| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Bihar Legislature" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
The Bihar Legislature (IAST: Bihar Vidhan Mandal) is the supreme legislative body of the state of Bihar. It is a bicameral legislature composed of two houses, The Bihar Legislative Council (Bihar Vidhan Parishad) and The Bihar Legislative Assembly (Bihar Vidhan Sabha). The Governor of Bihar in his role as head of the legislature has full powers to summon and prorogue either house of legislature or to dissolve the Legislative Assembly. The governor can exercise these powers only upon the advice of the Chief minister and his ministry.
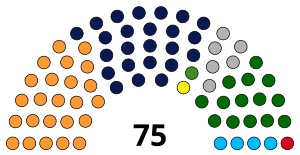
Those elected or nominated (by the governor) to either house of legislature are referred to as Member of the Legislative Assembly (India) (MLAs). The Member of the Legislative Assembly are directly elected by the Bihari public voting in single-member districts and the Member of the Legislative Council are elected by the MLAs, panchayat, teachers, graduates and local governing body by proportional representation. The Legislature has a sanctioned strength of 243 in the Legislative Assembly and 75 in the Legislative Council including 12 nominees from the expertise of different fields of literature, art, science, and social service. The Assembly meets at Bihar Legislative House in Patna.
References
- "Bihar Legislature". Commonwealth Parliamentary Association (CPA). Retrieved 22 November 2024.
- "Chapter 18, Administrative Set-Up of Bihar". Know Your State Bihar. Arihant Publication India Limited. 2020. p. 225. ISBN 9789313199755.