and Secession in International Law. OUP Oxford. p. 258. ISBN 9780191006913.
- "Morocco: Royal Succession and Other Developments". everycrsreport.com. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- "Morocco's king pardons satirist". BBC News. 7 January 2004. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 22 February 2011.
- "Morocco will not relinquish territory, King says". Retrieved 7 March 2002.
- "Chronology-Western Sahara -- a 50 year dispute". Reuters. 11 April 2007. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- "Africa's oldest territorial dispute rumbles on". Reuters. 16 April 2007. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- "Factbox-Some facts about Western Sahara dispute". reliefweb.int. 7 November 2010. Archived from the original on 15 September 2013. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- "Deadly clashes as Morocco breaks up Western Sahara camp". BBC News. 8 November 2010. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- "Spain withdraws after island deal - July 20, 2002". edition.cnn.com. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- "Spain deports illegal enclave migrants". Al Jazeera. 7 October 2005. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023.
- "Spain PM visits troubled enclaves". 31 January 2006. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- "Morocco king condemns royal visit". 7 November 2007. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- "Why has Morocco's king survived the Arab Spring?". BBC News. 24 November 2011. Archived from the original on 6 March 2014. Retrieved 13 August 2023.
- "Maroc: Mohammed VI nomme Abdelilah Benkirane chef du gouvernement". Jeune Afrique (in French). 29 November 2011. Archived from the original on 21 January 2016. Retrieved 13 August 2023.
- "Mass anti-government protest in Morocco". Al Jazeera. 28 May 2012. Archived from the original on 3 October 2023.
- bin Taher, Ahmed; Barakat, Mahmoud (20 December 2020). "Morocco, Israel: 6 decades of secret ties, cooperation". Anadolu Ajansı. Archived from the original on 16 February 2024.
- "Joint Declaration" (PDF). state.gov. 22 December 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 February 2024.
- Ahmed, Hamid Ould (25 August 2021). "Algeria cuts diplomatic relations with Morocco". Reuters. Archived from the original on 7 September 2023. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- "Timeline: The Deadly September 8 Earthquake in Morocco". moroccoworldnews.com. Archived from the original on 12 September 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ^ French, D. (2013). Statehood and Self-Determination: Reconciling Tradition and Modernity in International Law. Cambridge University Press. pp. 259–260. ISBN 978-1-107-02933-0. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- "Morocco" (PDF). IAEA.org. IAEA. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- Aïtel, Fazia (2014). We are Imazigen : the development of Algerian Berber identity in twentieth-century literature and culture. Gainesville, FL: University of Florida Press. ISBN 978-0-8130-4895-6. OCLC 895334326.
- "Morocco country profile". BBC News. 26 November 2023. Archived from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 26 November 2023.
- "Morocco wants normal ties with Algeria, king says". Reuters. 29 July 2023. Retrieved 3 January 2024.
- Meakin, James; Meakin, Kate (1911). "Morocco" . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 18 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 852.
- "Population Légale des Régions, Provinces, Préfectures, Municipalités, Arrondissements et Communes du Royaume D'Après Les Résultats du RGPH 2014" (in Arabic and French). High Commission for Planning, Morocco. 8 April 2015. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 29 September 2017.
- ^ "English country names and code elements". International Organization for Standardization. 15 May 2008. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- "Morocco - Summary". ClimateChangeKnowledgePortal.WorldBankGroup.org. The World Bank Group. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ "Climate Change Risk Profile Morocco" (PDF). USAID.gov. United States Agency for International Development. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- Gaussen, H. (1964). Genre Cedrus. Les Formes Actuelles. Trav. Lab. For. Toulouse T2 V1 11: 295-320
- ^ Ahmed Derdouri (2023). "Spatiotemporal Thermal Variations in Moroccan Cities: A Comparative Analysis". Sensors. 23 (13): 6229. Bibcode:2023Senso..23.6229D. doi:10.3390/s23136229. PMC 10346751. PMID 37448080.
- "Climate Change Risk Profile Morocco" (PDF). World Bank Group. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- W. Hammoudy; R. Ilmen; M. Sinan (2022). "Impact of climate change on extremes events in Morocco". IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 1090 (1): 012034. Bibcode:2022E&ES.1090a2034H. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/1090/1/012034.
- "Morocco: Ranked second worldwide in climate change control". Afrik 21. 30 April 2020. Archived from the original on 10 December 2020. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- Myers, Norman; Mittermeier, Russell A.; Mittermeier, Cristina G.; da Fonseca, Gustavo A. B.; Kent, Jennifer (2000). "Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities". Nature. 403 (6772): 853–858. Bibcode:2000Natur.403..853M. doi:10.1038/35002501. PMID 10706275. S2CID 4414279.
- "Profile on Morocco". African Conservation Foundation. Archived from the original on 2 March 2004. Retrieved 10 May 2007.
- Bergier, P.; Thévenot, M. (2006). "Liste des oiseaux du Maroc" (PDF). Go-South Bull. 3: 51–83. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 January 2012.
- Nowell K, Jackson P, ed. (1996). "Panthera Leo" (PDF). Wild Cats: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group. pp. 17–21. ISBN 978-2-8317-0045-8. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 August 2007. Retrieved 20 March 2011.
- "Crocodiles in the Sahara Desert: An Update of Distribution, Habitats and Population Status for Conservation Planning in Mauritania Archived 10 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine". PLOS ONE. 25 February 2011.
- Nijman, Vincent; Bergin, Daniel; Lavieren, Els van (1 July 2015). "Barbary macaques exploited as photo-props in Marrakesh's punishment square". ResearchGate. Jul–Sep. Archived from the original on 31 October 2018. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
- Bergin, Daniel; Nijman, Vincent (21 December 2015). "Potential benefits of impending Moroccan wildlife trade laws, a case study in carnivore skins". Biodiversity and Conservation. 25 (1): 199–201. doi:10.1007/s10531-015-1042-1. S2CID 34533018. Archived from the original on 7 January 2020. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
- Bergin, Daniel; Nijman, Vincent (1 November 2014). "Open, Unregulated Trade in Wildlife in Morocco's Markets". ResearchGate. 26 (2). Archived from the original on 31 October 2018. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
- Nijman, Vincent; Bergin, Daniel; Lavieren, Els van (1 September 2016). "Conservation in an ever-globalizing world: wildlife trade in, from, and through Morocco, a gateway to Europe". ResearchGate. Archived from the original on 5 September 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
- Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- "Democracy Index 2022: Frontline democracy and the battle for Ukraine" (PDF). Economist Intelligence Unit. 2023. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 March 2023. Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- "Morocco / Western Sahara". rsf.org. 19 May 2023. Archived from the original on 2 July 2023. Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- Schemm, Paul (17 June 2011) King declares Morocco a constitutional monarchy. Associated Press.
- Moroccan king in referendum win Archived 24 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine. The Irish Times. 2 July 2011.
- "Morocco - House of Councillors". Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- Amraoui, Ahmed El. "Morocco election: Everything you need to know". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 10 December 2023. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- "Morocco". US Department of State. 11 March 2008. Archived from the original on 6 December 2023. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- "Morocco: Government". globaledge.msu.edu. Archived from the original on 5 June 2023. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- "2021 Elections: High Turnout in Southern Provinces, Tangible Proof of Attachment to Morocco - Mauritanian Political Parties | MapNews". www.mapnews.ma. 14 September 2021. Archived from the original on 1 June 2024. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- "Morocco elections: Islamists suffer losses as liberal parties gain ground". The Guardian. 9 September 2021. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- "Décret fixant le nom des régions" (PDF). Portail National des Collectivités Territoriales (in French). Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
- "Morocco Prefectures". www.statoids.com. Archived from the original on 16 May 2017. Retrieved 4 November 2006.
- "Encyclopedia of the Nations: Morocco Foreign Policy". Archived from the original on 5 February 2010. Retrieved 23 October 2009.
- "GCC Countries Invest Heavily in Morocco". Archived from the original on 7 August 2018. Retrieved 23 October 2009.
- "Morocco rejoins African Union". Worldbulletin. 30 January 2017. Archived from the original on 20 July 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2017.
- "Morocco to rejoin African Union despite Western Sahara dispute". BBC News. bbc.com. 30 January 2017. Archived from the original on 15 April 2020. Retrieved 31 January 2017.
- "Algeria cuts diplomatic ties with Morocco over 'hostile actions'". Al-Jazeera. 24 August 2021. Archived from the original on 4 April 2023. Retrieved 29 August 2021.
- Tremlett, Giles (13 July 2002). "Moroccans seize Parsley Island and leave a bitter taste in Spanish mouths". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 16 April 2019. Retrieved 3 April 2024.
- "US rewards Morocco for terror aid". BBC News. 4 June 2004. Archived from the original on 29 November 2020. Retrieved 7 November 2021.
- "Morocco - European Commission". neighbourhood-enlargement.ec.europa.eu. 1 February 2024. Archived from the original on 3 April 2024. Retrieved 3 April 2024.
- "Paragraph 37". Report of the Secretary-General on the situation concerning Western Sahara (S/2006/249). United Nations Security Council. p. 10. Archived from the original on 18 October 2017. Retrieved 29 June 2017.
- Majid, Jacob. "Biden reportedly won't reverse Trump recognition of Western Sahara as Morocco's Archived 16 October 2021 at the Wayback Machine", The Times of Israel (1 May 2021).
- Fabiani, Riccardo (3 August 2023). "The Western Sahara conflict: A fragile path to negotiations". AtlanticCouncil.org. Atlantic Council. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- "Report of the Secretary-General on the situation concerning Western Sahara". UN Security Council. 13 April 2007. Archived from the original on 28 February 2010. Retrieved 18 May 2007.
- Migdalovitz, Carol (3 February 2010). Morocco: Current Issues Archived 25 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Congressional Research Service.
- ICTJ Activity in Morocco – International Center for Transitional Justice (ICTJ) Archived 28 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "Morocco's Truth Commission: Honoring Past Victims during an Uncertain Present: V. Constraints on the ERC". hrw.org. Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- "Morocco and Western Sahara: Events of 2015". Morocco and Western Sahara. 12 January 2016. Archived from the original on 29 May 2017. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- "afrol News – Western Sahara activists released, re-arrested in riots". www.afrol.com. Archived from the original on 27 July 2017. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- "Morocco/Western Sahara: Sahrawi human rights defender on trial". Amnesty International. Archived from the original on 22 April 2006.
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (5 March 2007). "Refworld | Morocco: The treatment of homosexuals, including protection offered by the state and the attitude of the population". UNHCR. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- "Laws on Homosexuality in African Nations". Library of Congress. 2015. Archived from the original on 19 June 2017. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- Saeed, A.; Saeed, H. (2004). Freedom of Religion, Apostasy and Islam. Ashgate. p. 19. ISBN 9780754630838.
- "Une famille française arrêtée pour prosélytisme à Marrakech". bladi.net (in French). 4 July 2015. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- "Morocco criminalises violence against women and sexual harassment". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 13 September 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
- "Moroccan man jailed for five years for criticising king in Facebook posts". Guardian. Agence France-Presse. 3 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- Leonard, Thomas M. (2006). Encyclopedia of the Developing World. Taylor & Francis. p. 1085. ISBN 978-0-415-97663-3.
- Morocco major economic player in Africa, researcher Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Moroccobusinessnews.com (16 December 2009). Retrieved 17 April 2015.
- "Democracy Index 2020". Economist Intelligence Unit. Archived from the original on 3 March 2021. Retrieved 17 May 2022.
- "IMF Gives Morocco Positive Review. nuqudy.com (2012-02-09)". Archived from the original on 30 June 2017. Retrieved 12 February 2012.
- Hudman, Lloyd E.; Jackson, Richard H. (2003). Geography of Travel & Tourism. Cengage Learning. ISBN 0766832562.
- "Morocco sets the goal of attracting 20 million tourists by 2020". India's leading B2B travel news website. Archived from the original on 27 July 2014. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- "Dashboards". Kingdom of Morocco, Ministry of Tourism. Archived from the original on 29 March 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ Hudman, Lloyd E. (2002). Geography of Travel & Tourism. Thomson Delmar Learning. p. 367. ISBN 0-7668-3256-2.
- The Middle East and North Africa 2003. Europa Publications, Routledge. 2002. p. 863. ISBN 978-1-85743-132-2.
- "Home". Morocco berber trips. Archived from the original on 11 August 2020. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- "Yves Saint Laurent's Ashes Scattered In Marrakesh". The New York Times. 11 June 2008. Retrieved 14 June 2008.
- Shackley, Myra (2006). Atlas of Travel And Tourism Development. Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 43–44. ISBN 978-0-7506-6348-9.
- "Morocco | Infoplease".
- "Climate Risk Profile: Morocco". Climatelinks. 9 December 2016. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- Rayne, Louise; Brandolini, Filippo; Makovics, Jen Lavris; Hayes-Rich, Emily; Levy, Jackson; Irvine, Hope; Assi, Lima; Bokbot, Youssef (8 November 2023). "Detecting desertification in the ancient oases of southern Morocco". Scientific Reports. 13 (1): 19424. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-46319-1. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 10632388. PMID 37940666.
- "Morocco - Corporate - Tax credits and incentives".
- "Economy Profiles".
- "Morocco - Infrastructure | export.gov". www.export.gov. Archived from the original on 13 December 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- "Tanger Med Port Authority – Containers Activity". Archived from the original on 2 September 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- "Morocco – electricity production from coal sources". Archived from the original on 8 August 2011. Retrieved 18 May 2011.
- ^ "Natural Gas to Fuel Morocco. Nuqudy.com (2012-04-12)". Archived from the original on 30 June 2017. Retrieved 15 April 2012.
- "Ain Beni Mathar, Morocco Solar Thermal Power Station Project". Archived from the original on 6 April 2011. Retrieved 18 May 2011.
- Sschemm, Paul (6 June 2012). "Solar-powered plane lands in Morocco". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 21 April 2017. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
- "Historique de la culture de cannabis au Maroc d'après l'UNODC". Laniel.free.fr. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 9 January 2013.
- Nations Unies. Office pour le contrôle des drogues et la prévention du crime (2004). Rapport mondial sur les drogues. United Nations Publications. ISBN 978-92-1-248122-7.
- "Mildt – Mission interministérielle de lutte contre la drogue et la toxicomanie". Interieur.gouv.fr. 1 October 2006. Archived from the original on 9 February 2009. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- "Central Intelligence Agency". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 29 December 2010. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- "National Sanitation Programme | European Investment Bank". www.eib.org. Archived from the original on 20 March 2022. Retrieved 4 April 2024.
- SciDev.Net (9 June 2009). "Morocco to boost investment in science". Archived from the original on 1 March 2012. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
- World Intellectual Property Organization (2024). "Global Innovation Index 2024: Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship". www.wipo.int. World Intellectual Property Organization. p. 18. doi:10.34667/tind.50062. ISBN 978-92-805-3681-2. Retrieved 6 October 2024.
- ^ Zou'bi, Moneef; Mohamed-Nour, Samia; El-Kharraz, Jauad; Hassan, Nazar (2015). Arab States. In: UNESCO Science Report: towards 2030 (PDF). Paris: UNESCO. pp. 431–469. ISBN 978-92-3-100129-1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 June 2017. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
- Agénor, P.R.; El-Aynaoui, K. (2015). Morocco: Growth Strategy for 2025 in an Evolving International Environment. Rabat: Policy Centre of the Office chérifien des phosphates.
- Developing Scientific Research and Innovation to Win the Battle of Competitiveness: an Inventory and Key Recommendations. Rabat: Hassan II Academy of Science and Technology. 2012.
- "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- Maaroufi, Youssef. "Population du Maroc par année civile (en milliers et au milieu de l'année) par milieu de résidence : 1960 – 2050". Archived from the original on 27 December 2012. Retrieved 7 January 2012.
- OECD (2017). Talent Abroad: A Review of Moroccan Emigrants. OECD Publishing. p. 167. ISBN 978-9264264281. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 31 August 2017.
- De Azevedo, Raimondo Cagiano (1994) Migration and development co-operation. Archived 1 November 2022 at the Wayback Machine. Council of Europe. p. 25. ISBN 92-871-2611-9.
- Spain: Forging an Immigration Policy Archived 21 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Migration Information Source
- OFFICE OF INTERNATIONAL RELIGIOUS FREEDOM (2022). "2022 Report on International Religious Freedom: Morocco". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 22 February 2024. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- "Población extranjera por sexo, país de nacionalidad y edad (hasta 85 y más).". Avance del Padrón a 1 de enero de 2009. Datos provisionales. Spain: Instituto Nacional de Estadística. 2009. Archived from the original on 10 July 2019. Retrieved 13 June 2009.
- "Morocco: From Emigration Country to Africa's Migration Passage to Europe". Migrationinformation.org. October 2005. Archived from the original on 10 February 2014. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- "Table 2.8 – Jews, by country of origin and age" (PDF). Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 October 2021. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- "Morocco - University of Texas Libraries GeoData". geodata.lib.utexas.edu. Retrieved 28 September 2022.
- El Haimeur, Amar (2017). "Ethnolinguistic Identity in Morocco". Field Notes: A Journal of Collegiate Anthropology. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- "Maroc : population". Larousse (in French). Retrieved 21 November 2024.
- Ibriz, Lina (30 August 2024). "Budget, RSU, langue ... : à la veille du RGPH 2024, Lahlimi Alami fait un dernier point". Le Desk.
- Hannoum, Abdelmajid, ed. (2021), "Language, Race, and Territory", The Invention of the Maghreb: Between Africa and the Middle East, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 123–169, doi:10.1017/9781108937337.004, ISBN 978-1-108-83816-0, retrieved 21 November 2024
- ^ Teebi, Ahmad S.; Farag, Talaat I. (1997). Genetic Disorders Among Arab Populations. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-509305-6.
Majority Arabs, 35% Berbers
- ^ Picard, Louis A.; Buss, Terry F.; Seybolt, Taylor B.; Lelei, Macrina C. (22 April 2015). Sustainable Development and Human Security in Africa: Governance as the Missing Link. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4822-5543-0.
Although the majority of Moroccans are Arabs, the Berbers (or Amazigh) represent 30%. Berbers are spread out in rural areas: the Rif Mountains, Middle High, and Anti-Atlas, and southern Souss Valley, as well as Morocco's major cities.
- ^ The Report: Morocco 2012. Oxford Business Group. 2012. ISBN 978-1-907065-54-5. Archived from the original on 7 March 2023. Retrieved 28 December 2022.
Morocco's population is approximately 67% Arab, 31% indigenous Berber and 2% Sahrawi
- ^ Son, George Philip &; Press, Oxford University (26 December 2002). Encyclopedic World Atlas. Oxford University Press, USA. ISBN 978-0-19-521920-3.
Arab 70%, Berber 30%
- Sun, Xiaoming (12 December 2019). World Health Systems. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-119-50887-8.
More than 80% of Moroccans are Arab, while the remaining 20% are Berber
- Arnold, Guy (27 January 2014). Guide to African Political and Economic Development. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-97062-8.
Arab 70%
- "Who Are the Berber People?". WorldAtlas. 1 August 2017. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
The majority of the Berber people live in Morocco accounting for at least 35% of the population and in Algeria where they form at least 15% of the population.
- Picard, Louis A.; Buss, Terry F.; Seybolt, Taylor B.; Lelei, Macrina C. (22 April 2015). Sustainable Development and Human Security in Africa: Governance as the Missing Link. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4822-5543-0.
Although the majority of Moroccans are Arabs, the Berbers (or Amazigh) represent 30%. Berbers are spread out in rural areas: the Rif Mountains, Middle High, and Anti-Atlas, and southern Souss Valley, as well as Morocco's major cities.
- Arauna, Lara R.; Mendoza-Revilla, Javier; Mas-Sandoval, Alex; Izaabel, Hassan; Bekada, Asmahan; Benhamamouch, Soraya; Fadhlaoui-Zid, Karima; Zalloua, Pierre; Hellenthal, Garrett; Comas, David (February 2017). "Recent Historical Migrations Have Shaped the Gene Pool of Arabs and Berbers in North Africa". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 34 (2): 318–329. doi:10.1093/molbev/msw218. ISSN 0737-4038. PMC 5644363. PMID 27744413.
- "Haratin (social class)". Britannica Online Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 13 August 2014. Retrieved 23 June 2022.
- ^ "Saharawis in Western Sahara". Minority Rights Group. Retrieved 21 November 2024.
- "Climate of Morocco". Britannica. 23 August 2024.
- "Religious Composition by Country" (PDF). Global Religious Landscape. Pew Forum. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 March 2013. Retrieved 9 July 2013.
- "Morocco". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 12 September 2022. Archived from the original on 2 December 2022. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- "Survey Shows Faith in Decline in Morocco, in the Arab World". Arab Barometer. Archived from the original on 25 August 2020. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- "Data Analysis Tool – Arab Barometer". Archived from the original on 21 August 2023. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- "Losing Our Religion? Two Thirds of People Still Claim to Be Religious". Gallup International. 8 June 2015. Archived from the original on 11 April 2022. Retrieved 11 November 2022.
- ^ F. Nyrop, Richard (1972). Area Handbook for Morocco. University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. p. 97. ISBN 9780810884939.
- ^ "International Religious Freedom Report for 2023 – Morocco".
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "Refworld – Morocco: General situation of Muslims who converted to Christianity, and specifically those who converted to Catholicism; their treatment by Islamists and the authorities, including state protection (2008–2011)". Refworld. Archived from the original on 1 March 2019. Retrieved 27 August 2015.
- ^ "International Religious Freedom Report for 2011 – Morocco". Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. Archived from the original on 25 March 2017. Retrieved 21 May 2019.
- "Christian Converts in Morocco Fear Fatwa Calling for Their Execution". Christianity Today. Morning Star News. Archived from the original on 9 June 2013.
- "'House-Churches' and Silent Masses —The Converted Christians of Morocco Are Praying in Secret – VICE News". 23 March 2015. Archived from the original on 7 July 2018. Retrieved 26 June 2016.
- "Christians want marriages recognized in Morocco". reuters. 8 June 2018. Archived from the original on 4 August 2018. Retrieved 13 June 2020.
- "Pope Francis' Visit to Morocco Raises Hopes for Its Christians". The New York Times. 29 March 2019. Archived from the original on 1 October 2019. Retrieved 13 June 2020.
- Carnes, Nat (2012). Al-Maghred, the Barbary Lion: A Look at Islam. University of Cambridge Press. p. 253. ISBN 9781475903423.
. In all an estimated 40,000 Moroccans have converted to Christianity
- "Morocco's 'hidden' Christians to push for religious freedom". AfricanNews. 30 January 2017. Archived from the original on 16 July 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
There are no official statistics, but leaders say there are about 50,000 Moroccan Christians, most of them from the Protestant Evangelical tradition.
- Stearns, Peter N. (ed.). Encyclopedia of World History (6th ed.). The Houghton Mifflin Company/Bartleby.com.
p. 966
- Sergio DellaPergola, World Jewish population Archived 3 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine, 2012, p. 62.
- "The Jews of Morocco". The Museum of the Jewish People at Beit Hatfutsot. Archived from the original on 10 August 2020. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
- Government of Morocco. "BO_5964-Bis_Ar.pdf" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 March 2012.
- Wehr, Hans (1979). A Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic: (Arab.-Engl.). Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 319. ISBN 3447020024. Retrieved 30 September 2017.
- Babas, Latifa (18 December 2024). "How many Moroccans consider Tamazight their mother tongue, and where do they live ?". Yabiladi.
- James Cohen; Kara T. McAlister; Kellie Rolstad; Jeff MacSwan, eds. (2005), "From Monolingualism to Multilingualism: Recent Changes in Moroccan Language Policy" (PDF), ISB4: Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Bilingualism, Somerville, MA: Cascadilla Press, pp. 1487–1500, retrieved 30 April 2017
- "Le dénombrement des francophones" (PDF). Organisation internationale de la Francophonie. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 October 2013. Retrieved 9 January 2013.
- Site institutionnel du Haut-Commissariat au Plan du Royaume du Maroc Archived 29 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Hcp.ma. Retrieved 23 July 2011.
- "Spanish". Ethnologue. Archived from the original on 23 November 2017. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- Leyre Gil Perdomingo and Jaime Otero Roth (2008) "Enseñanza y uso de la lengua española en el Sáhara Occidental" Archived 24 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine, in Analysis of the Real Instituto Elcano nº 116
- Saga, Ahlam Ben. Instituto Cervantes: 1.7 Million Moroccans Speak Spanish Archived 15 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine, Morocco World News, 29 Nov 2018. Retrieved 11 Apr 2022.
- ^ Rouchdy, Aleya (2002). Language Contact and Language Conflict in Arabic: Variations on a Sociolinguistic Theme. Psychology Press. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-7007-1379-0.
- Baisse du taux d'analphabétisme au Maroc à 28% Archived 1 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Lavieeco.com (6 September 2013). Retrieved 17 April 2015.
- "2006 UNESCO Literacy Prize winners announced". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 12 December 2019. Retrieved 27 September 2006.
- "CCIS Ifrane Morocco Summer Study Abroad Program". Ccisabroad.org. 1 April 2010. Archived from the original on 26 February 2009. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- Meri, Josef W. (ed.): Medieval Islamic Civilization: An Encyclopedia, Vol. 1, A–K, Routledge, 2006, ISBN 978-0-415-96691-7, p. 257 (entry "Fez")
- "Qarawiyin". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 29 November 2011. Retrieved 8 December 2011.
- The Guinness Book Of Records, 1998, p. 242, ISBN 0-553-57895-2.
- "Classement meilleurs école d'études supérieures au Maroc". Etudes superieures au Maroc. 23 December 2019. Archived from the original on 17 January 2023. Retrieved 17 January 2023.
- ^ Ruger JP, Kress D (July 2007). "Health financing and insurance reform in Morocco". Health Affairs. 26 (4): 1009–16. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.26.4.1009. PMC 2898512. PMID 17630444.
- ^ "Mortality rate, infant (per 1,000 live births)". data.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 17 December 2018. Retrieved 10 December 2018.
- ^ "Maternal mortality ratio (modeled estimate, per 100,000 live births)". data.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 17 December 2018. Retrieved 10 December 2018.
- ^ "WHO | Morocco takes a stride forward for mothers and children". WHO. Archived from the original on 2 March 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2018.
- "Current health expenditure (% of GDP) | Data". data.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 1 February 2022. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- "Current health expenditure per capita, PPP (current international $) | Data". data.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 12 June 2021. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- "World Health Organization". Archived from the original on 5 February 2022. Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- Travel, D. K. (1 February 2017). DK Eyewitness Travel Guide Morocco. Dorling Kindersley Limited. ISBN 978-0-241-30469-3.
- e.g. Khalid Amine and Marvin Carlson, The Theatres of Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia: Performance Traditions of the Maghreb (Dordrecht NL: Springer, 2011), 124–28. ISBN 0230358519
- "Royal Letter of His Majesty King Mohammed VI of Morocco". whc.unesco.org. Archived from the original on 17 June 2023. Retrieved 24 October 2023.
- "Morocco town's Hollywood connection". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 28 October 2017. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- "Return to Morocco". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 24 September 2017. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- "Boujloud: Morocco's unique Halloween". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 28 October 2017. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- ^ Gaudio, Attilio (1982). Fès: Joyau de la civilisation islamique. Paris: Les Presse de l'UNESCO: Nouvelles Éditions Latines. ISBN 2723301591.
- ^ Marçais, Georges (1954). L'architecture musulmane d'Occident. Paris: Arts et métiers graphiques.
- ^ Parker, Richard (1981). A practical guide to Islamic Monuments in Morocco. Charlottesville, VA: The Baraka Press.
- Touri, Abdelaziz; Benaboud, Mhammad; Boujibar El-Khatib, Naïma; Lakhdar, Kamal; Mezzine, Mohamed (2010). Le Maroc andalou : à la découverte d'un art de vivre (2 ed.). Ministère des Affaires Culturelles du Royaume du Maroc & Museum With No Frontiers. ISBN 978-3902782311.
- Barrucand, Marianne; Bednorz, Achim (1992). Moorish architecture in Andalusia. Taschen. ISBN 3822876348.
- ^ Bennison, Amira K. (2016). "'The most wondrous artifice': The Art and Architecture of the Berber Empires". The Almoravid and Almohad Empires. Edinburgh University Press. pp. 276–328. ISBN 9780748646821.
- ^ Golvin, Lucien (1989). "Architecture berbère". Encyclopédie Berbère (in French) (6): 865–877. doi:10.4000/encyclopedieberbere.2582. Retrieved 13 December 2022.
- "Ksar of Ait-Ben-Haddou". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 16 April 2020.
- Becker, Cynthia (2010). "Deconstructing the History of Berber Arts: Tribalism, Matriarchy, and a Primitive Neolithic Past". In Hoffman, Katherine E.; Miller, Susan Gilson (eds.). Berbers and Others: Beyond Tribe and Nation in the Maghrib. Indiana University Press. p. 200. ISBN 978-0-253-35480-8.
- Wright, Gwendolyn (1991). The Politics of Design in French Colonial Urbanism. University of Chicago Press.
- Gilson Miller, Susan; Petruccioli, Attilio; Bertagnin, Mauro (2001). "Inscribing Minority Space in the Islamic City: The Jewish Quarter of Fez (1438-1912)". Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians. 60 (3): 310–327. doi:10.2307/991758. JSTOR 991758.
- M. Bloom, Jonathan; S. Blair, Sheila, eds. (2009). "Morocco, Kingdom of". The Grove Encyclopedia of Islamic Art and Architecture. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195309911.
- "Hassan II Mosque". Archnet. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- "Desert Blooms: The Contemporary Architecture of Morocco - Architizer Journal". Journal. 2 July 2019. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- "Modern Morocco: Building a New Vernacular". ArchDaily. 26 November 2019. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- Mohammed Benjelloun Touimi, Abdelkbir Khatibi and Mohamed Kably, Ecrivains marocains, du protectorat à 1965, 1974 éditions Sindbad, Paris and Hassan El Ouazzani, La littérature marocaine contemporaine de 1929 à 1999 (2002, ed. Union des écrivains du Maroc and Dar Attaqafa)
- "Wellesnet: Filming Othello". www.wellesnet.com. Archived from the original on 17 August 2020. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- "The Art of Moroccan Cuisine". 10 October 2007. Archived from the original on 5 November 2013. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- "Moroccan Couscous Recipe" Archived 31 May 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Maroccan Kitchen Recipes Archived 31 May 2014 at the Wayback Machine (Website). Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- Benlafquih, Christine. "klii". About.com. Archived from the original on 11 July 2014. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- "Morocco to stage the 2015 African Nations Cup – ESPN Soccernet". ESPN FC. 29 January 2011. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- "Africa Cup of Nations: Morocco will not host finals over Ebola fears". BBC Sport. 11 November 2014. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 13 February 2018.
- Hamaan, Jasper (24 June 2023). "Morocco Emerges As 'Top-Class' Golf Destination". Moroccan World News. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- El Kanouni, Zakaria (12 May 2024). "Moroccan Tennis Teams Triumph at African Championships, Despite Talent Oversight". Moroccan World News. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- Nxumalo, Lee (20 December 2020). "Basketball's next frontier is Africa". New Frame. Archived from the original on 16 January 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2021.
- ^ Bath, Richard (ed.) The Complete Book of Rugby (Seven Oaks Ltd, 1997 ISBN 1-86200-013-1) p71
- F.H.M. van Gemert (1 October 2019). "Kickboksen, een Marokkaanse route naar succes?". Tijdschrift voor Veiligheid. 18 (3–4). doi:10.5553/TvV/187279482019018304004. hdl:1871.1/879c2ee1-a047-4286-94bb-fbb3e2ed01bf.
- Herbertson, Daniel (28 September 2011). "Badr Hari to Retire From Kickboxing". MMAFighting.com. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
Sources
 This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0. Text taken from UNESCO Science Report: towards 2030, 431–467, UNESCO, UNESCO Publishing.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0. Text taken from UNESCO Science Report: towards 2030, 431–467, UNESCO, UNESCO Publishing.
Further reading
- Pennell, C. R. Morocco Since 1830: A History, New York University Press, 2000. ISBN 9780814766774
- Pennell, C. R. Morocco: From Empire to Independence, Oneworld Publications, 2013. ISBN 9781780744551 (preview Archived 5 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine)
- Stenner, David. Globalizing Morocco: Transnational Activism and the Postcolonial State (Stanford UP, 2019). online review Archived 22 May 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- Terrasse, Henri. History of Morocco, Éd. Atlantides, 1952.
- In French
- Bernard Lugan, Histoire du Maroc, Éd. Perrin, 2000. ISBN 2-262-01644-5
- Michel Abitbol, Histoire du Maroc, Éd. Perrin, 2009. ISBN 9782262023881
External links
- Official website of the government of Morocco Archived 19 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- Official bulletins of the government of Morocco Archived 20 June 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- Parliament of Morocco Archived 10 February 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Official website of the Moroccan National Tourist Office Archived 19 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- Census results of 1994 and 2004 Archived 24 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- Morocco Archived 2 December 2022 at the Wayback Machine. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Morocco web resources provided by GovPubs at the University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Morocco profile Archived 20 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine from the BBC News
 Wikimedia Atlas of Morocco
Wikimedia Atlas of Morocco- Key Development Forecasts for Morocco Archived 8 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine from International Futures
- EU Neighbourhood Info Centre: Morocco Archived 11 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Morocco Archived 12 May 2014 at the Wayback Machine
| Morocco articles | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
|  | ||||||||||
| Geography | ||||||||||||
| Politics | ||||||||||||
| Economy | ||||||||||||
| Culture |
| |||||||||||
32°N 6°W / 32°N 6°W / 32; -6
Categories:- Morocco
- Countries in Africa
- 1956 establishments in Africa
- 1956 establishments in Morocco
- Countries and territories where Arabic is an official language
- Maghrebi countries
- Member states of the African Union
- Member states of the Arab League
- Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
- Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
- Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean
- Member states of the United Nations
- North African countries
- Saharan countries
- States and territories established in 1956
