| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
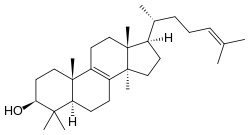
| IUPAC name Lanosta-8,24-dien-3β-ol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (1R,3aR,5aR,7S,9aS,11aR)-3a,6,6,9a,11a-Pentamethyl-1--2,3,3a,4,5,5a,6,7,8,9,9a,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopentaphenanthren-7-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 2226449 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.105 |
| EC Number |
|
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Lanosterol |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C30H50O |
| Molar mass | 426.71 g/mol |
| Melting point | 138 to 140 °C (280 to 284 °F; 411 to 413 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast, plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol. In the eyes of vertebrates, lanosterol is a natural constituent, having a role in maintaining health of the lens. Lanosterol is the precursor to cholesterol.
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of lanosterol has been intensively investigated.
| Description | Illustration | Enzyme |
|---|---|---|
| Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate condense with reduction by NADPH to form squalene | squalene synthase | |
| Squalene is oxidized to 2,3-oxidosqualene (squalene epoxide) |  |
squalene monooxygenase |
| 2,3-Oxidosqualene is converted to a protosterol cation and finally to lanosterol |  |
lanosterol synthase |
| (step 2) | 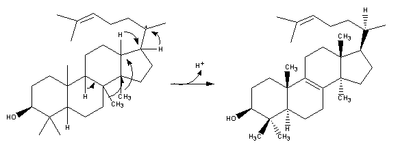 |
(step 2) |
Elaboration of lanosterol under enzyme catalysis leads to other steroids. 14-Demethylation of lanosterol by CYP51 eventually yields cholesterol.

Research as an eye drop supplement
As a molecule naturally enriched in the eye lens, lanosterol is a component involved in maintenance of lens clarity. Its proposed mechanism of action is to inhibit the aggregation of crystallin proteins, which contribute to the clouding of vision by forming cataracts.
Lanosterol is under research for its potential as a therapeutic additive in eye drops to inhibit the aggregation of crystallin proteins and dissolve cataracts. However, supplemental lanosterol in eye drops appears to have limited solubility and poor bioavailability in the eye, and has not proved effective for inhibiting cataracts, as of 2020.
See also
- Cycloartenol
- CYP51
- Other tetracyclic triterpenes: cycloartenol, euphol, tirucallol, and cucurbitacin.
References
- Schaller, Hubert (May 2003). "The role of sterols in plant growth and development". Progress in Lipid Research. 42 (3): 163–175. doi:10.1016/S0163-7827(02)00047-4. PMID 12689617.
- ^ Nes, W. David (2011). "Biosynthesis of cholesterol and other sterols". Chemical Reviews. 111 (10): 6423–6451. doi:10.1021/cr200021m. PMC 3191736.
- ^ Daszynski DM, Santhoshkumar P, Phadte AS, et al. (June 2019). "Failure of oxysterols such as lanosterol to restore lens clarity from cataracts". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 8459. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-44676-4. PMC 6560215. PMID 31186457.
- ^ Xu J, Fu Q, Chen X, Yao K (November 2020). "Advances in pharmacotherapy of cataracts". Annals of Translational Medicine. 8 (22): 1552. doi:10.21037/atm-20-1960. PMC 7729355. PMID 33313297.
| Cholestanes, membrane lipids: sterols | |
|---|---|
| Cholesterol and steroid metabolic intermediates | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mevalonate pathway |
| ||||||||||
| Non-mevalonate pathway | |||||||||||
| To Cholesterol | |||||||||||
| From Cholesterol to Steroid hormones |
| ||||||||||
| Nonhuman |
| ||||||||||