
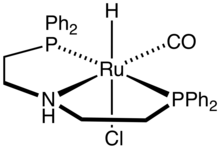
In homogeneous catalysis, MACHO catalysts are metal complexes containing MACHO ligands, which are of the type HN(CH2CH2PR2)2, where R is typically phenyl or isopropyl. Complexes with ruthenium(II) and iridium(III) have received much attention for their ability to hydrogenate polar bonds such as those in esters and even carbon dioxide. The catalysts appear to operate via intermediates where the amine proton and the hydride ligand both interact with the substrate. The Ru-MACHO catalyst have been commercialized for the synthesis of 1,2-propanediol from bio-derived methyl lactate.
See also
- 1,5-Diaza-3,7-diphosphacyclooctanes, phosphine amine ligands used in hydrogen evolution
- Noyori asymmetric hydrogenation, another family of amine-phosphine catalysts
- Shvo catalyst, a related bifunctional catalyst for hydrogen transfer
References
- Yao, Qingwei (2015). "Ruthenium, carbonyl[2-(diphenylphosphino-κP)-N-[2-(diphenylphosphino-κP)ethyl]ethanamine-κN][tetrahydroborato(1-)-κH]-hydrido, (OC-6-13)-". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. pp. 1–3. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01801. ISBN 9780470842898.
- Kothandaraman, Jotheeswari; Goeppert, Alain; Czaun, Miklos; Olah, George A.; Prakash, G. K. Surya (2016). "Conversion of CO2 from Air into Methanol Using a Polyamine and a Homogeneous Ruthenium Catalyst". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 138 (3): 778–781. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b12354. PMID 26713663.
- Kuriyama, Wataru; Matsumoto, Takaji; Ogata, Osamu; Ino, Yasunori; Aoki, Kunimori; Tanaka, Shigeru; Ishida, Kenya; Kobayashi, Tohru; Sayo, Noboru; Saito, Takao (2012). "Catalytic Hydrogenation of Esters. Development of an Efficient Catalyst and Processes for Synthesising (R)-1,2-Propanediol and 2-(l-Menthoxy)ethanol". Organic Process Research & Development. 16: 166–171. doi:10.1021/op200234j.
- Dub, Pavel A.; Gordon, John C. (2018). "The role of the metal-bound N–H functionality in Noyori-type molecular catalysts". Nature Reviews Chemistry. 2 (12): 396–408. doi:10.1038/s41570-018-0049-z. S2CID 106394152.